Top 15 Database Scaling Techniques
When your application is small, with just a few hundred users, a single database server is usually enough to handle all the reads, writes, and transactions.
But as your user base grows, so does the volume of data and database operations. More users mean more queries per second, more concurrent connections, and larger datasets.
If you don’t scale your database to handle the increased load, it can slow down your app and cause problems.
In this article we will explore the Top 15 Database Scaling Techniques to ensure your application keeps operating at optimal performance without the database becoming a bottleneck.
1. Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling, also known as scaling up, is the process of increasing the capacity of a single database server by adding more resources—CPU, RAM, disk storage, or network bandwidth.
How is it Implemented?
-
Upgrading Hardware – You replace the existing machine with a higher-capacity one. This might involve switching to a server with more CPU cores, higher memory, or better disk performance (e.g., moving from HDDs to NVMe SSDs).
-
Increasing Resource Allocations – If you’re using a cloud provider (AWS, GCP, Azure), you can resize instances dynamically. For example, upgrading from an AWS RDS
db.t3.mediuminstance to adb.m6g.4xlargeinstance. -
Database Engine Optimizations – Tuning configurations such as increasing buffer pool size in MySQL (
innodb_buffer_pool_size) or allocating more shared memory in PostgreSQL (shared_buffers). -
Using Faster Storage – Moving from traditional HDDs to SSDs or leveraging NVMe storage to reduce disk I/O bottlenecks.
When Should You Consider Using Vertical Scaling?
-
When your workload fits within the limits of a single machine and you want simpler maintenance without introducing the complexity of distributed databases.
-
When latency is critical, and distributing queries across multiple nodes introduces unwanted overhead.
-
When your application is still growing, and horizontal scaling (sharding or replication) is unnecessary.
-
When you need a quick and cost-effective solution in the short term without redesigning the system architecture.
Limitations of Vertical Scaling
-
Hardware Limits – There’s a ceiling to how much you can scale a single machine. Even the largest cloud instance has limits.
-
Single Point of Failure – A vertically scaled database is a single machine. If it crashes, everything goes down unless there’s a failover mechanism.
-
Expensive Beyond a Certain Point – The cost of high-end machines grows exponentially. A top-tier AWS RDS instance can cost thousands of dollars per month.
-
Downtime During Upgrades – Increasing CPU, memory, or disk space often requires downtime, especially in on-premise setups.
Vertical scaling is simple, effective, and easy to implement, making it a great first step for scaling a database. However, as traffic grows, a single machine will eventually hit a hard limit, forcing a move toward horizontal scaling techniques like sharding or replication.
2. Indexing
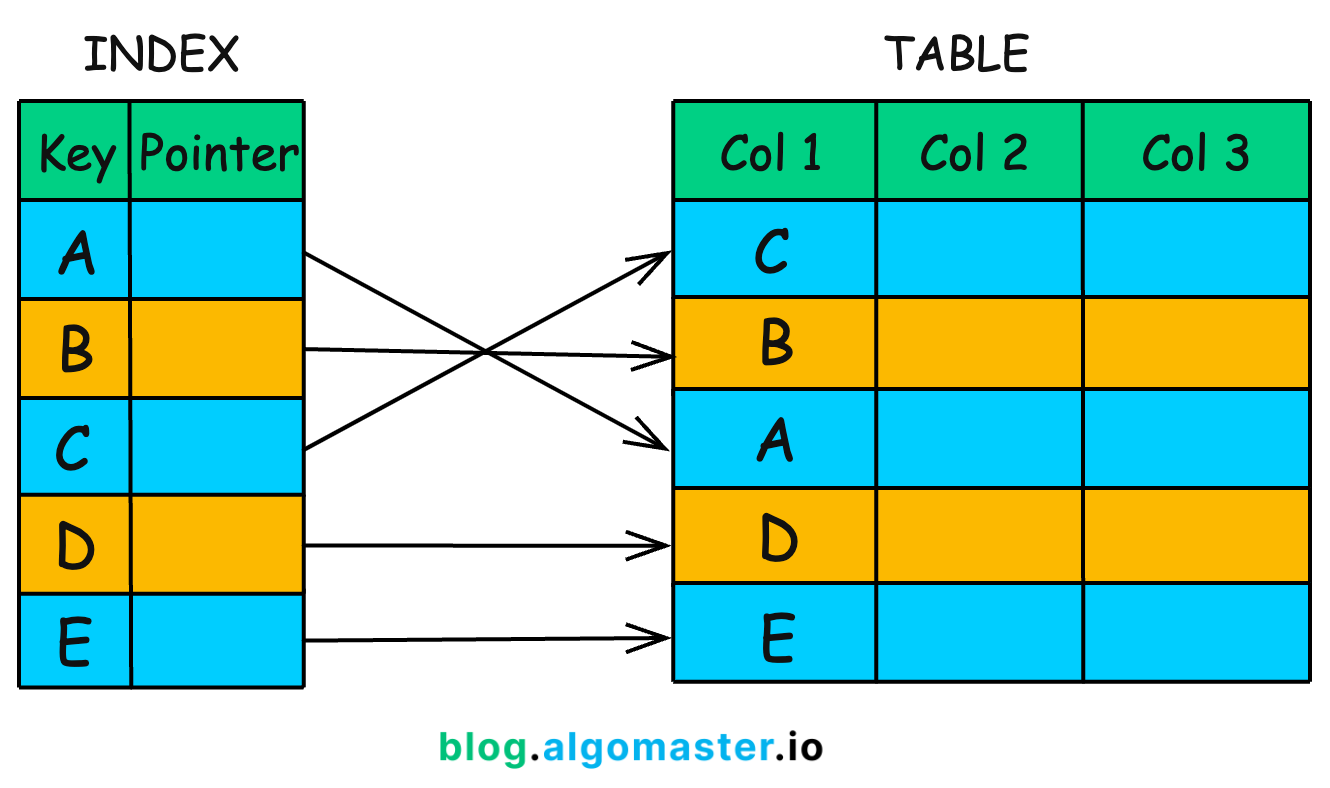
Indexing is a technique used to speed up database queries by creating a data structure that allows for faster lookups. Instead of scanning the entire table to find relevant rows, an index acts like a table of contents in a book—helping the database locate data quickly.
Imagine searching for a word in a dictionary. Without an index, you’d have to read every page. But with an alphabetically sorted index, you can jump directly to the correct section. That’s exactly how a database index works.
How is it Implemented?
1. Single-Column Index
Creating an index on a single column that is frequently used in WHERE clauses. Example:
CREATE INDEX idx_users_email ON users(email);2. Composite Index
An index on multiple columns, useful when queries filter by multiple conditions. Example:
CREATE INDEX idx_orders_customer_date ON orders(customer_id, order_date);When Should You Consider Using Indexing?
-
When queries frequently filter or sort by a specific column (
WHERE,ORDER BY,GROUP BY). -
When performing JOIN operations on large tables.
-
When optimizing read-heavy applications, where fast lookups are more critical than fast writes.
Limitations of Indexing
-
Slower Write Operations – Every
INSERT,UPDATE, orDELETEoperation must also update the index, increasing overhead. -
Increased Storage Usage – Indexes consume additional disk space, sometimes larger than the actual table.
-
Not Useful for Every Query – If a query retrieves a large portion of the table, an index may not help and could even slow it down.
-
Risk of Over-Indexing – Too many indexes can slow down performance instead of improving it. Choosing the right indexes is key.
Indexing is one of the most powerful ways to scale a database without adding more hardware. However, it requires careful planning. The right indexes can improve query performance by orders of magnitude, while unnecessary indexes can slow down writes and waste storage.
3. Caching
Caching is the process of storing frequently accessed data in a fast, in-memory store to reduce database load and improve response times. Instead of repeatedly querying the database for the same data, applications can retrieve it from a cache, which is significantly faster.
There are multiple caching strategies (read through, cache aside, write back etc.,) each suited for different use cases.
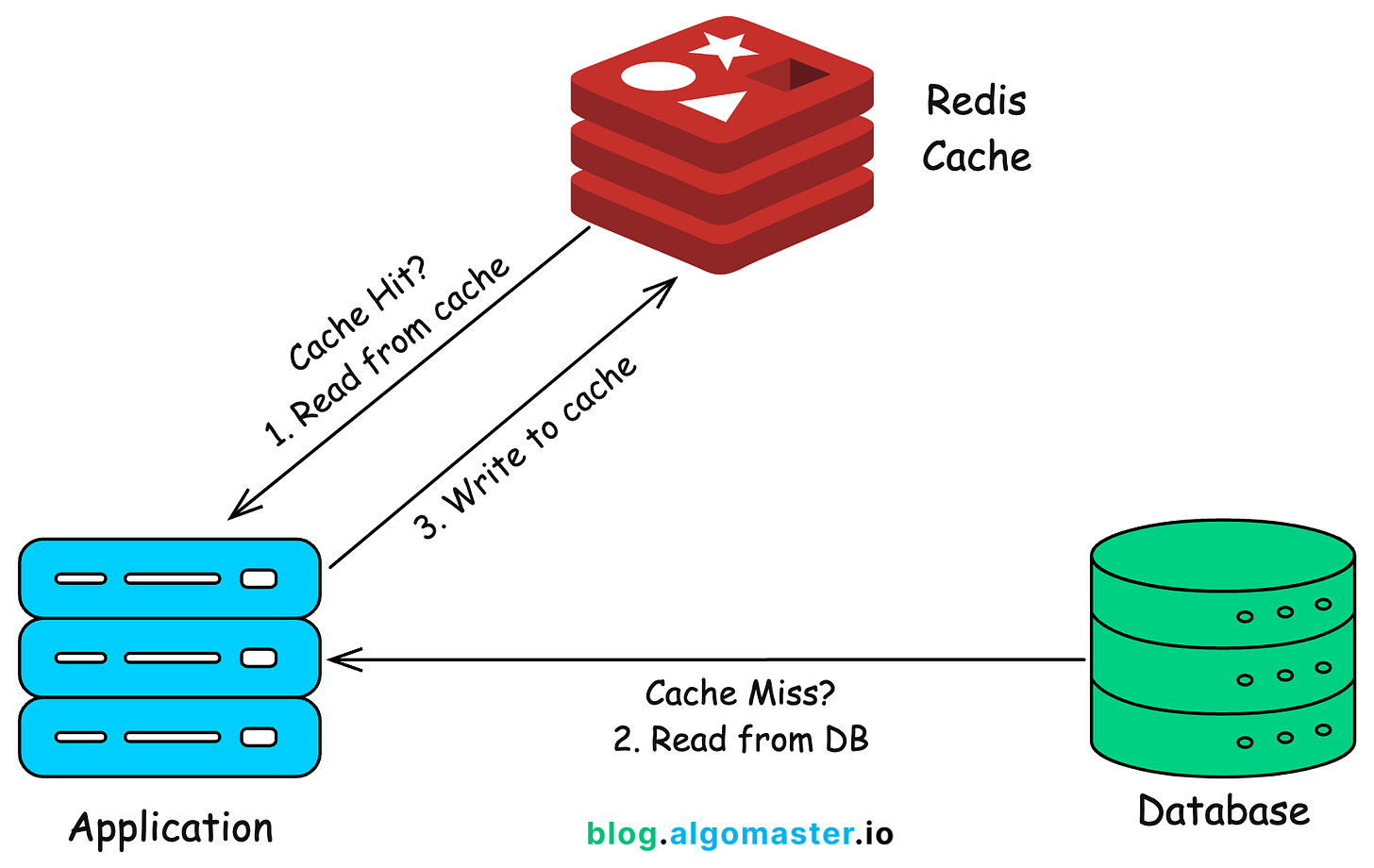
The cache-aside pattern is widely used because it gives the application full control over caching logic.
-
When a client requests data, the application first checks the cache.
-
If the data exists in cache (cache hit), it is returned instantly.
-
If data is not found (cache miss), it is fetched from the database, stored in the cache for future requests, and returned to the client.
Content Delivery Network (CDN) Caching
For web applications, static content (images, videos, scripts) is cached at CDN edge servers, reducing database and server load.
When Should You Consider Using Caching?
-
When the same data is frequently accessed, such as user profiles, product catalogs, or search results.
-
When you need low-latency responses, especially for real-time applications.
-
When your database is experiencing high read traffic and you want to reduce direct database queries.
-
When serving static content like images, CSS, and JavaScript in web applications.
Limitations of Caching
-
Stale Data – If the cache is not updated when the database changes, users might see outdated information.
-
Cache Invalidation Complexity – Deciding when to refresh or expire cached data is challenging.
-
Memory Consumption – Caching requires additional memory (RAM), which can be expensive at scale.
-
Not Ideal for Write-Heavy Applications – Since caches mainly optimize read performance, write-heavy applications don’t benefit as much.
Caching is one of the most effective database scaling techniques because it reduces query load and improves response times. However, it requires careful cache invalidation strategies to ensure data consistency.