What is an API Gateway?
APIs, or Application Programming Interfaces, are a set of rules and protocols that allows two software applications or services to communicate with each other.
As applications grow in size, the number of APIs increases too. Without the right tools and infrastructure, managing these APIs can quickly become a challenge.
This is where API Gateway comes into play.
An API Gateway acts as a central server that sits between clients (e.g., browsers, mobile apps) and backend services.
Instead of clients interacting with multiple microservices directly, they send their requests to the API Gateway. The gateway processes these requests, enforces security, and forwards them to the appropriate microservices.
In this article, we will explore why do we need an API gateway, the key features it provides and how it works step by step.
If you’re finding this newsletter valuable and want to deepen your learning, consider becoming a paid subscriber.
As a paid subscriber, you’ll receive an exclusive deep-dive article every week, access to a structured System Design Resource (100+ topics and interview questions), and other premium perks.
1. Why Do We Need an API Gateway?
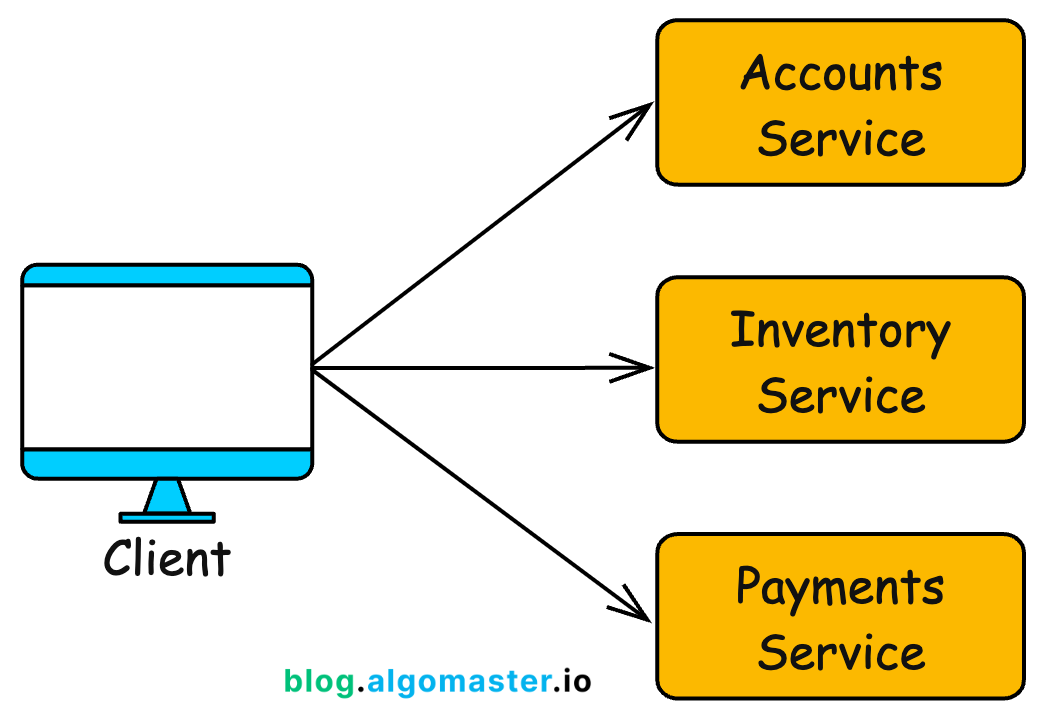
Modern applications, especially those built using microservices architecture, have multiple backend services managing different functionalities.
For example, in an e-commerce service:
-
One service handles user accounts.
-
Another handles payments.
-
Another manages product inventory.
Without an API Gateway:
-
Clients would need to know the location and details of all backend services.
-
Developers would need to manage authentication, rate limiting, and security for each service individually.
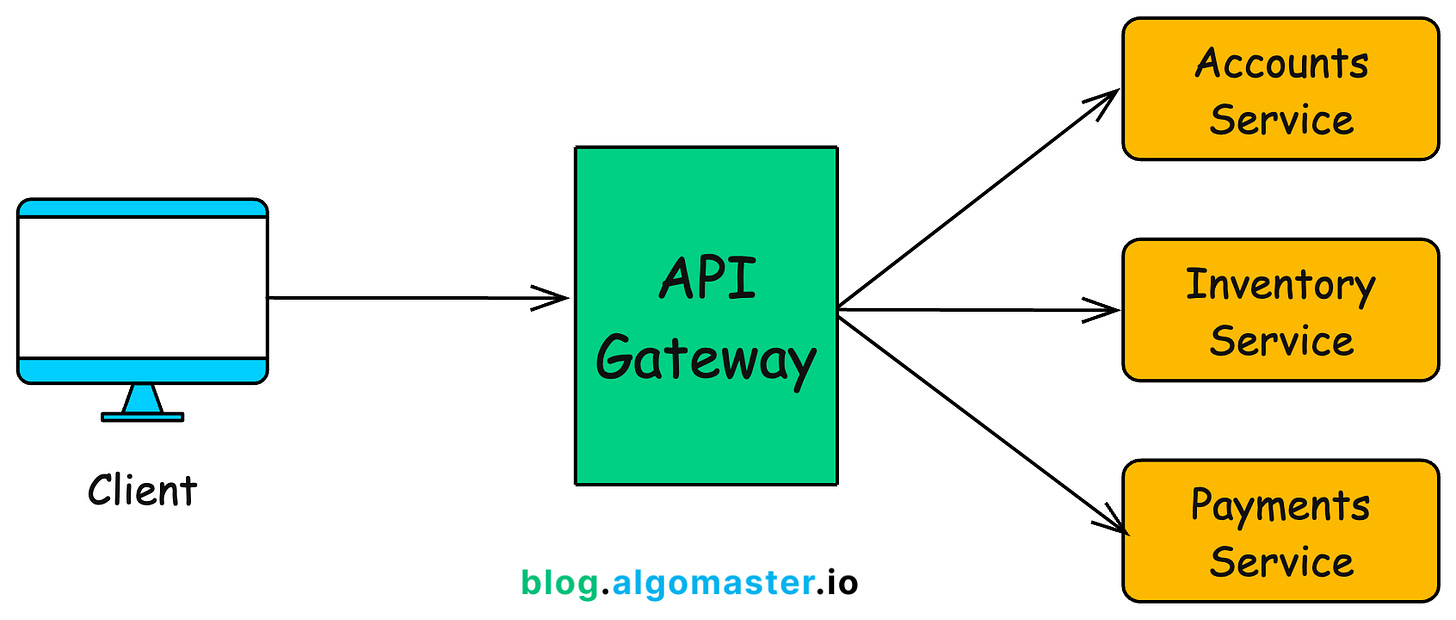
With an API Gateway:
-
Clients send all requests to one place – the API Gateway.
-
The API Gateway takes care of routing, authentication, security, and other operational tasks, simplifying both client interactions and backend management.
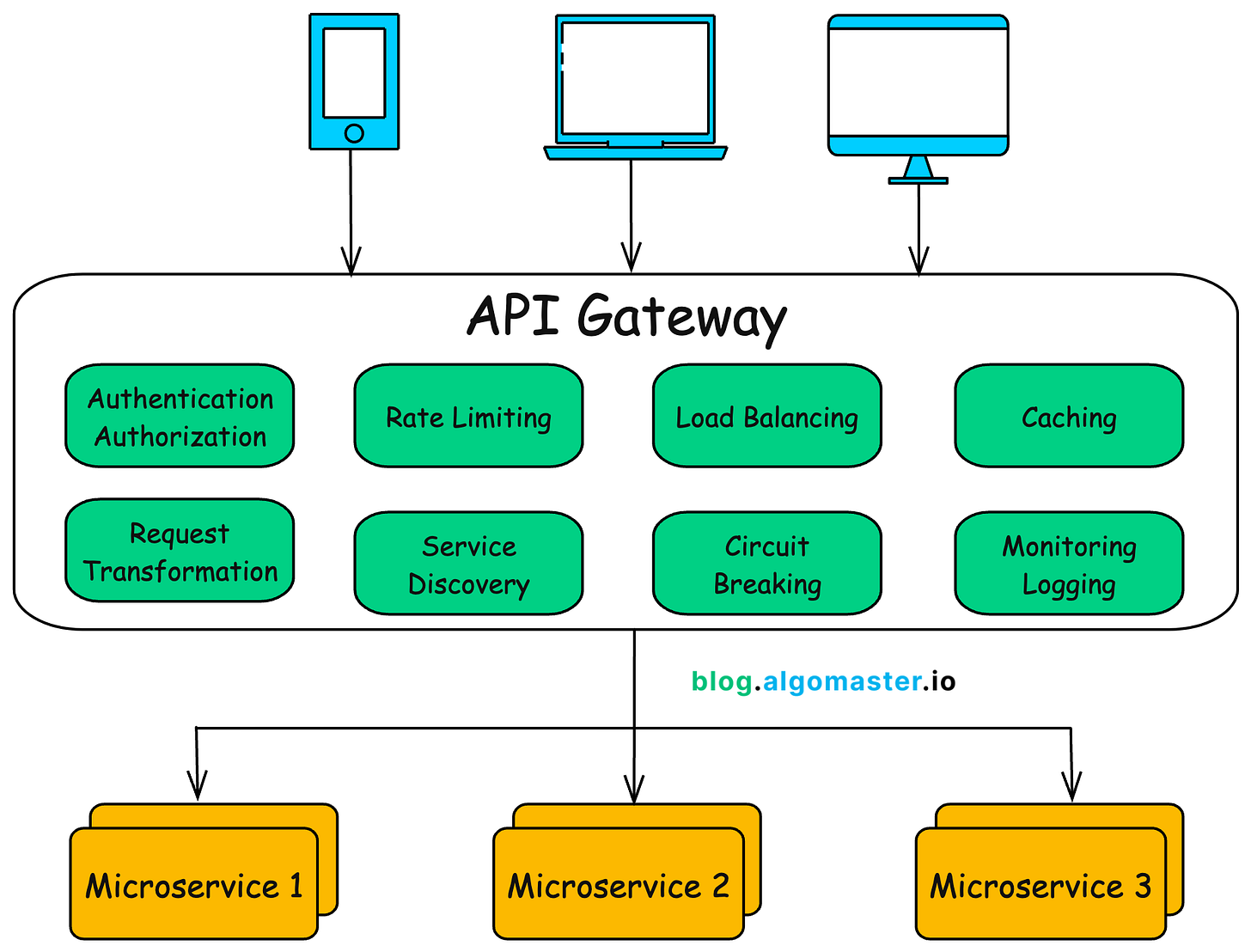
2. Core Features of an API Gateway
1. Authentication and Authorization
API Gateway secures the backend systems by ensuring only authorized users and clients can access backend services.
It handles tasks like:
-
Authentication: Verifying the identity of the client using tokens (e.g., OAuth, JWT), API keys, or certificates.
-
Authorization: Checking the client’s permissions to access specific services or resources.
By centralizing these tasks, the API gateway eliminates the need for individual services to handle authentication, reducing redundancy and ensuring consistent access control across the system.
2. Rate Limiting
To prevent abuse and ensure fair usage of resources, most API Gateways implement rate limiting.
This feature:
-
Controls the frequency of requests a client can make within a given timeframe.
-
Protects backend services from being overwhelmed by excessive traffic or potential denial-of-service (DoS) attacks.
For example, a public API might allow a maximum of 100 requests per minute per user. If a client exceeds this limit, the API Gateway will block additional requests until the rate resets.
3. Load Balancing
High-traffic applications rely on load balancing to distribute incoming requests evenly across multiple instances of a service.
The API Gateway can:
-
Redirect requests to healthy service instances while avoiding ones that are down or overloaded.
-
Use algorithms like round-robin, least connections, or weighted distribution to manage traffic intelligently.
4. Caching
To improve response times and reduce the strain on backend services, most API Gateways provide caching.
They temporarily store frequently requested data, such as:
-
Responses to commonly accessed endpoints (e.g., product catalogs or weather data).
-
Static resources like images or metadata.
Caching helps in reducing latency and enhancing user experience while lowering the operational cost of backend services.
5. Request Transformation
In systems with diverse clients and backend services, request transformation is essential for compatibility.
An API Gateway can:
-
Modify the structure or format of incoming requests to match the backend service requirements.
-
Transform responses before sending them back to the client, ensuring they meet the client’s expectations.
For instance, it might convert XML responses from a legacy service into JSON for modern frontend applications.
6. Service Discovery
Modern systems often involve microservices that scale dynamically.
The service discovery feature of an API Gateway dynamically identifies the appropriate backend service instance to handle each request.
This ensures seamless request routing even in environments where services frequently scale up or down.
7. Circuit Breaking
Circuit breaking is a mechanism that temporarily stops sending requests to a backend service when it detects persistent failures, such as:
-
Slow responses or timeouts.
-
Server errors (e.g., HTTP 500 status codes).
-
High latency or unavailability of a service.
The API Gateway continuously monitors the health and performance of backend services and uses circuit breaking to block requests to a failing service.
8. Logging and Monitoring
API Gateways provide robust monitoring and logging capabilities to track and analyze system behavior.
These capabilities include:
-
Logging detailed information about each request, such as source, destination, and response time.
-
Collecting metrics like request rates, error rates, and latency.
This data helps system administrators detect anomalies, troubleshoot issues, and optimize the system’s performance. Many API Gateways also integrate with monitoring tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or AWS CloudWatch.
3. How Does an API Gateway Work?
Imagine you’re using a food delivery app to order dinner. When you tap “Place Order” your phone makes an API request. But instead of talking directly to various backend services, it communicates with an API Gateway first.
Step 1: Request Reception
When you tap “Place Order,” the app sends a request to the API Gateway, asking it to process your order.
This request includes things like:
-
Your user ID
-
Selected restaurant and menu items
-
Delivery address
-
Payment method
-
Authentication tokens
The API Gateway receives the request as the single entry point to the backend system.
Step 2: Request Validation
Before forwarding the request, the API Gateway validates it to ensure:
-
The required parameters or headers are present.
-
The data is in the correct format (e.g., JSON).
-
The request conforms to the expected structure or schema.
// Example of initial request handling
app.post('/api/v1/orders', async (req, res) => {
// Check if request has required headers
if (!req.headers['content-type'].includes('application/json')) {
return res.status(400).send('Invalid content type');
}
// Continue processing...
});If any information is missing or incorrect, the gateway immediately rejects the request and notifies the app with an appropriate error message.
Step 3: Authentication & Authorization
The gateway now verifies your identity and permissions to ensures only legitimate users can place orders:
-
It forwards your authentication token (e.g., OAuth or JWT) to an identity provider to confirm your identity.
-
It checks your permissions to ensure you’re authorized to use the app for placing an order.
const authenticateRequest = async (req) => {
// Extract JWT token from header
const token = req.headers.authorization?.split(' ')[1];
// Verify token and get user details
const user = await verifyToken(token);
// Check if user has permission to place orders
return user.permissions.includes('place_orders');
};If authentication or authorization fails, the API Gateway sends a 401 Unauthorized or 403 Forbidden error back to the app.
Step 4: Rate Limiting
To prevent abuse, the API Gateway checks how many requests you’ve made recently. For example:
-
If you’ve made 10 “Place Order” requests in the last minute (maybe by accident), the gateway might block additional requests temporarily and return
429 Too Many Requestsresponse.
const checkRateLimit = async (userId) => {
const key = `rate_limit:order:${userId}`;
const current = await redis.incr(key);
// If first request in window, set expiry
if (current === 1) {
await redis.expire(key, 60); // 1 minute window
}
return current <= 10; // Allow 10 order requests per minute
};This ensures the system remains stable and fair for all users specially during traffic spikes or malicious attacks, such as distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attempts.
Step 5: Request Transformation (if needed)
If any of these backend services require specific data formats or additional details, the API Gateway transforms the request.
For example:
-
The app sends the delivery address in plain text, but the Delivery Service expects GPS coordinates. The API Gateway converts the address into coordinates before forwarding the request.
const transformRequest = async (originalRequest) => {
const address = originalRequest.deliveryAddress;
// Convert address to GPS coordinates using a geocoding API
const coordinates = await getCoordinatesFromAddress(address);
if (!coordinates) {
throw new Error('Failed to fetch GPS coordinates');
}
// Transform the request for the Delivery Service
return {
orderId: originalRequest.orderId,
customerName: originalRequest.customerName,
deliveryLocation: {
latitude: coordinates.lat,
longitude: coordinates.lng
},
deliveryInstructions: originalRequest.instructions || ""
};
};Step 6: Request Routing
The API Gateway now needs to coordinate several backend services to process your order.
Using service discovery, it identifies:
-
Order Service: To create a new order record.
-
Inventory Service: To check if the restaurant has your selected items available.
-
Payment Service: To process your payment.
-
Delivery Service: To assign a delivery driver to your order.
The gateway dynamically routes the request to these services using a load balancing algorithm, ensuring it connects to available and healthy service instances.
const routeRequest = async (req, serviceType) => {
// Get service registry
const services = await serviceDiscovery.getServices(serviceType);
// Select instance
const targetService = selectServiceInstance(services);
// Forward request
return await axios.post(
`${targetService.url}/api/orders`,
req.body,
{ headers: req.headers }
);
};Step 7: Response Handling
Once the API Gateway receives the response(s) from the backend service(s), it performs the following tasks:
-
Transformation: Adjusts the response format or structure to match the client’s requirements.
-
Caching (Optional): Stores the response temporarily for frequently accessed data, reducing future latency.
const handleResponse = async (serviceResponse) => {
// Transform response if needed
const transformedResponse = {
orderId: serviceResponse.order_reference,
estimatedDelivery: serviceResponse.eta,
status: serviceResponse.current_status
};
// Cache response if applicable
if (serviceResponse.cacheable) {
await cacheResponse(
transformedResponse.orderId,
transformedResponse
);
}
return transformedResponse;
};Finally, the API Gateway sends the processed response back to the client in a format they can easily understand.
Step 8: Logging & Monitoring
Throughout this process, the gateway records important metrics to track each request:
const logRequest = async (req, res, timing) => {
await logger.log({
timestamp: new Date(),
path: req.path,
method: req.method,
responseTime: timing,
statusCode: res.statusCode,
userId: req.user?.id
});
};Thank you for reading!
If you found it valuable, hit a like ❤️ and consider subscribing for more such content every week.
If you have any questions or suggestions, leave a comment.
P.S. If you’re finding this newsletter helpful and want to get even more value, consider becoming a paid subscriber.
As a paid subscriber, you’ll receive an exclusive deep dive every week, access to a comprehensive system design learning resource , and other premium perks.
There are group discounts, gift options, and referral bonuses available.
Checkout my Youtube channel for more in-depth content.
Follow me on LinkedIn, X and Medium to stay updated.
Checkout my GitHub repositories for free interview preparation resources.
I hope you have a lovely day!
See you soon,
Ashish