An Internet Standard protocol called Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is used to gather and organize information about managed devices, and monitor, and manage the exchange of information between managed devices on IP networks.
SNMP User Table in Wireshark:
The SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) user table is used by Wireshark to decrypt and authenticate SNMPv3 packets.
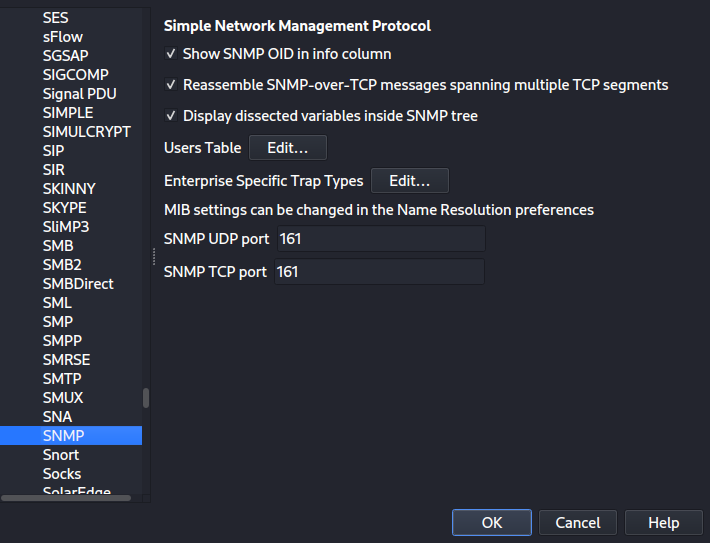
This table is a user table that consists of the following fields:
- Engine ID: Only packets whose engine ID is this will be used if this entry is provided. A hexadecimal string in the format 0102030405 is accepted in this field.
- Username: This is the username. If a user possesses multiple passwords for different SNMP engines then the first entry that matches both are taken, if a catch-all engine-id (empty) is required, the last entry should be used.
- Authentication Model: Define auth model that should be used.
- Privacy protocol: It defines the protocol in use.
- Privacy Password: A privacy password is like a security code. If a character is not printable, use /xDD. A string of characters beginning with “xDD” must be used to enter a hexadecimal password. To enter the hex password 010203040506 for instance, enter x01×02×03×04×05×06. The” character must be entered as “x5C” or “x5c” to indicate that it is not a printable character.
Decryption of SNMPv3 Packets Using Wireshark:
Following are the steps for Decrypting SNMPv3 packets while using Wireshark:
- Use the Wireshark program to view the collected packets.
- Secondly, select Edit → Preferences → Protocols.
- From the list of protocols, choose SNMP.
- Modify the user table’s configurations:
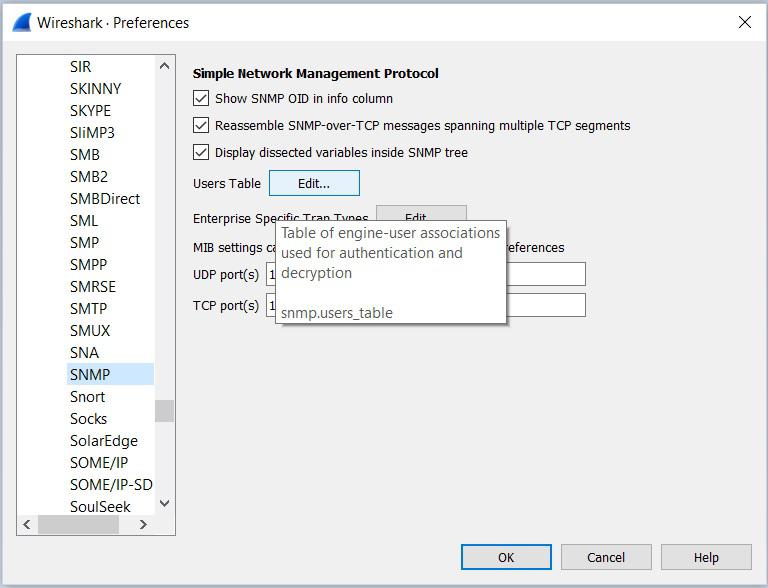
5. Click the Add button and enter the following information:
- SNMPv3 username for the engine ID
- Select an authentication method (MD5 or SHA1).
- Authentication Model Password
- DES, AES, AES192, or AES256 are the available privacy protocols.
- Specify your private password.
Engine ID can be found in the device support file or by using the CLI command to manage SNMP global engine-id to get the Wireshark recordings. To do so, examine the SNMP header and look for the Engine ID string.
Conclusion:
If you are using SNMPv3 credentials, the information in each captured packet’s “info” section may be encrypted, making it impossible for you to read while capturing SNMP packets in Wireshark. Instead, you will observe:
"encryptedPDU: privkey Unknown"
The packets can be decrypted and the information displayed in the info area by adding your SNMPv3 credentials to Wireshark’s Preferences.




