What is Distributed Caching?
When one cache server is not enough
Caching is used to temporarily store copies of frequently accessed data in high-speed storage layers (such as RAM) to reduce latency and load on the server or database.
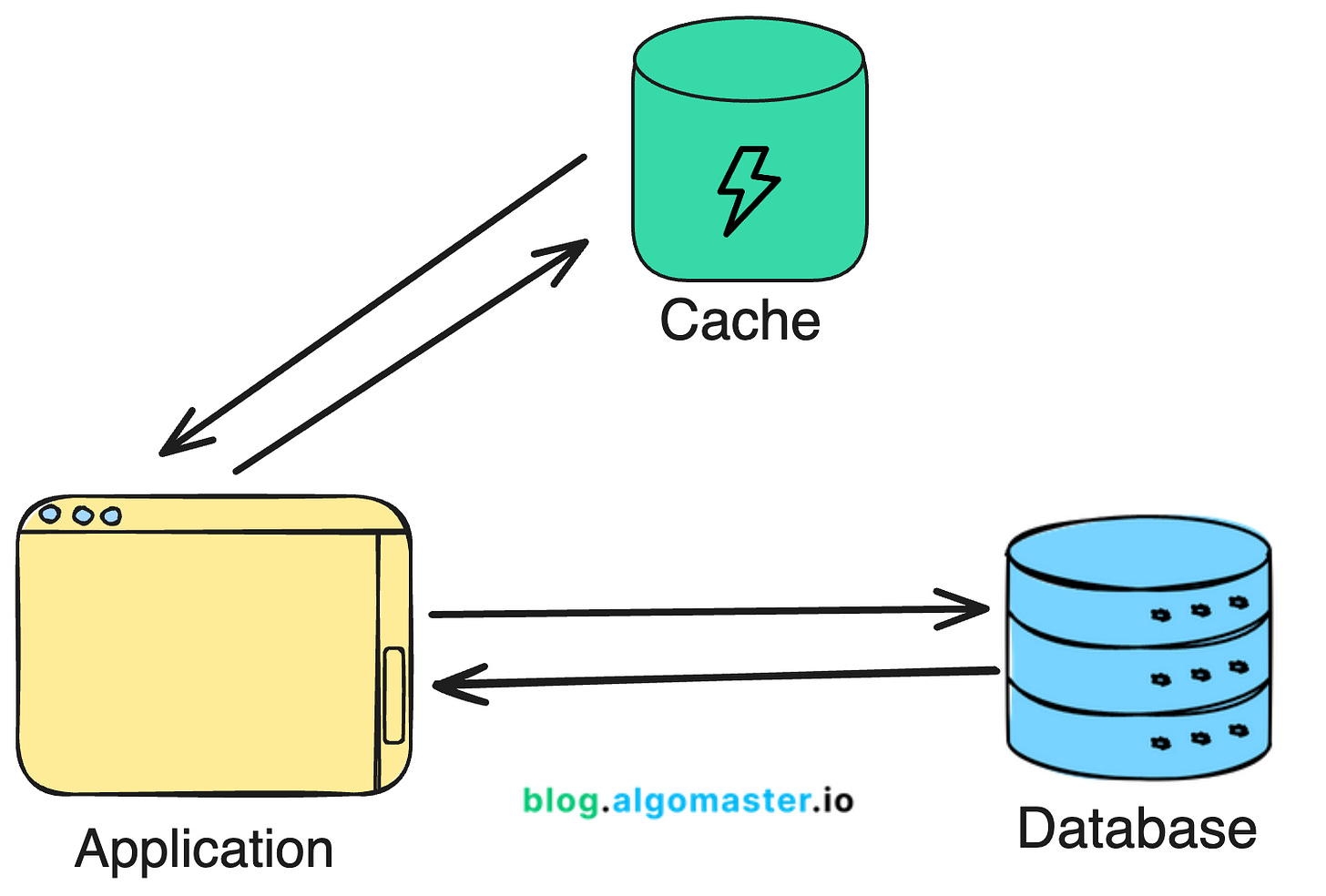
When your dataset size is small, it’s usually enough to keep all the cache data on one server.
But as the system gets bigger, the cache size also gets bigger and a single-node cache often falls short when scaling to handle millions of users and massive datasets.
In such scenarios, we need to distribute the cache data across multiple servers.
This is where distributed caching comes into play.
In this article, we will explore distributed caching in detail, including what it is, why it’s important, how it works, it’s components, challenges, best practices and popular distributed caching solutions.
If you’re finding this newsletter valuable and want to deepen your learning, consider becoming a paid subscriber.
As a paid subscriber, you’ll receive an exclusive deep-dive article every week, access to a structured System Design Resource (100+ topics and interview questions), and other premium perks.
1. What is Distributed Caching?
Distributed caching is a technique where cache data is stored across multiple nodes (servers) instead of being confined to a single machine.
This allows the cache to scale horizontally and accommodate the needs of large-scale applications.
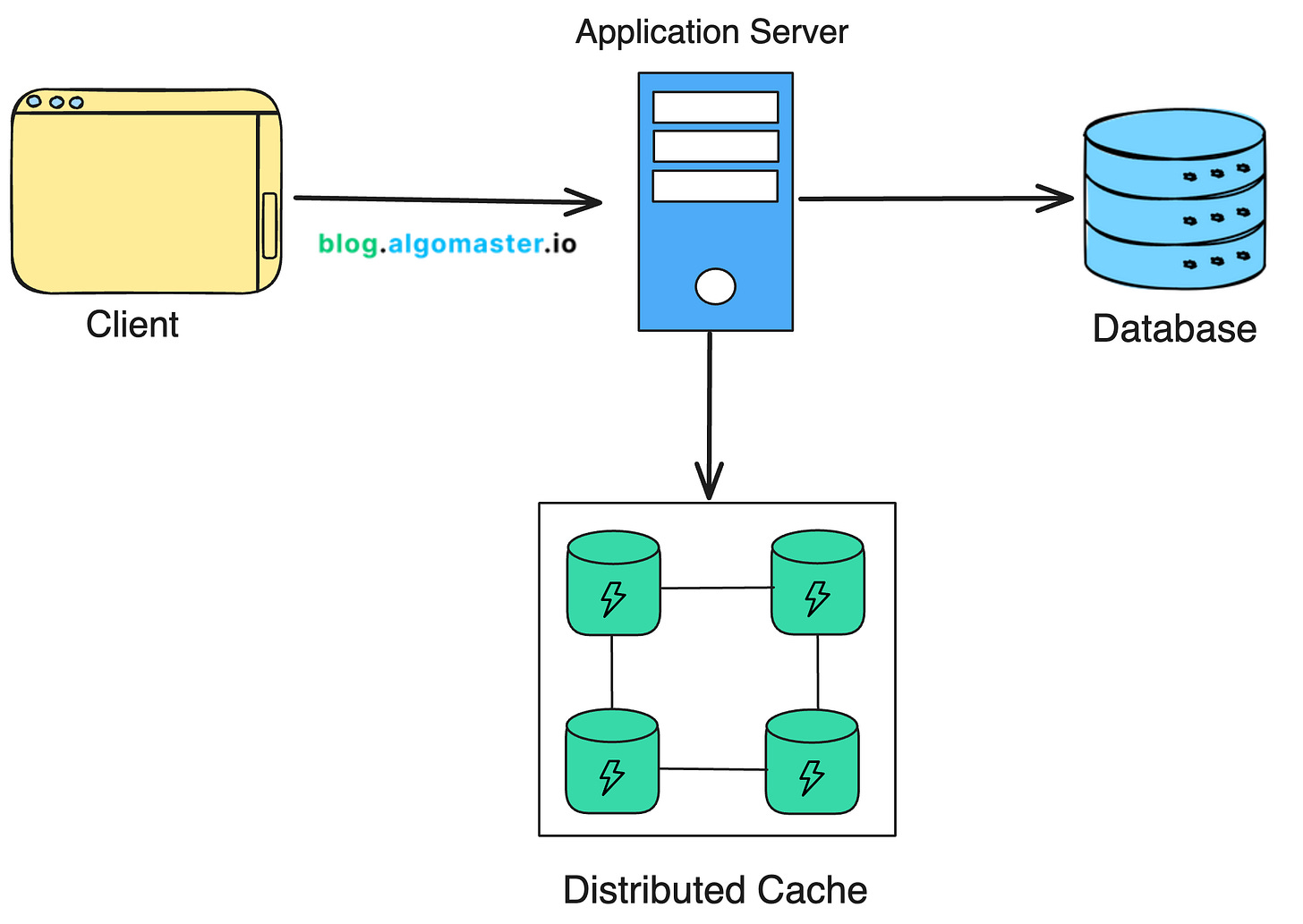
2. Why Use Distributed Caching?
1. Scalability
Distributed caching allows applications to scale horizontally by adding more cache nodes.
This helps manage more traffic without a significant drop in performance.
2. Fault Tolerance
Since data is spread across multiple nodes, the failure of a single node doesn’t result in the loss of the entire cache.
Remaining nodes can continue to serve requests allowing the system to recover gracefully.
3. Load Balancing
By distributing the cache across several nodes, the load is spread evenly.
This helps prevent any single node becoming a bottleneck.
3. Components of Distributed Caching
A distributed cache system typically consists of the following components:
-
Cache Nodes: These are the individual servers where the cache data is stored. Each node is a part of the overall cache cluster.
-
Client Library/Cache Client: Applications use a client library to talk to the distributed cache. This library handles the logic of connecting to cache nodes, distributing data, and retrieving cached data.
-
Consistent Hashing: This method spreads data evenly across cache nodes. It ensures that adding or removing nodes has minimal impact on the system.
-
Replication: To make the system more reliable, some distributed caches replicate data across multiple nodes. If one node goes down, the data is still available on another.
-
Sharding: Data is split into shards, and each shard is stored on a different cache node. It helps distribute the data evenly and allows the cache to scale horizontally.
-
Eviction Policies: Caches implement eviction policies like LRU (Least Recently Used), LFU (Least Frequently Used), or TTL (Time to Live) to get rid of old or less-used data and make space for new data.
-
Coordination and Synchronization: Coordination mechanisms like distributed locks or consensus protocols ensure that cache nodes remain synchronized, especially when multiple nodes try to change the same data at the same time.
4. Dedicated Cache Servers vs. Co-located Cache
When designing a caching strategy for a distributed system, one of the critical decisions you need to make is where to host the cache.
The two primary options are using dedicated cache servers or co-locating the cache with application servers.
1. Dedicated Cache Servers
Dedicated cache servers are standalone machines or virtual instances used only for caching.
They are separate from the application servers and are optimized for caching.
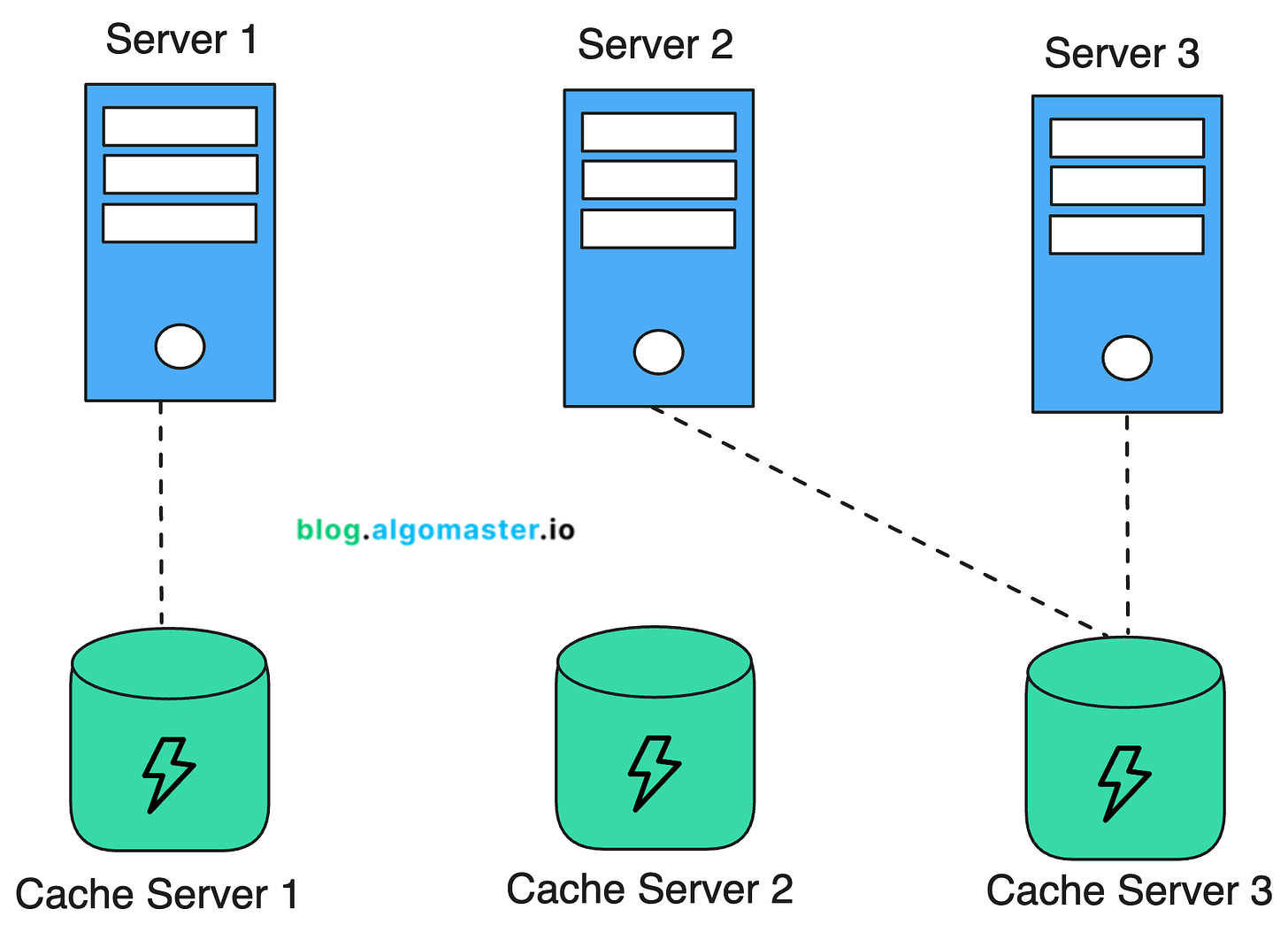
Advantages:
-
Scalability: They can be scaled independently of the application servers. You can add more cache nodes without impacting the application layer.
-
Resource Isolation: Keeping cache on separate servers means it won’t slow down your main servers.
Disadvantages:
-
Cost: Running dedicated cache servers can be pricey, especially if you need many such nodes.
-
Network Latency: Since they are separate from the application servers, it might take longer to fetch data from the cache.
2. Co-located Cache
Co-located cache means running the cache and the application on the same server.
In this setup, the application and the cache share the same hardware resources, such as CPU, memory, and network interfaces.
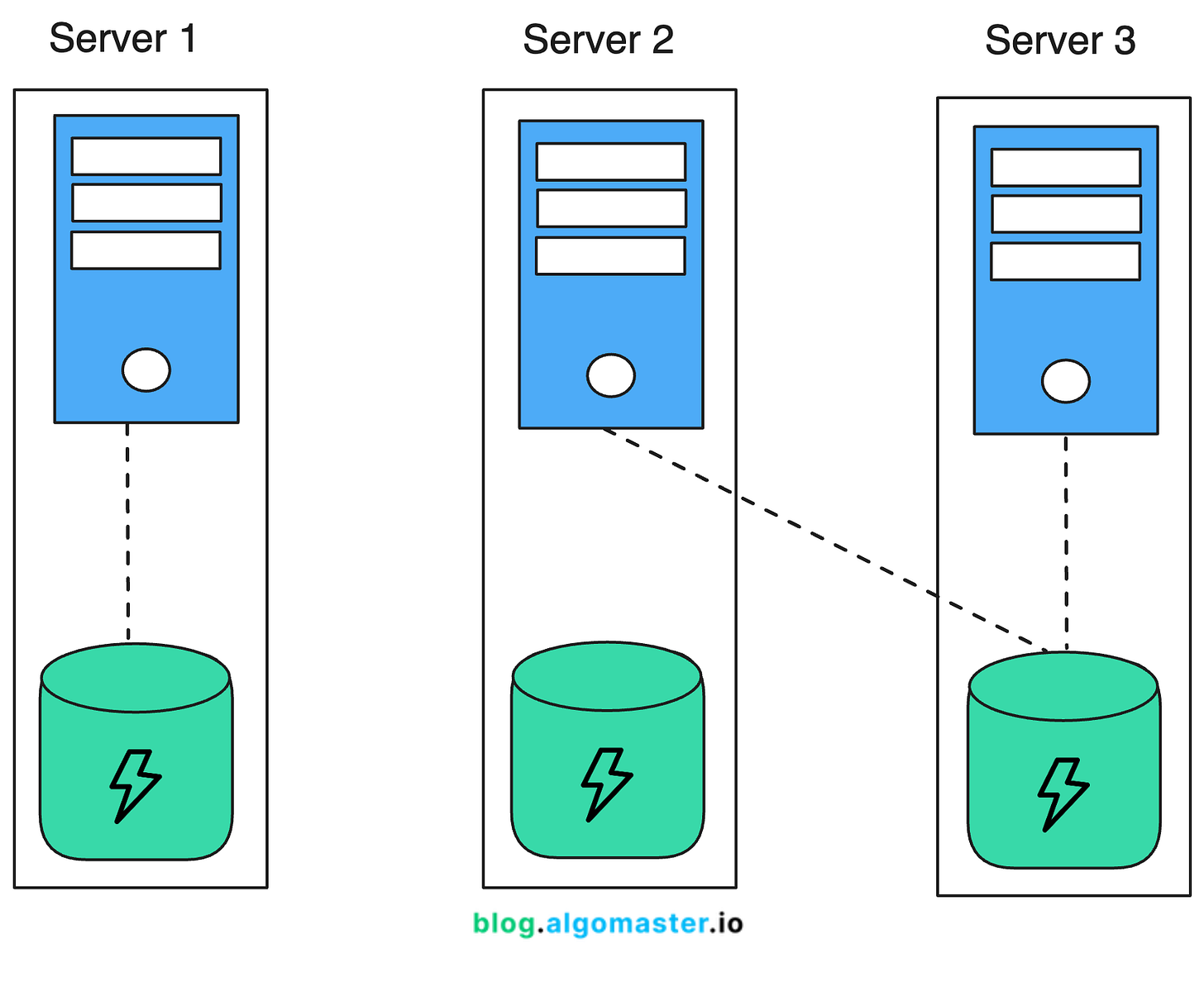
Advantages:
-
Low Latency: Since both the cache and the application are on the same server, accessing the cache is very quick. This is ideal for applications where every millisecond counts, like real-time gaming or high-frequency trading platforms.
-
Cost Efficiency: Co-locating the cache with the application can be more cost-effective, especially for small to medium-sized applications.
Disadvantages:
-
Resource Contention: The cache and the application use the same server resources like CPU memory, and I/O. This can slow things down under high load, if both demand significant resources.
-
Limited Scalability: Co-located caching is less scalable compared to dedicated cache servers. Scaling the cache might require upgrading the entire server.
-
Complex Cache Invalidation: When using co-located caches in a distributed environment, keeping the cache up-to-date and getting rid of old data can become tricky.
If you need your system to handle a lot of users, keep resources separate, and have the budget for it, using dedicated cache servers is likely the better option.
But if your app is smaller, you want to save money, or need it to be super fast, putting the cache and app on the same server can work well.
5. How Does Distributed Caching Work?
-
Data Distribution: When data is cached, the client library typically hashes the key associated with the data to determine which cache node will store it.
-
Data Replication: For reliability, the cache system replicates the cached data across multiple nodes. So, if one node, say A, stores the data, it might also be copied to another node, like B, as a backup.
-
Data Retrieval: To get data from the cache, application provides the key to the client library. The client library uses this key to find and query the node which has the data. If the data is present (a cache hit), it’s returned to the application. If not (a cache miss), the data is fetched from the primary data store (e.g., a database), and it can be cached for future use.
-
Cache Invalidation: To keep the cache data in sync with the primary data source, it needs to be invalidated or updated periodically. Cache systems implement strategies like time-based expiration or event-based expiration for cache invalidation.
-
Cache Eviction: Since caches have limited space, they need an eviction policy to make room for new data. Common eviction policies include:
-
Least Recently Used (LRU): Evicts the data that hasn’t been accessed for the longest time.
-
Least Frequently Used (LFU): Evicts data that has been accessed the least frequently.
-
Time-to-Live (TTL): Evicts data that has been in the cache longer than a specified duration.
-
6. Challenges in Distributed Caching
-
Data Consistency: Ensuring that all cache nodes have consistent data can be challenging, especially in a write-heavy application.
-
Cache Invalidation: Deciding when to invalidate or update the cache can be complex, particularly when dealing with multiple cache nodes.
-
Network Partitioning: In a distributed system, network partitions can occur, leading to situations where cache nodes are unable to communicate with each other.
-
Scalability and Load Balancing: As the system scales, ensuring that the cache is evenly balanced across nodes without any one node becoming a bottleneck requires sophisticated load balancing strategies.
7. Best Practices for Implementing Distributed Caching
To get the most out of your distributed caching system, consider the following best practices:
-
Cache Judiciously: Not all data benefits from caching. Focus on frequently accessed, relatively static data.
-
Set Appropriate TTLs: Use Time-To-Live (TTL) values to automatically expire cached data and reduce staleness.
-
Implement Cache-Aside Pattern: Load data into the cache only when it’s requested, to avoid unnecessary caching.
-
Monitor and Tune: Regularly monitor cache hit rates, memory usage, and network traffic to optimize performance.
-
Plan for Failure: Design your system to gracefully handle cache node failures without significant impact on the application.
-
Implement Cache Warming: Develop strategies to pre-populate critical data in the cache to avoid cold starts.
8. Popular Distributed Caching Solutions
1. Redis
Redis is an open-source, in-memory data store that supports storing a wide range of data structures, including strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets, bitmaps, hyperloglogs, and geospatial indexes.
It supports data replication and persistence making it a popular choice for applications that require data durability and fault tolerance.
2. Memcached
Memcached is another open-source, in-memory caching system designed for speed and simplicity.
It is widely used for caching small chunks of data such as results of database queries, API calls, or page rendering.
Memcached is a pure in-memory cache with no persistence layer. This makes it ideal for use cases where data does not need to be stored permanently, such as caching results from database queries.
3. Amazon ElastiCache
Amazon ElastiCache is a fully managed in-memory caching service provided by AWS. It supports both Redis and Memcached, allowing developers to choose the caching engine that best suits their needs.
ElastiCache supports multi-AZ (Availability Zone) deployments with automatic failover, ensuring that the cache remains available even in the event of an AZ outage.
It can automatically scale the number of nodes in the cache cluster based on demand, allowing the cache to handle varying levels of traffic without manual intervention.
9. Conclusion
Distributed caching is an essential technique for building scalable, high-performance applications.
By distributing data across multiple nodes, it allows for greater scalability, fault tolerance, and load balancing.
However, it also introduces complexities, such as data consistency, cache invalidation, and network partitioning, which must be carefully managed.
Make sure to carefully evaluate your needs, choose the right architecture, and follow best practices to ensure a successful implementation.
Thank you for reading!
If you found it valuable, hit a like ❤️ and consider subscribing for more such content every week.
If you have any questions or suggestions, leave a comment.
P.S. If you’re finding this newsletter helpful and want to get even more value, consider becoming a paid subscriber.
As a paid subscriber, you’ll receive an exclusive deep dive every week, access to a comprehensive system design learning resource , and other premium perks.
There are group discounts, gift options, and referral bonuses available.
Checkout my Youtube channel for more in-depth content.
Follow me on LinkedIn, X and Medium to stay updated.
Checkout my GitHub repositories for free interview preparation resources.
I hope you have a lovely day!
See you soon,
Ashish

