The Distributed Reflection Denial of Service attack was one of the first attacks that made recent hacking history. A DDOS is a form of attack in which an attacker sends an overwhelming number of requests to a target website in order to overwhelm its servers and make it unavailable to legitimate users. It is also referred to as DDoS for short, which stands for Distributed Denial-of-Service Attack. This type of attack is considered the “biggest” and most disruptive form of cyber attack in existence because once the site becomes inaccessible, many people will be unable to maintain their normal business operations.
Distributed Reflection Denial of Service:
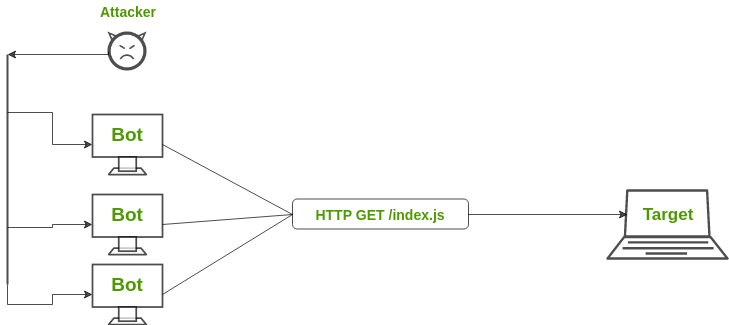
When an attacker plans to launch a DDOS attack, they usually start by sending crafted requests to a Web server that is vulnerable to this type of attack. When the Web server receives these requests, it will process them in order to meet the information needs of legitimate users. This can be done as quickly as possible. However, if an attacker sends so many requests that the server cannot handle its load, it will crash or become unavailable and then be taken down by the attackers. This results in a Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack. In other words, a DDOS is “a form of cyber-attack designed to make use of several computers communicating with each other through a network service such as the Internet. The distributed part of the attack is distinguished from other similar forms of attack by the use of more than one source (distributed) to flood a victim with requests in an attempt to make a service, such as a web server, become unavailable to legitimate users.”
However, this type of attack can also come in the form of Distributed Reflection Denial-of-Service (DRDoS). This type of DRDoS is a more recent method that hackers use to launch DDOS attacks. DRDoS occurs when attackers take advantage of how multiple servers reflect and amplify packets back to the source. The attackers place spoofed IP addresses on outgoing packets that they want sent back to their intended victims. This attack is “reflection” because the servers are reflecting the packets that the attackers did not originally generate. This attack is also known as “amplification” because these spoofed IP addresses are used to amplify the amount of traffic that is sent to the intended victim. A DRDoS attack is more powerful than a regular DoS attack because it utilizes servers that have been compromised in order to increase its power. Normal DoS attacks use only one server and do not need additional computers in order to be successful. The reason this type of DDOS attack became so prevalent was because of how simple it was for hackers to carry out.
Important points:
- The DDOS attack is usually initiated by sending malicious packets over a TCP connection to the target Web server.
- The DoS (Denial of Service) occurs when the server becomes overloaded because of too many requests being sent in one direction at one time and cannot handle this traffic.
- The amplification is carried out by the way the packets are reflected back from the server to the source at a high volume, thus increasing the amount of actual traffic that can be sent to the target at any given time.
- There are multiple sources (servers) behind each target Internet address that are all working together in order to perform and amplify this DDOS attack.
Countermeasures:
- The most important thing that network administrators should do is to implement a firewall and make sure it is armed with an updated IP packet filter.
- If the firewall has been properly configured, it will be able to detect suspicious packets and prevent them from entering the network.
- In addition, computers can be protected using a personal firewall in order to create an extra layer of protection, which means it is highly recommended.
- In other words, “a personal firewall is a computer program that monitors connectivity between services and the Internet on your computer or network.” This will monitor traffic from applications such as e-mail programs, instant-messaging programs, peer-to-peer (P2P) applications, games, and any other application on the computer.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, we can see that DDOS and DRDoS attacks are something that computer systems administrators should always be aware of. Hackers have developed so many different ways to compromise systems and cause them to crash because they know that an effective DoS attack can be used against multiple targets at the same time. This is also why this type of attack is rarely used by an individual hacker. DDOS attacks bring down a lot of attention and generally mean big fines for whoever is responsible for the attack if the victims decide to pursue legal action. It means a lot of work for computer security experts who are trying to figure out how these attacks were carried out, who did them, and how they can prevent similar attacks from happening in the future.




