What are Message Queues and When to Use Them?
#26 System Design – Message Queues
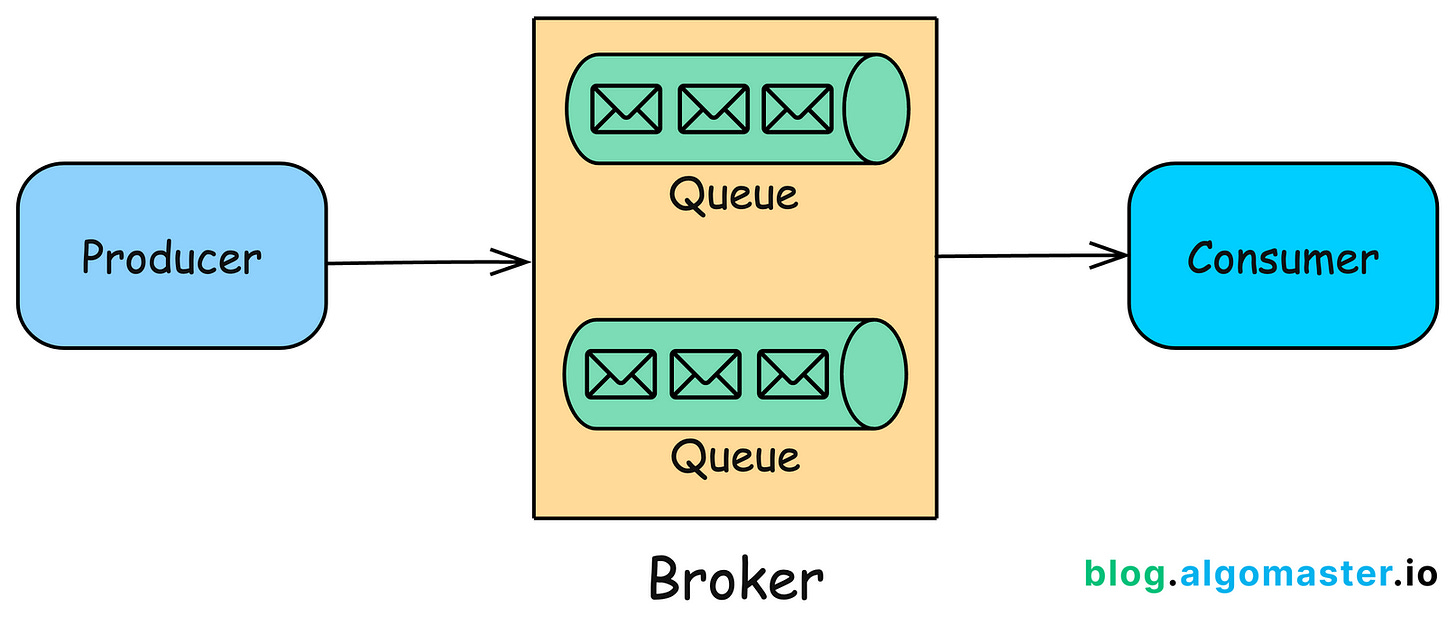
A message queue is a communication mechanism that enables different parts of a system to send and receive messages asynchronously.
It acts as an intermediary that temporarily holds messages sent from producers (or publishers) and delivers them to consumers (or subscribers).
The key characteristic of a message queue is that it allows components to communicate without needing to be aware of each other’s existence, leading to a decoupled architecture.
If you’re finding this newsletter valuable and want to deepen your learning, consider becoming a paid subscriber.
As a paid subscriber, you’ll receive an exclusive deep-dive article every week, access to a structured System Design Resource (100+ topics and interview questions), and other premium perks.
1. Core Components of a Message Queue
1. Producer/Publisher
The entity that sends messages to the queue. Producers push messages into the queue without worrying about the consumer’s state.
2. Consumer/Subscriber
The entity that reads messages from the queue. Consumers pull messages from the queue and process them.
3. Queue
The data structure that stores messages until they are consumed.
4. Broker/Queue Manager
The software or service that manages the message queue, handles the delivery of messages, and ensures that messages are routed correctly between producers and consumers.
5. Message
The unit of data sent through the queue. A message typically contains the payload (the actual data being sent) and metadata (such as headers, timestamps, and priority).
2. How Do Message Queues Work?
The basic workflow of a message queue can be broken down into the following steps:
-
Message Creation: A producer generates a message containing the necessary data and metadata.
-
Message Enqueue: The producer sends the message to the queue, where it is stored until a consumer retrieves it.
-
Message Storage: The queue stores the message in a persistent or transient manner based on its configuration.
-
Message Dequeue: A consumer retrieves the message from the queue for processing. Depending on the queue’s configuration, messages can be consumed in order, based on priority, or even in parallel.
-
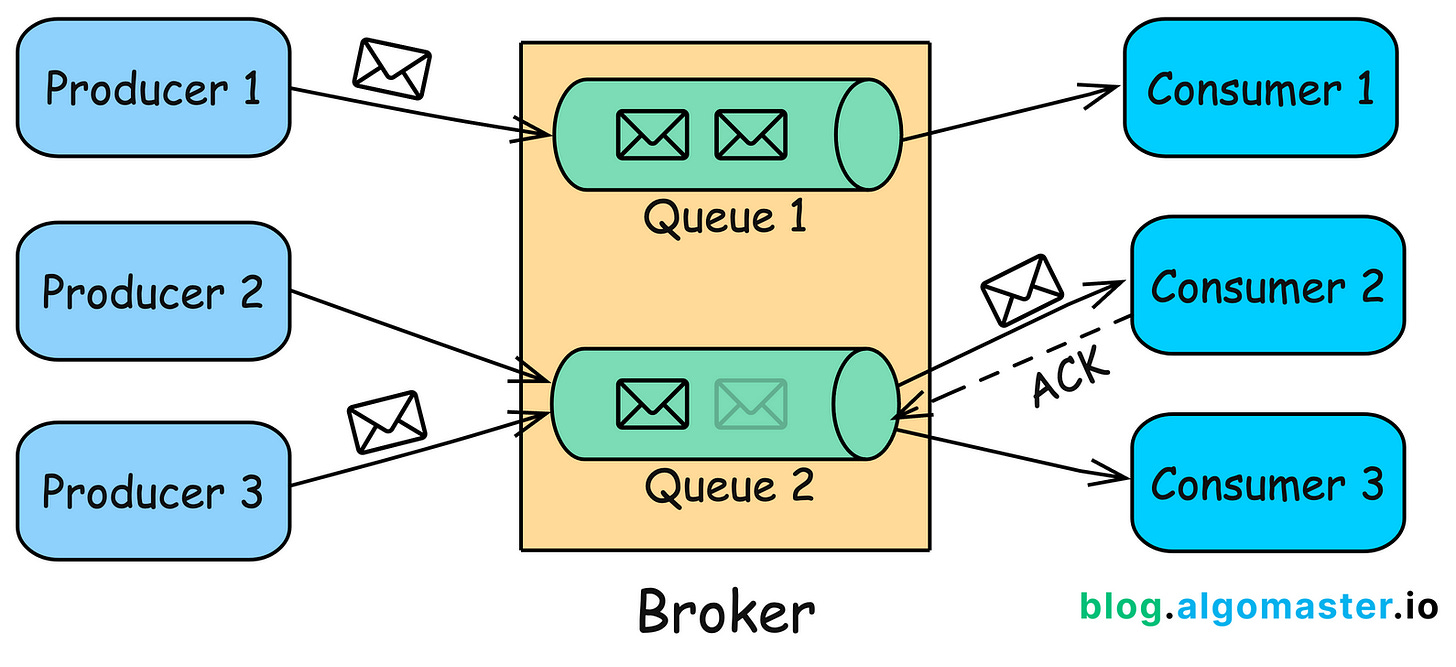
Acknowledgment: Once the consumer processes the message, it may send an acknowledgment back to the broker, confirming that the message has been successfully handled.
-
Message Deletion: After acknowledgment, the broker removes the message from the queue to prevent it from being processed again.
3. Types of Message Queues
There are several types of message queues, each designed to solve specific problems:
1. Point-to-Point (P2P) Queue
In this model, messages are sent from one producer to one consumer.
Used when a message needs to be processed by a single consumer, such as in task processing systems.
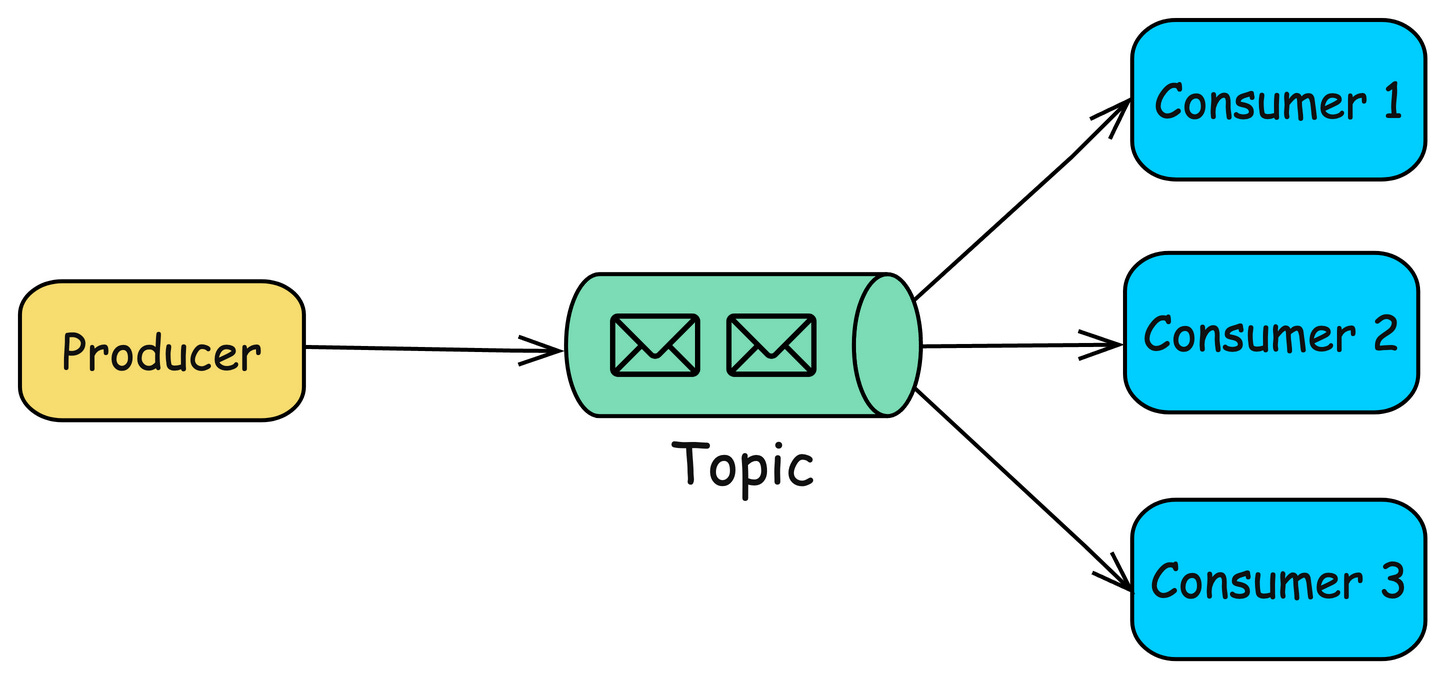
2. Publish/Subscribe (Pub/Sub) Queue
In this model, messages are published to a topic, and multiple consumers can subscribe to that topic to receive messages.
Used for broadcasting messages to multiple consumers, such as in notification systems.
3. Priority Queue
Messages in the queue are assigned priorities, and higher-priority messages are processed before lower-priority ones.
Used when certain tasks need to be handled more urgently than others.
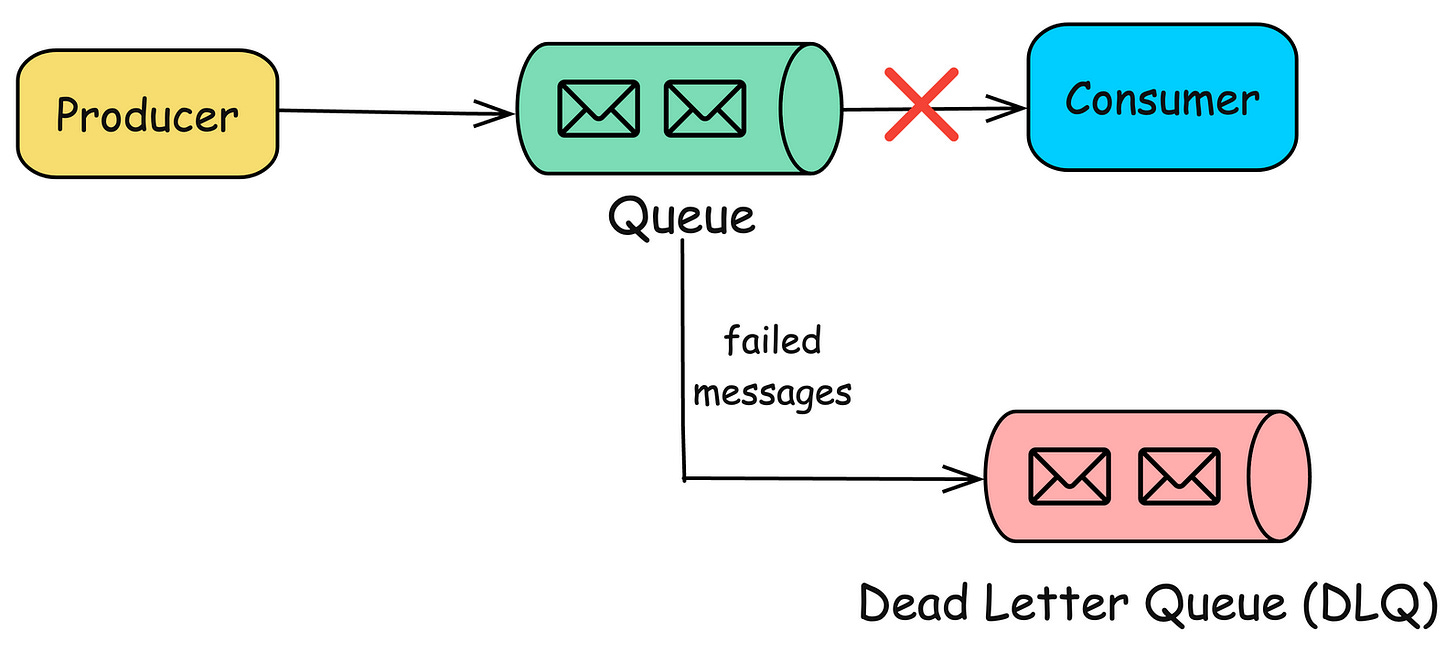
4. Dead Letter Queue (DLQ)
A special type of queue where messages that cannot be processed (due to errors or retries) are sent.
Useful for troubleshooting and handling failed messages.
4. Advantages of Using Message Queues
Message queues offer several benefits including:
-
Decoupling: Message queues decouple producers and consumers, allowing them to operate independently. This enables more flexible and scalable architectures.
-
Asynchronous Processing: Producers can send messages to the queue and move on to other tasks without waiting for consumers to process the messages. This improves overall system throughput.
-
Load Balancing: Multiple consumers can pull messages from the queue, allowing work to be distributed and balanced across different consumers.
-
Fault Tolerance: Persistent message queues ensure that messages are not lost even if a consumer or producer fails. They also allow for retries and error handling.
-
Scalability: Message queues can handle a high volume of messages, allowing systems to scale horizontally by adding more consumers.
-
Throttling: Message queues can help control the rate of message processing, preventing consumers from being overwhelmed.
5. When to Use Message Queues
Message queues aren’t always the best solution, but they are very useful in certain situations:
1. Microservices Architecture
-
Problem: Microservices need to communicate with each other, but direct communication can lead to tight coupling and cascading failures.
-
Solution: Use message queues to enable asynchronous communication between microservices, allowing each service to operate independently and resiliently.
2. Task Scheduling and Background Processing
-
Problem: Certain tasks, such as image processing or sending emails, are time-consuming and should not block the main application flow.
-
Solution: Offload these tasks to a message queue and have background workers (consumers) process them asynchronously.
3. Event-Driven Architectures
-
Problem: Events need to be propagated to multiple services or components, but direct communication would be inefficient.
-
Solution: Use a Pub/Sub message queue to broadcast events to all interested consumers, ensuring that all parts of the system receive the necessary updates.
4. Load Leveling
-
Problem: Sudden spikes in requests can overwhelm a system, leading to degraded performance or failures.
-
Solution: Queue incoming requests using a message queue and process them at a steady rate, ensuring that the system remains stable under load.
5. Reliable Communication
-
Problem: Communication between components needs to be reliable, even in the face of network or service failures.
-
Solution: Use persistent message queues to ensure that messages are not lost and can be retried if delivery fails.
6. Best Practices for Implementing Message Queues
-
Idempotency: Ensure that your consumers can handle duplicate messages gracefully, as message queues may deliver the same message more than once.
-
Message Durability: Choose between persistent and transient messages based on the criticality of the data. Persistent messages ensure reliability but may come with performance trade-offs.
-
Error Handling: Implement robust error handling, including retries, dead-letter queues, and alerting mechanisms to deal with failed message processing.
-
Security: Secure your message queues by implementing encryption, authentication, and access control to protect the data in transit and at rest.
-
Monitoring and Metrics: Set up monitoring and metrics to track the performance and health of your message queues, including message throughput, queue length, and consumer lag.
-
Scalability: Plan for scalability by choosing a message queue solution that can grow with your system, whether by adding more consumers, partitioning queues, or using a distributed messaging system.
7. Popular Message Queue Systems
Several message queue systems are widely used in the industry, each with its own strengths and use cases:
-
RabbitMQ: A widely-used open-source message broker that supports multiple messaging protocols, including AMQP. It’s known for its reliability and extensive features.
-
Apache Kafka: A distributed streaming platform that excels at handling large volumes of data. Kafka is often used for real-time data processing and event streaming.
-
Amazon SQS: A fully managed message queue service provided by AWS. SQS is highly scalable and integrates well with other AWS services.
-
Google Cloud Pub/Sub: A fully managed message queue service offered by Google Cloud, designed for real-time analytics and event-driven applications.
-
Redis Streams: A feature of Redis that provides a simple, in-memory message queue with high performance, suitable for lightweight tasks.
-
ActiveMQ: An open-source message broker that supports various messaging protocols and is used in enterprise environments for reliable messaging.
8. Conclusion
To conclude, message queues are a powerful tool to enable asynchronous communication, decouple components, and improve the scalability and resilience of modern software systems.
As with any architectural decision, it’s important to consider your specific use case and requirements when deciding to implement message queues in your system.
Thank you for reading!
If you found it valuable, hit a like ❤️ and consider subscribing for more such content every week.
If you have any questions or suggestions, leave a comment.
P.S. If you’re finding this newsletter helpful and want to get even more value, consider becoming a paid subscriber.
As a paid subscriber, you’ll receive an exclusive deep dive every week, access to a comprehensive system design learning resource , and other premium perks.
There are group discounts, gift options, and referral bonuses available.
Checkout my Youtube channel for more in-depth content.
Follow me on LinkedIn, X and Medium to stay updated.
Checkout my GitHub repositories for free interview preparation resources.
I hope you have a lovely day!
See you soon,
Ashish