Top 15 Strategies to Reduce Latency
Latency is the time it takes for a system to respond to a user’s action. In simple terms, it’s the delay between:
-
When a user makes a request
-
And when they receive a response
Even small delays can have a significant impact. To put it into perspective:
Amazon estimates that every 1-second increase in latency could cost them $1.6 billion in annual sales.
On the flip side, low latency means smoother interactions, and a better overall user experience.
In this article, we’ll explore
-
The different types of latency that exist across your stack
-
And the top 15 strategies to reduce latency
Types of Latency
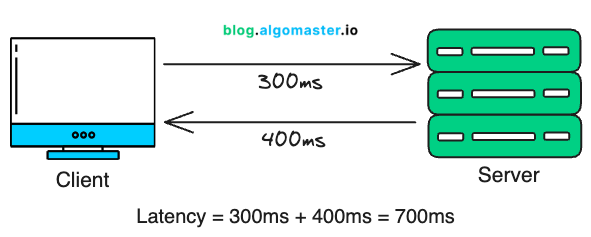
1. Network Latency
Network latency is the time it takes for data to travel across a network—from the client (e.g., a browser or mobile app) to the server and back. It’s often the first and most noticeable form of latency a user experiences.
What Causes High Network Latency?
-
Physical Distance: Data travels at near the speed of light, but if your server is in New York and your user is in Sydney, that distance adds real delay.
-
DNS Resolution Time: Before the request even hits your app, the domain must be resolved into an IP address. Poor DNS configuration or slow DNS providers can add 20–100ms.
-
TCP Handshake & TLS Negotiation: Establishing a connection (especially over HTTPS) requires multiple back-and-forth steps.
-
Packet Routing & Congestion: Packets may take inefficient routes or hit overloaded network segments.
-
Firewall and Proxy Overhead: Security appliances or proxies along the path can introduce additional hops and inspection delays.
2. Application Latency
Application latency is the time your backend system takes to:
-
Receive a request (after it hits the server)
-
Process the request (run logic, call services, query databases)
-
Generate a response and send it back
It’s the delay introduced by the backend code and often one of the biggest contributors to total latency in a system.
What Causes High Application Latency?
-
Inefficient Business Logic: Poorly written algorithms, redundant loops, or unoptimized code paths
-
Blocking Operations: Synchronous calls to databases, APIs, or file systems without using async/concurrent patterns
-
Service-to-service Chaining (Microservices): If one API calls another which calls another, latency compounds quickly
-
Poor Error Handling or Retries: Excessive retries or long timeouts can delay responses unnecessarily
-
Lack of Caching: Recomputing results that could have been fetched from cache
-
Heavy Serialization/Deserialization: Large JSON payloads, XML parsing, or inefficient marshaling
3. Database Latency
Database latency is the round-trip time between:
-
Sending a query to the database
-
The database executing the query (compute, read, write, etc.)
-
Receiving the result back in your application
In most backend applications, databases are the #1 bottleneck. A single slow query can hold up an entire request, and at scale, even small inefficiencies compound into major performance issues.
What Causes High Database Latency?
-
Unindexed Queries: Full table scans instead of using indexes
-
N+1 Query Problems: Querying inside a loop, leading to dozens or hundreds of queries per request
-
Large Result Sets: Fetching more data than needed (e.g.,
SELECT *on large tables) -
Poor Schema Design: Lack of normalization or too many unnecessary relations
-
Lock Contention or Deadlocks: Multiple transactions competing for the same rows
-
Resource Saturation: High CPU, memory, or I/O usage on the database server
4. Client-side Latency
Once your backend has done its job and the response reaches the user’s device, there’s still one more critical step: the client needs to render and display the data. That final stretch is what we call client-side latency.
Client-side latency is the delay between receiving data on the client (browser, mobile app, etc.) and displaying the usable content or UI to the user.
What Causes High Client-side Latency?
-
Large JavaScript Bundles: Too much JavaScript needs to be downloaded, parsed, and executed before anything appears on screen.
-
Slow DOM Manipulation: Poorly optimized DOM updates or frequent reflows/repaints can choke rendering.
-
Inefficient Rendering Logic: Complex, deeply nested components or unoptimized React/Vue/Svelte code can slow rendering.
-
Image & Asset Load Time: Uncompressed or unoptimized media assets (images, fonts, videos) block the UI from displaying.
-
Excessive Client-side Computation: Performing heavy calculations, filtering, or formatting on the frontend delays rendering.
-
Blocking Resources: CSS or fonts that are render-blocking can delay the first paint or cause layout shifts.
Top 15 Strategies to Reduce Latency
These strategies are not ranked in any particular order. In practice, you’ll often need to apply multiple techniques together, depending on your system’s architecture, scale, and latency goals.
1. Caching
When users expect blazing-fast responses, hitting your backend or database for every request just doesn’t scale. That’s where caching comes in.
Caching is the process of storing a copy of data closer to where it’s needed, typically in fast-access memory like RAM.
When the cache contains the required data (a cache hit), the application avoids slower downstream operations like database queries or API calls. This can cut response times from hundreds of milliseconds to single-digit milliseconds.
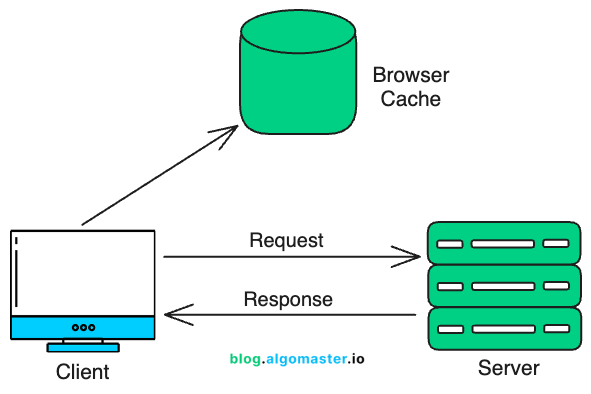
Client-side Caching
Client-side caching stores data on the user’s device, typically in the browser or mobile app. It reduces the need to re-fetch resources from the network.
You can cache static assets like images, JavaScript, CSS, or even API responses that rarely change.
-
Browser Cache: When you specify proper HTTP caching headers (e.g.,
Cache-Control,ETag,Expires), the browser stores assets locally. On subsequent requests, it can quickly load these from the local cache rather than fetching them again from the server. -
Local Storage / IndexedDB: Modern browsers offer persistent storage options. For example, you could store user preferences, profile data or application settings in
localStorageorIndexedDBso that the next time the user visits, the application can load instantly without waiting for the server.
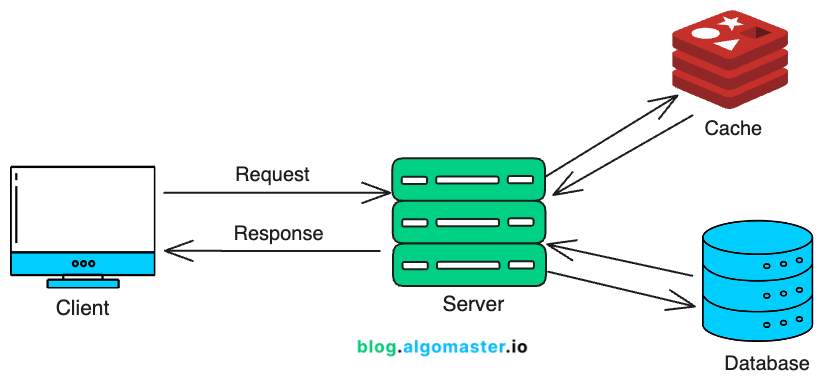
Server-side Caching
Server-side caching stores frequently requested data on the server, reducing the load on your database and speeding up responses.
-
In-memory Caches: In-memory caches (e.g., Redis) keep data in a server’s main memory (RAM) for extremely fast access. An application server can check the cache first before hitting the database.
-
Application-level Caches: Application level caches (e.g., caffeine in java) run directly in your application’s memory, storing frequently used data like computed values, or common database query results right where requests are processed.
2. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
Every millisecond counts when a user loads your website or app. If your server is located in India but your user is in New York, every request travels halfway across the world.
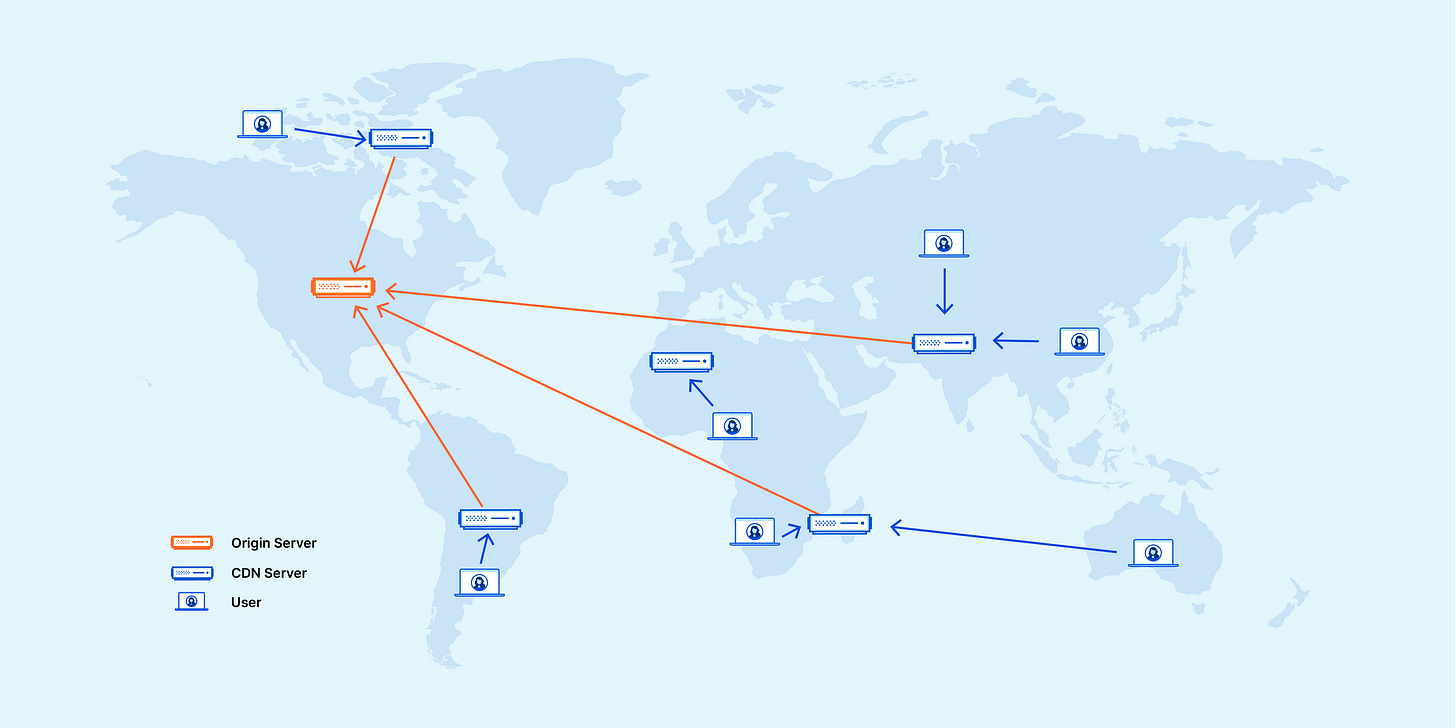
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) solve this by caching your static assets (and sometimes dynamic content) in data centers around the world, so users can access them from a location geographically close to them.
A CDN is a globally distributed network of edge servers that cache and deliver content like images, JavaScript, CSS, videos, and even full page to users based on their location.
When a user requests content, the nearest CDN server delivers it instead of reaching all the way to the origin server.
This significantly reduces latency, bandwidth usage, and server load.
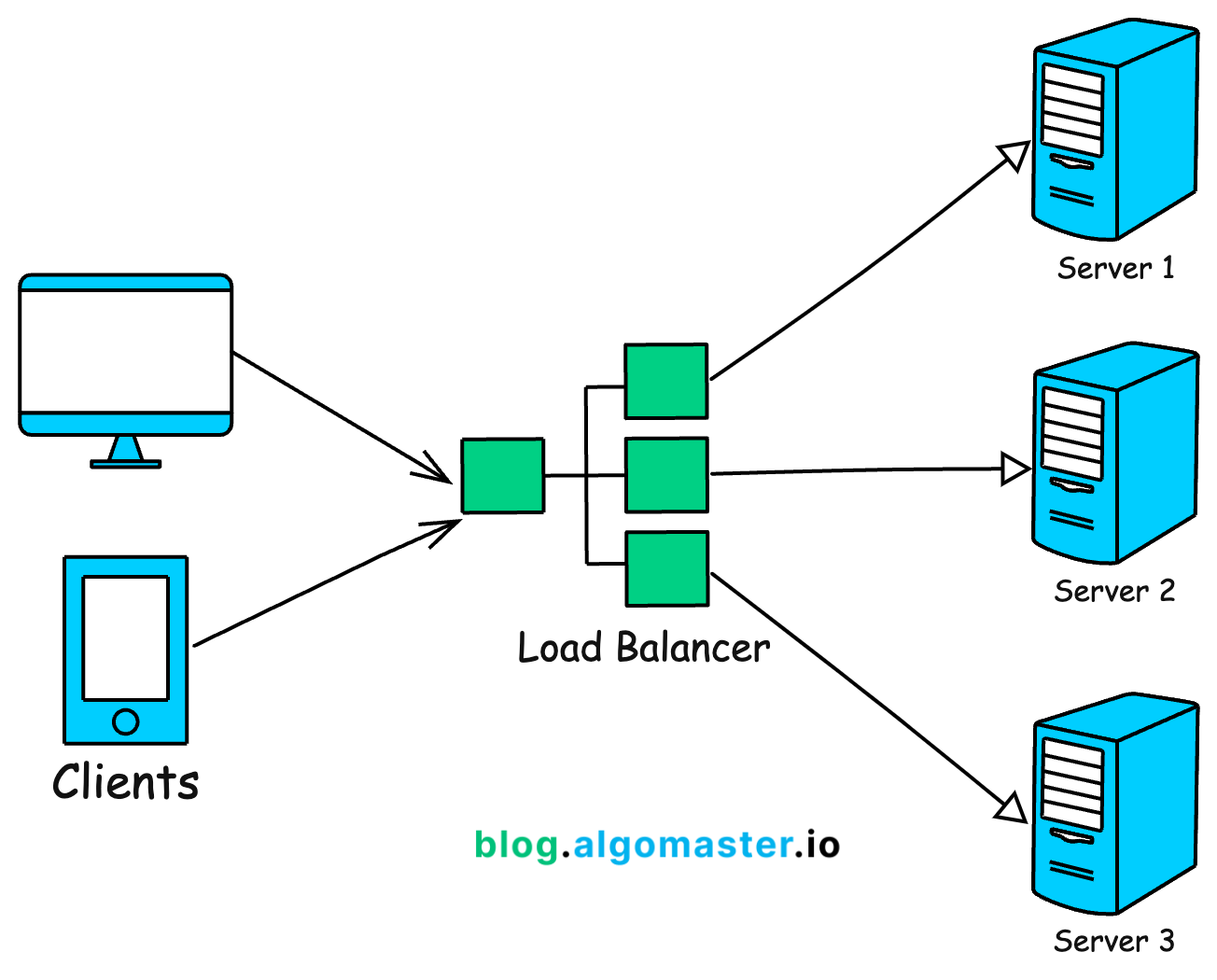
3. Load Balancing
When your application starts receiving thousands (or millions) of concurrent requests, a single server might struggle to handle the load. To scale horizontally, you add more servers. But to ensure those requests are distributed efficiently, you need a load balancer.
A load balancer acts like an intelligent traffic cop. It distributes incoming requests across multiple backend servers to ensure no single server is overwhelmed. This ensures high availability and keeps response times low, even during traffic spikes.
Load Balancing Algorithms
-
Round Robin: Sends each request to the next server in a loop. Good for evenly sized tasks.
-
Least Connections: Chooses the server with the fewest active connections. Ideal when some requests are long-lived (e.g., WebSockets).
-
IP Hash / Consistent Hashing: Routes requests based on client IP or hashed key. Useful for session persistence or cache affinity.
-
Weighted Load Balancing: Assigns more traffic to powerful servers. Great for heterogeneous infrastructure.
-
Latency-based Routing: Routes traffic based on server response time. Perfect for multi-region setups.