What is Change Data Capture (CDC)?
Modern applications often rely on multiple systems (e.g., search engines, caches, data lakes, microservices), all of which need up-to-date data.
Traditional batch ETL jobs are slow, introduce latency, and often lead to stale data and inconsistencies.
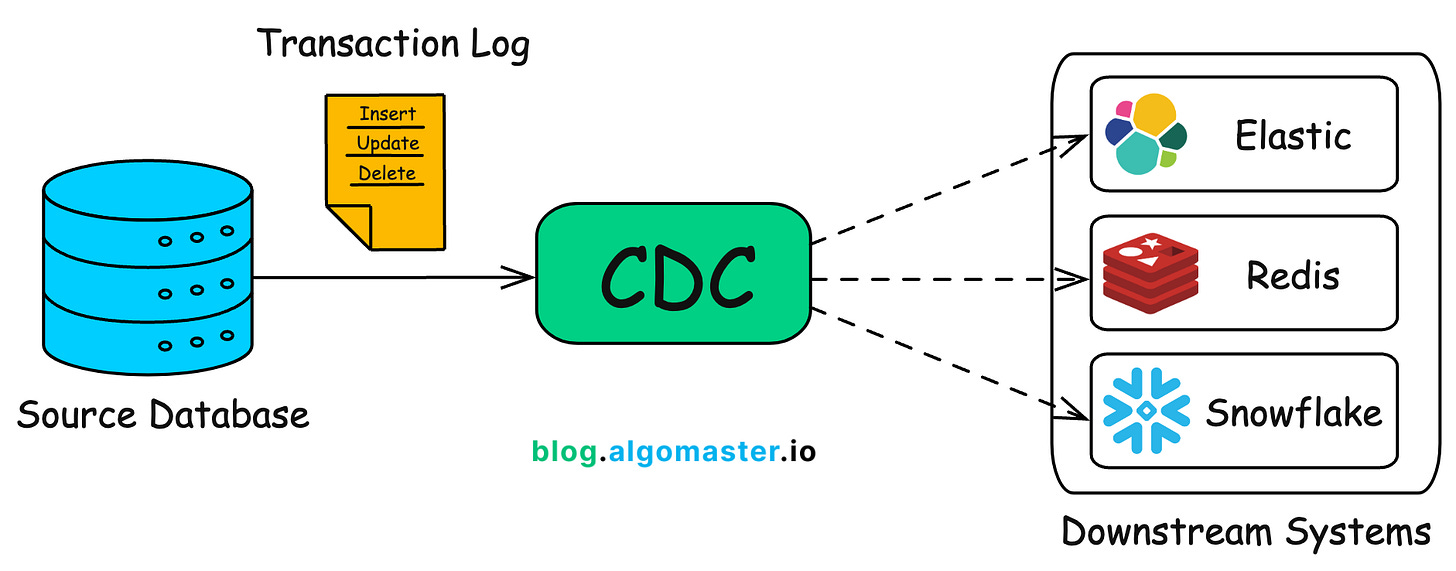
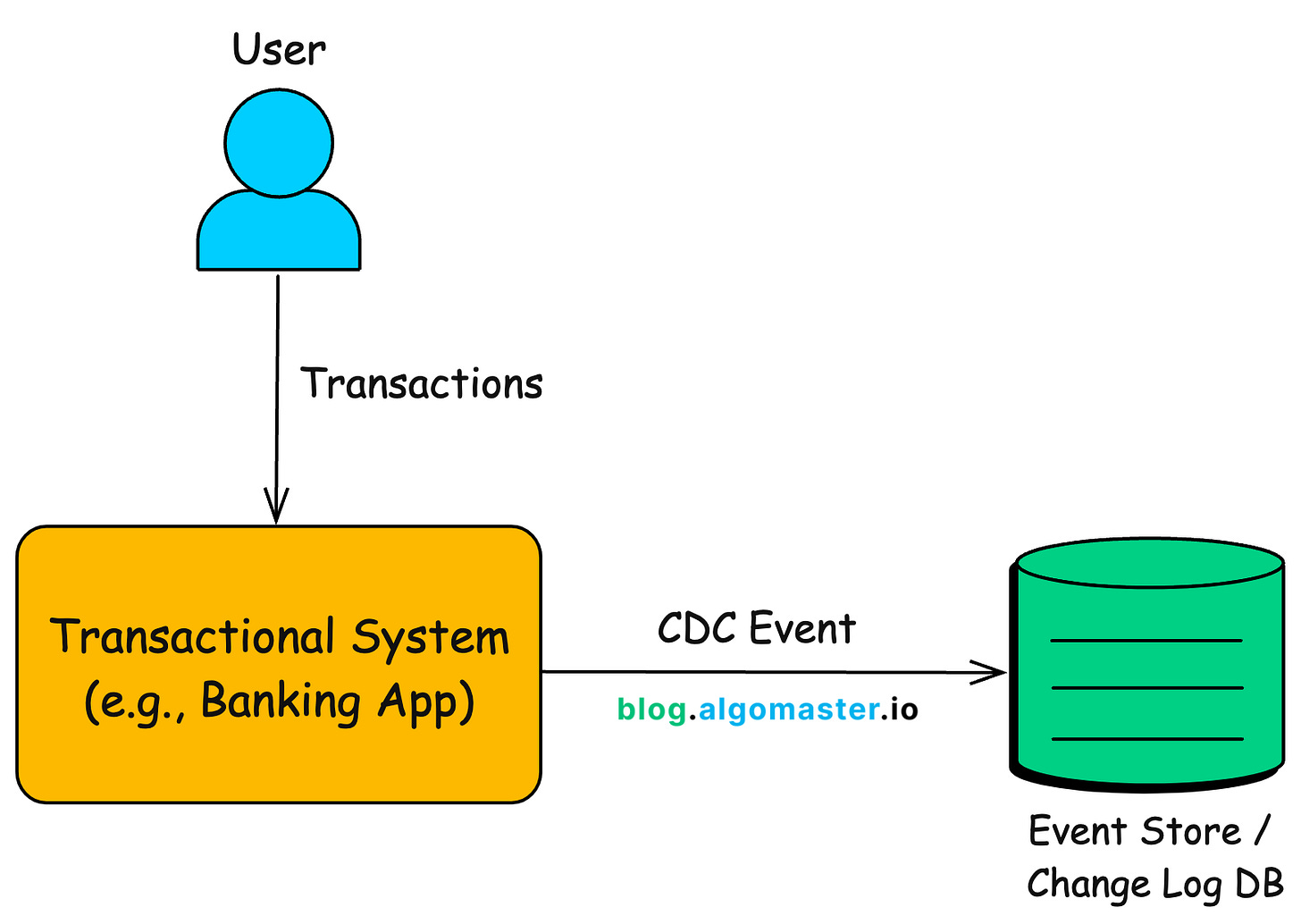
Change Data Capture (CDC) is a design pattern used to track and capture changes in a database (inserts, updates, deletes) and stream those changes in real time to downstream systems.
This ensures downstream systems remain in sync without needing expensive batch jobs.
In this article, we’ll dive into how CDC works, explore different implementation strategies, it’s real-world use cases, challenges and considerations.
1. How CDC Works
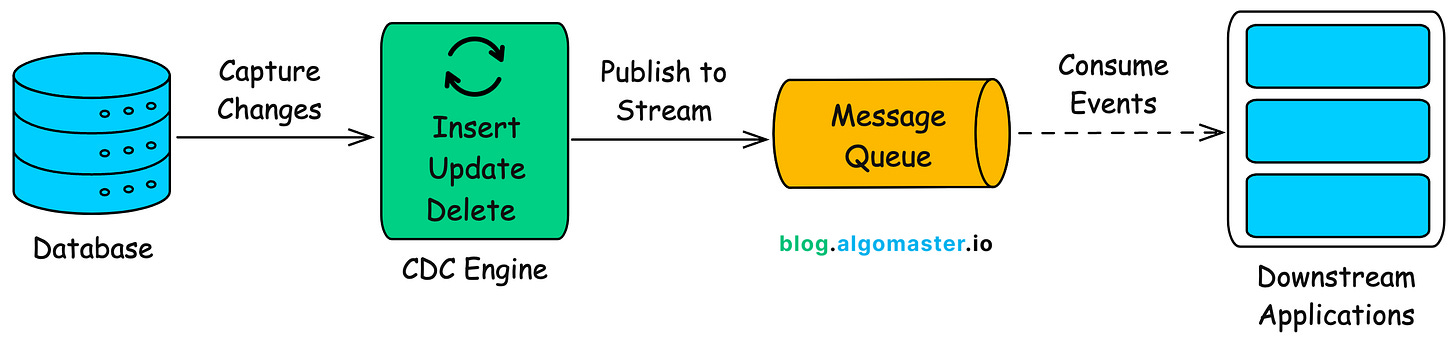
At a high level, CDC works by continuously monitoring a database for data changes (insertions, updates, and deletions).
When a change occurs, CDC captures the change event and makes the information available for processing.
The process typically involves:
-
Monitoring: Detecting changes from source systems. This can be achieved through database triggers, reading transaction logs, or using specialized CDC tools.
-
Capturing: Extracting details about the change event (such as before and after values) along with metadata (e.g., timestamp, changed table).
-
Delivering: Transmitting the change event to consumers, which might include message queues, data pipelines, or real-time analytics systems.
This helps in achieving event-driven architectures where applications respond to data changes as they happen.
2. CDC Implementation Approaches
There are three main approaches to implementing CDC:
2.1 Timestamp-Based CDC
This approach relies on adding a last_updated or last_modified column to your database tables.
Every time a row is inserted or modified, this column is updated with the current timestamp. Applications then query the table for rows where the last_updated time is later than the last sync time.
Example Query:
SELECT * FROM orders WHERE last_updated > '2024-02-15 12:00:00';Pros:
-
Simplicity: Easy to implement without major changes to the database architecture.
-
No External Dependencies: Can be executed with basic SQL operations, making it accessible for smaller projects or legacy systems.
Cons:
-
Incomplete Capture: This method may not capture deleted records since the timestamp is typically updated on existing rows.
-
Performance Overhead: As your data grows, frequent querying based on timestamps can impact performance, especially if indexing is not optimally configured.
-
Potential Data Gaps: Misconfigured timestamp updates or clock skew issues can result in missed changes.
2.2 Trigger-Based CDC
Trigger-Based CDC involves setting up database triggers that automatically log changes to a separate audit table whenever an insert, update, or delete operation occurs.
This audit table then serves as a reliable source of change records, which can be pushed to other systems as needed.
Example Trigger:
CREATE TRIGGER order_changes
AFTER UPDATE ON orders
FOR EACH ROW
INSERT INTO order_audit (order_id, old_status, new_status, changed_at)
VALUES (OLD.id, OLD.status, NEW.status, NOW());Pros:
-
Real-Time Capture: Triggers capture changes immediately when they occur.
-
Detailed Auditing: Offers a granular record of changes, including before-and-after values, which is useful for audit trails and debugging.
-
Flexibility: Can be tailored to capture specific columns or changes.
Cons:
-
Performance Impact: Triggers execute during the transaction, potentially slowing down database write operations.
-
Complexity in Maintenance: Changes in database schema often require corresponding updates to trigger definitions.
-
Resource Intensive: In high-transaction environments, the additional load of maintaining an audit table can become significant.
2.3 Log-Based CDC
Log-Based CDC reads changes directly from the database’s write-ahead log (WAL) or binary log (binlog). This method intercepts the low-level database operations, enabling it to capture every change made to the database without interfering with the application’s normal workflow.
Examples Tools:
-
Debezium: An open-source platform that streams database changes.
-
Kafka Connect: Often used in conjunction with Debezium to integrate with Apache Kafka.
-
AWS DMS: A managed service for data migration and CDC in the cloud.
Pros:
-
High Efficiency: Minimizes the impact on the primary database since it leverages existing logs.
-
Scalability: Well-suited for large, high-transaction environments.
-
Comprehensive Change Capture: Accurately captures every change, including inserts, updates, and deletes.
-
Minimal Latency: Provides near real-time data movement, essential for dynamic data-driven systems.
Cons:
-
Complex Setup: May require additional configuration and understanding of the underlying database logs.
-
Dependency on Database Features: Not all databases expose their logs in a manner that is easy to consume.
-
Tooling Overhead: Often necessitates integration with additional tools or services, which can add to the overall system complexity.
In modern applications, Log-based CDC is generally preferred because it efficiently captures all types of changes (inserts, updates, and deletes) directly from transaction logs, minimizes impact on the primary database, and scales well with high data volumes.
3. Real-World Use Cases of CDC
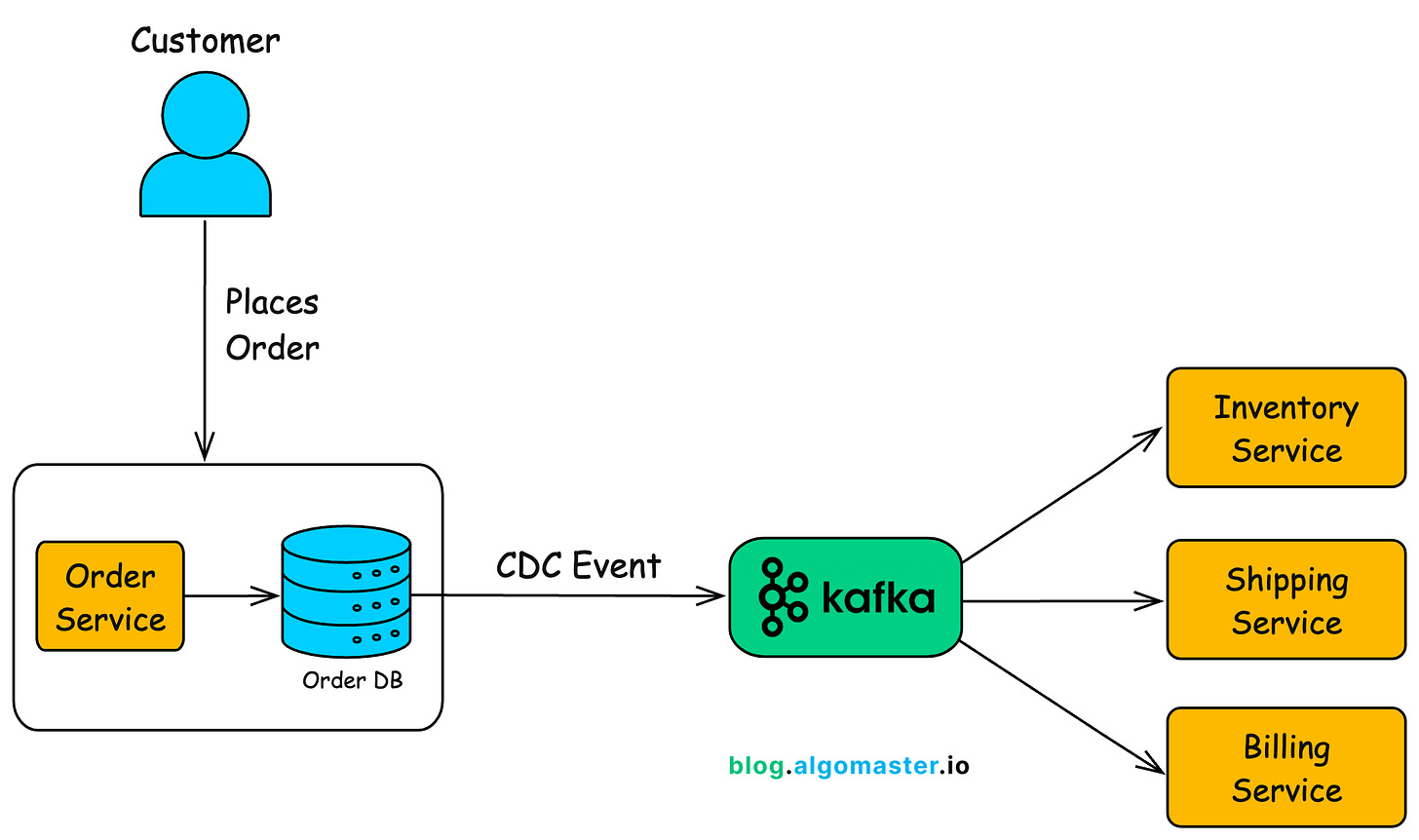
3.1. Microservices Communication
In a microservices architecture, individual services often need to communicate and share state changes without being tightly coupled.
With CDC in place, the change is captured and propagated via a messaging system (such as Kafka) so that each microservice can stay updated on the relevant changes in other services’ databases without needing direct service-to-service calls.
3.2 Event Sourcing
Event sourcing involves recording every change to an application state as a sequence of events. CDC can be leveraged to capture these changes in real time, building a complete log of all modifications.
Example:
Consider a financial application that logs every transaction. Instead of simply updating an account’s balance, every deposit, withdrawal, or transfer is recorded as an event. CDC captures these events and builds a detailed log of all state changes. This audit trail can later be used to reconstruct any account’s history or to debug issues.
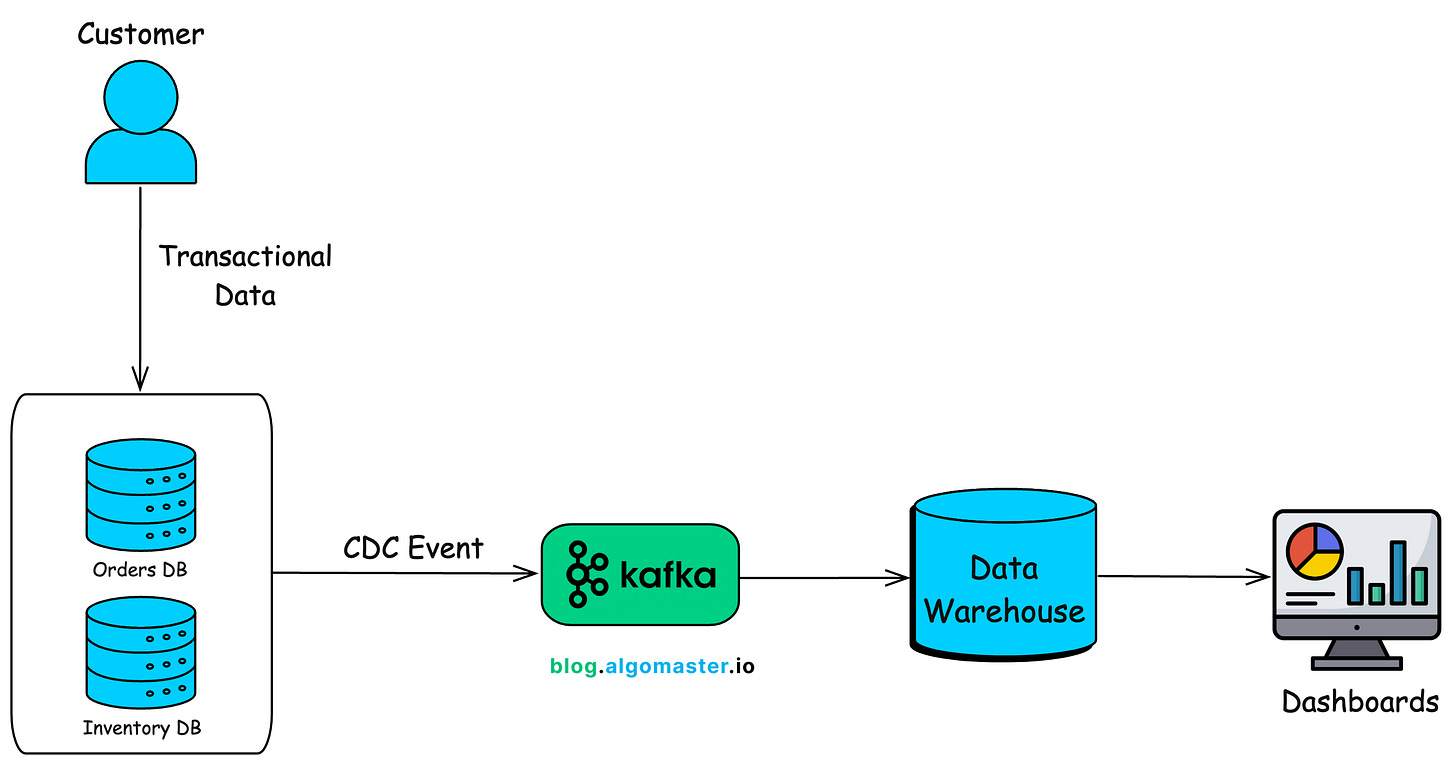
3.3 Data Warehousing
Data warehousing involves consolidating large volumes of transactional data for analysis and reporting. CDC can capture database changes as they happen and push them into a data warehouse in near real-time.
Analysts and decision-makers then use up-to-date data for reporting, analytics and dashboards.
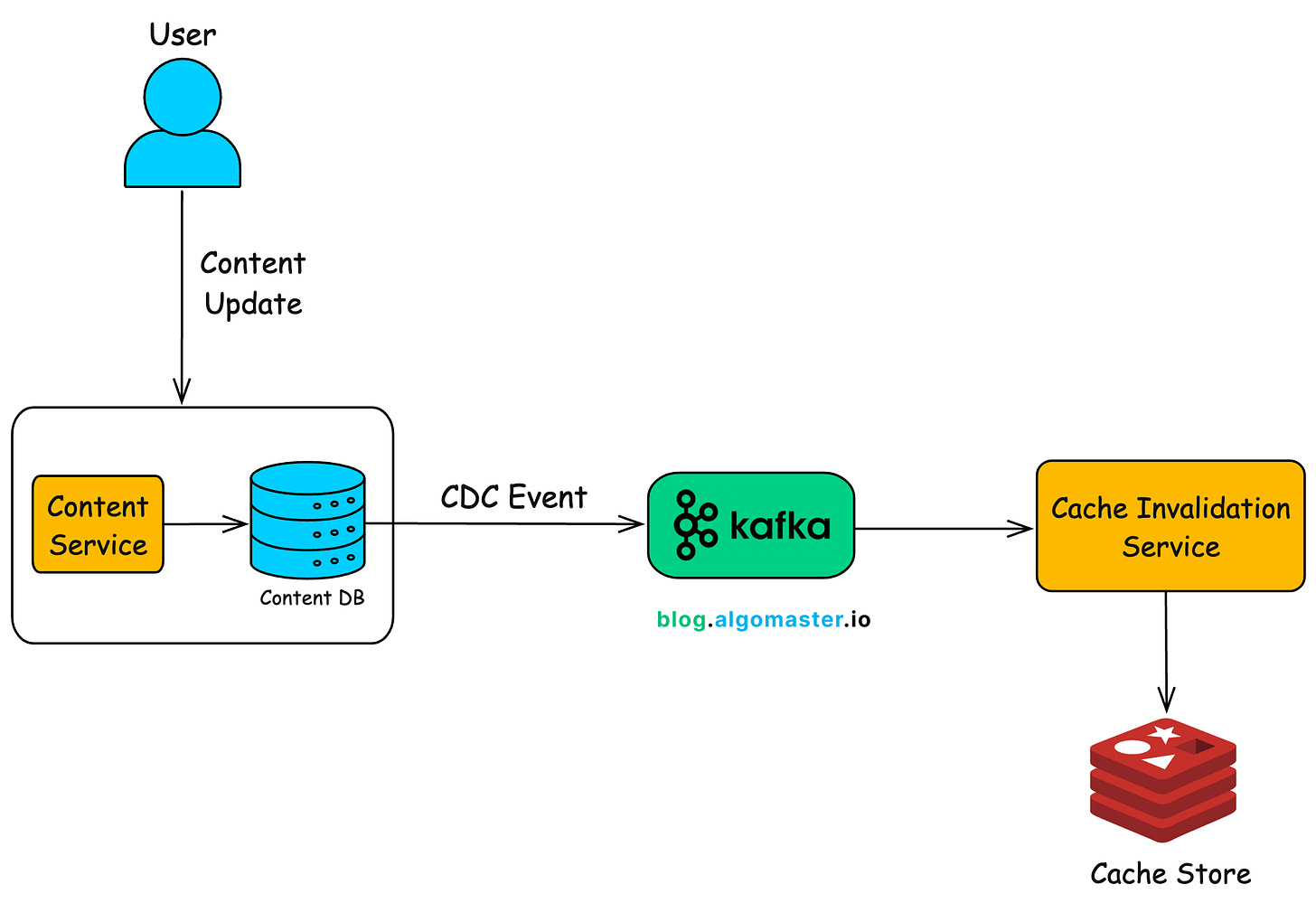
3.4 Cache Invalidation
Caches are used to improve application performance by storing frequently accessed data. However, stale cache data can cause issues, leading to outdated or incorrect information being displayed.
CDC can trigger cache updates automatically whenever the underlying data changes.
Example:
An online news platform uses caching to speed up page loads for popular articles. However, when an article is updated (e.g., a correction is issued or new content is added), the cache must be invalidated to prevent serving stale content.
With CDC, changes in the content database are captured and automatically trigger cache updates, ensuring readers always see the most current information.
4. Implementing CDC with Debezium and Kafka
Debezium is a popular open-source tool that provides log-based CDC for various databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB.
When integrated with Apache Kafka, Debezium can capture and stream database changes in near real time.
Step 1: Set Up Kafka and Debezium
Before configuring Debezium, you need to have a running Kafka cluster.
# Start Zookeeper
bin/zookeeper-server-start.sh config/zookeeper.properties &
# Start Kafka Broker
bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server.properties &Step 2: Configure Debezium Connector for MySQL
Next, create a Debezium connector configuration to capture changes from your MySQL database. This configuration tells Debezium which database and tables to monitor, along with necessary connection details.
{
"name": "inventory-connector",
"config": {
"connector.class": "io.debezium.connector.mysql.MySqlConnector",
"database.hostname": "localhost",
"database.port": "3306",
"database.user": "cdc_user",
"database.password": "password",
"database.server.id": "184054",
"database.include.list": "ecommerce",
"table.include.list": "ecommerce.orders",
"database.history.kafka.bootstrap.servers": "localhost:9092",
"database.history.kafka.topic": "dbhistory.inventory"
}
}Step 3: Listen for Changes
Once the Debezium connector is properly configured and running, it starts capturing change events from the MySQL database.
These events are then published to Kafka topics. You can consume these events using Kafka command-line tools or any Kafka consumer application.
bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic dbhistory.inventory --from-beginning5. Challenges and Considerations
While CDC is a powerful tool for real-time data integration, its implementation comes with several challenges that must be carefully managed:
-
Schema Evolution: Databases evolve over time, with changes such as adding or modifying columns. A robust CDC pipeline must gracefully adapt to schema alterations, ensuring that no data changes are lost or misinterpreted.
-
High Throughput Handling: In high-transaction environments, large volumes of data changes can occur rapidly. It’s essential to design a CDC system that can process and relay these events efficiently to avoid overwhelming downstream systems.
-
Ordering Guarantees: Maintaining the correct sequence of events is critical, especially in distributed architectures. The CDC solution should ensure that events are processed in the exact order they occurred, preserving data integrity across all consuming services.
-
Security and Compliance: Because CDC involves capturing detailed data changes, it can expose sensitive information if not properly managed. Implementing robust security measures such as encryption, data masking, and strict access controls is vital to protect data and comply with regulatory requirements.
Thank you for reading!
If you found it valuable, hit a like ❤️ and consider subscribing for more such content every week.
P.S. If you’re enjoying this newsletter and want to get even more value, consider becoming a paid subscriber.
As a paid subscriber, you’ll receive an exclusive deep dive every Thursday, access to a structured system design resource, and other premium perks.
There are group discounts, gift options, and referral bonuses available.