System Design: How to Scale a Database
#18 Scaling a Database
Let’s say you are building an application that needs to store user information.
When your app has a few hundred users, you can keep all the data on one database server.
But as your app grows and you get more users, you need to store more data.
If you don’t scale your database to handle the increased load, it can slow down your app and cause problems.
In this article we will explore 8 strategies to scale databases to ensure your application keeps operating at optimal performance without the database becoming a bottleneck.
If you’re finding this newsletter valuable and want to deepen your learning, consider becoming a paid subscriber.
As a paid subscriber, you’ll receive an exclusive deep-dive article every week, access to a structured System Design Resource (100+ topics and interview questions), and other premium perks.
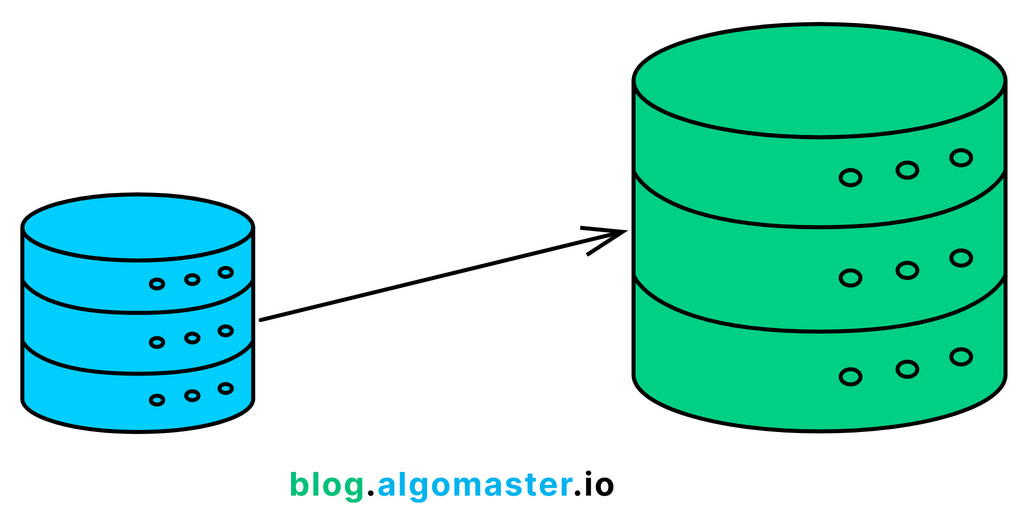
1. Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling involves adding more resources (CPU, RAM, storage) to a single database server.
It’s a quick and easy solution when you have a smaller database, but it has limitations.
It can become expensive, and there’s a limit on how much you can scale up.
Additionally, vertical scaling introduces a single point of failure, as all your eggs are in one basket.
Example: A small e-commerce website experiences increased traffic during a holiday sale. They vertically scale their database server by adding more RAM to handle the extra load.
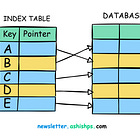
2. Indexing
Indexes at the back of a book help you quickly find specific information without having to go through every page.
In the same way, database indexes help find data much faster without scanning every single row in a table.
Indexes are usually created on most frequently queried columns to make read requests faster, but over-indexing can slow down the write performance due to overhead.
To learn database indexes in detail, check out my previous article:
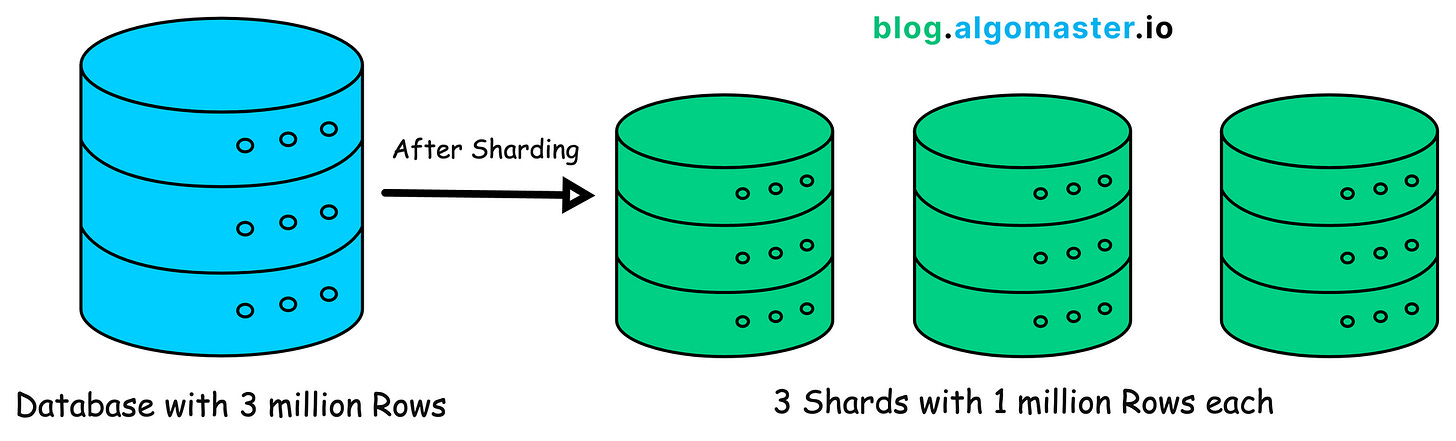
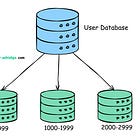
3. Sharding
A single machine can only hold so much data.
It will run out of space and slow down as more people start using your application.
To avoid this, you can split the data into smaller pieces (shards) and store them on different servers.
This process is called Database Sharding.
Distributing data in this way makes it easier to scale and handle more users.
To learn more about Database Sharding, you can read my previous article:
4. Vertical Partitioning
In situations where some columns are accessed more often than others, it’s a good idea to split the database table into smaller tables, each containing a subset of the columns from the original table.
This helps reduce the amount of data read during queries and can improve performance for specific access patterns.
Example: An e-commerce application might split their
producttable into:
A
"core_product"table with frequently accessed data (ID, name, price, category)A
"product_details"table with less frequently accessed data (description, specifications)A
"product_media"table with large binary data (images, videos)
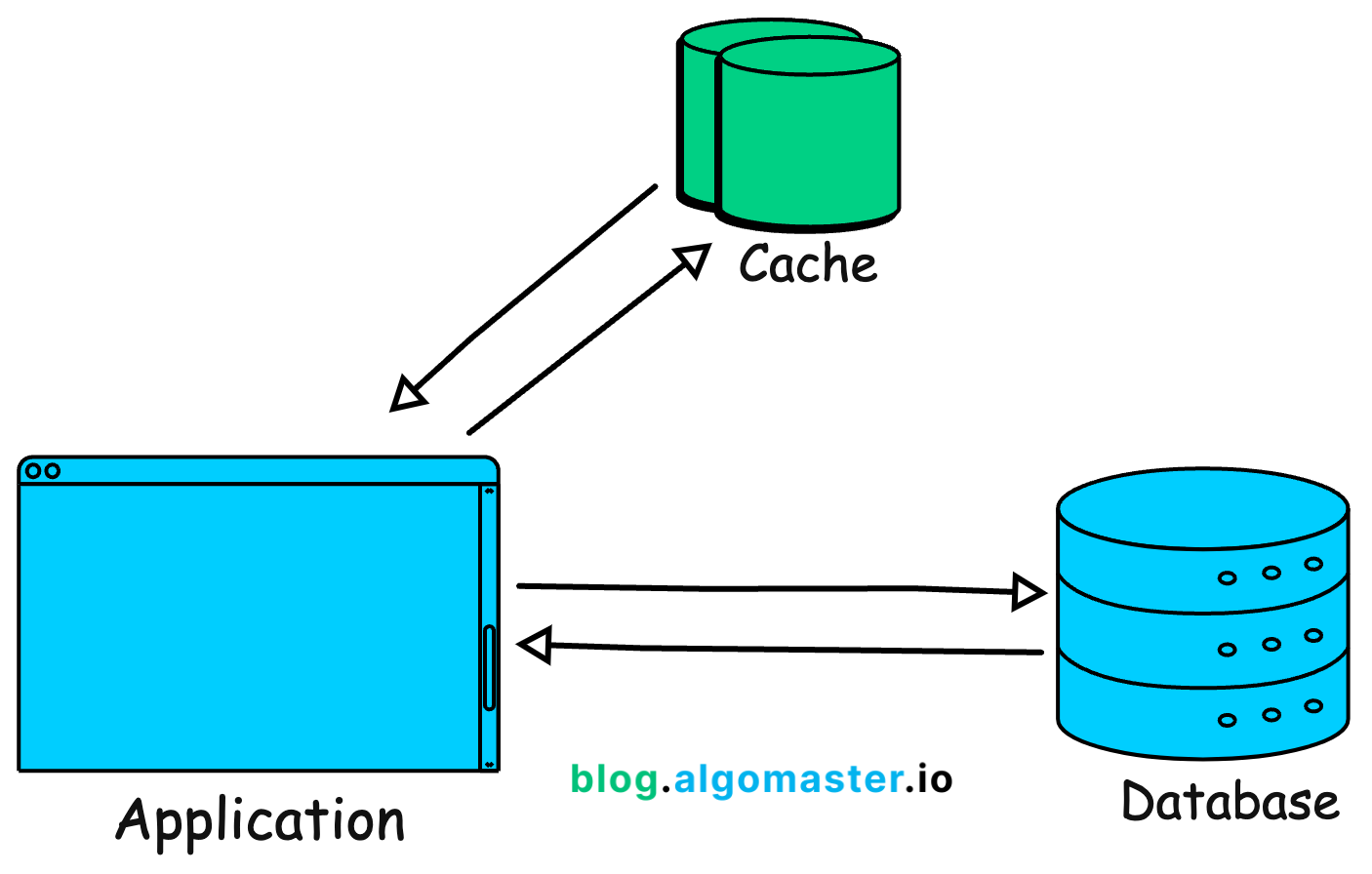
5. Caching
In almost every major application, some data is accessed more often than others.
For example:
-
In a blogging app, some articles are read more often than others.
-
In a social media app, some users use the platform more often than others.
-
In a streaming platform, some movies are watched more often than others.
It’s smart to store this frequently accessed data in a faster storage layer to speed up access and reduce the load on the database.
This is referred to as caching and it’s a popular choice to speed up queries for frequently accessed data.
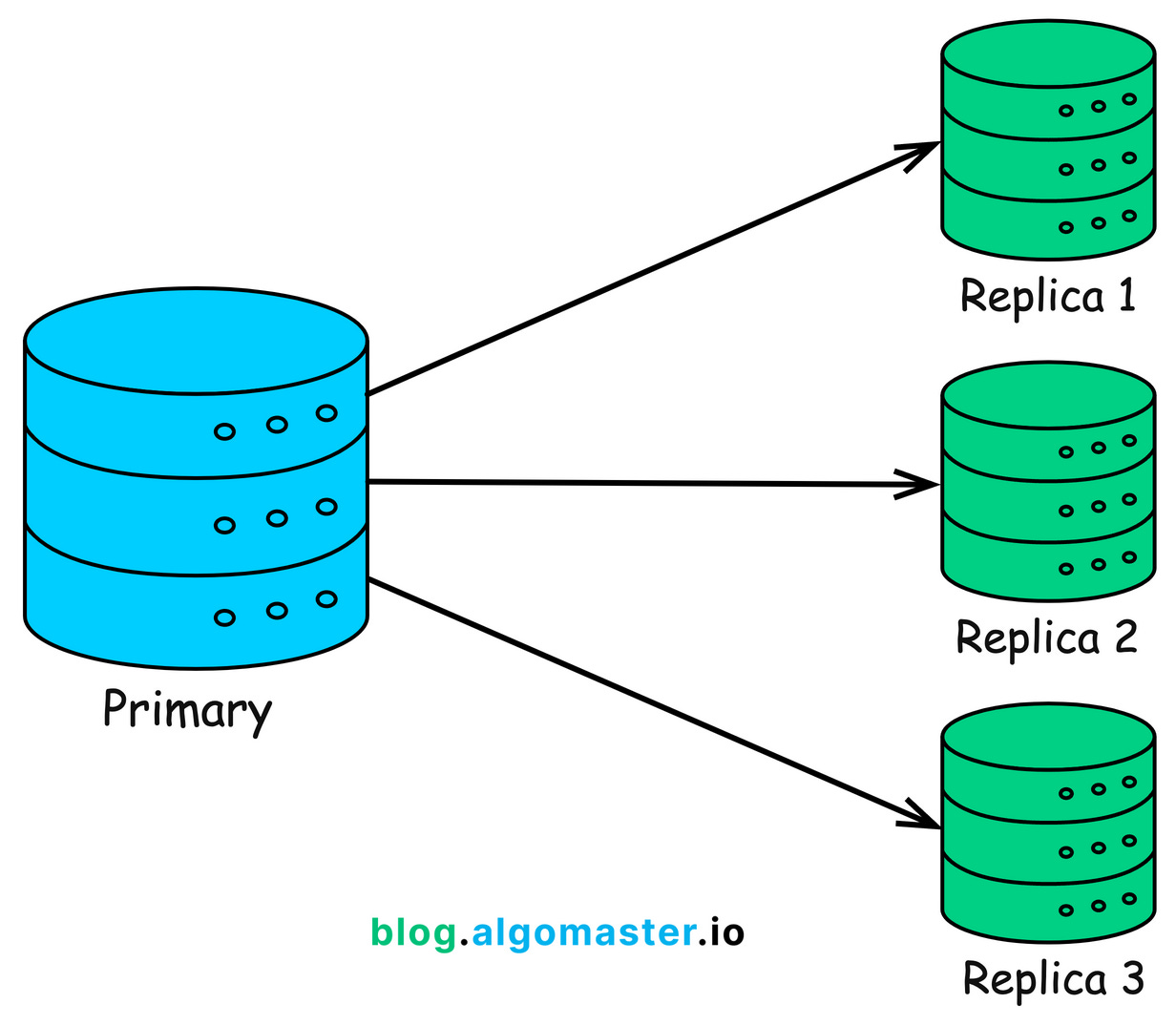
6. Replication
If your database servers are only located in one region, users from other regions may experience a higher latency.
To fix this, we can replicate the primary database to other regions and handle read requests locally.
This process is called Database Replication.
Simply put, database replication involves creating and maintaining multiple copies (replicas) of a database across different servers or locations to improve read performance, ensure high availability, and disaster recovery.
These replicas are synchronized with the original database (the primary), ensuring data consistency.
Types of Replication:
-
Synchronous Replication: Changes made to the primary database are immediately replicated to all replicas before the transaction is considered complete. This ensures strong data consistency but can impact performance due to the additional overhead.
-
Asynchronous Replication: Changes to the primary database are replicated to replicas with a slight delay. This offers better performance but with the trade-off of potential data inconsistency between the primary and replicas (known as replication lag).
7. Materialized Views
Some database queries are complex and can take a long time to run.
This can slow down the performance of the application if these queries are run often.
But, what if we pre-compute and store the results of these complex and frequent queries?
This is the idea behind Materialized Views.
Materialized views are pre-computed, disk-stored result sets of complex queries.
Unlike regular views, which are virtual and computed on-the-fly, materialized views physically store the results, making them readily available for fast retrieval.
It significantly improves the query performance for complex and resource-intensive operations.
Example:
An e-commerce platform needs to generate daily sales reports that aggregate sales data by date and product. These reports are accessed frequently by the management team to make business decisions.
Create Materialized View:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW daily_sales_summary
AS
SELECT date, product_id, SUM(quantity) AS total_quantity, SUM(amount) AS total_amount
FROM sales
GROUP BY date, product_id;Schedule Refresh:
CREATE OR REPLACE SCHEDULE job_refresh_sales_summary
ON SCHEDULE EVERY 1 DAY STARTS '2024-07-03 00:00:00'
DO
REFRESH MATERIALIZED VIEW daily_sales_summary;8. Data Denormalization
Some database queries may involve multiple tables and complex joins.
These queries are often slow and can make the application slower for large tables.
To avoid this, we can add redundancy by combining multiple tables into one to reduce the need for complex joins.
This is called Data denormalization.
It is the process of intentionally introducing redundancy into a database to optimize read performance by combining tables or adding redundant data.
Example:
A social media platform has a normalized database schema with separate tables for users, posts, comments, and likes.
Normalized Schema:
CREATE TABLE users (
user_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
username VARCHAR(100),
email VARCHAR(100)
);
CREATE TABLE posts (
post_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
user_id INT,
content TEXT,
created_at TIMESTAMP,
FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users(user_id)
);
CREATE TABLE comments (
comment_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
post_id INT,
user_id INT,
comment TEXT,
created_at TIMESTAMP,
FOREIGN KEY (post_id) REFERENCES posts(post_id),
FOREIGN KEY (user_id) REFERENCES users(user_id)
);The platform experiences high read traffic for user profiles and their associated posts and comments so it store posts and comments as JSON arrays within the user_profiles table.
Denormalized Schema:
CREATE TABLE user_profiles (
user_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
username VARCHAR(100),
email VARCHAR(100),
posts JSON,
comments JSON
);Each of these strategies has its own trade-offs in terms of complexity, consistency, and performance.
The best approach often involves a combination of these techniques, tailored to the specific needs and constraints of your application.
Thank you for reading!
If you found it valuable, hit a like ❤️ and consider subscribing for more such content every week.
If you have any questions or suggestions, leave a comment.
P.S. If you’re finding this newsletter helpful and want to get even more value, consider becoming a paid subscriber.
As a paid subscriber, you’ll receive an exclusive deep dive every week, access to a comprehensive system design learning resource , and other premium perks.
There are group discounts, gift options, and referral bonuses available.
Checkout my Youtube channel for more in-depth content.
Follow me on LinkedIn, X and Medium to stay updated.
Checkout my GitHub repositories for free interview preparation resources.
I hope you have a lovely day!
See you soon,
Ashish