Introduction
Data is, somewhat, everything in the business world. To state the least, it is hard to imagine the world without data analysis, predictions, and well-tailored planning! 95% of C-level executives deem data integral to business strategies. After all, it takes knowledge below the surface, unleashing greater possibilities, which is imperative for any organization to know to improve decision-making. But to have it all, you must understand the unmissable role of data management in this. What is data management? What is database system? Keep reading to know all about it!
Table of contents
- What is Data Management?
- Types of Data Management
- Data Management Lifecycle
- Importance of Data Management
- Key Concepts
- Technologies and Tools for Data Management
- Benefits of Effective Data Management
- Challenges
- Why Do Organizations Need Data Management?
- Future Trends and Innovations
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Data Management?
Data management is collecting, organizing, transforming, and storing data for an organization’s data analysis operations. The process only ensures clean, well-managed data for various purposes, like gaining insights and planning marketing campaigns. When data is easy to find, visualize, and tweak, it helps organizations gain actionable insights and make informed decision-making.
Types of Data Management
Data is any information that you use for your work or business, such as numbers, words, pictures, or videos. You need to collect, store, organize, and analyze your data to make it useful and safe. There are different ways to manage your data, depending on what kind of data you have and what you want to do with it. Here are four common types of data management:
- Relational data management: This is when you store your data in tables that have rows and columns. Each row is a record of data, and each column is a type of data. For example, you can have a table of customers, where each row is a customer and each column is their name, email, phone number, etc. You can use a software called a relational database management system (RDBMS) to create and manage your tables.
- Object-oriented data management: This is when you store your data as objects that have properties and methods. Properties are the data that describe the object, and methods are the actions that the object can do. For example, you can have an object of a car, where the properties are the color, model, speed, etc., and the methods are start, stop, accelerate, etc. You can use a software called an object-oriented database management system (OODBMS) to create and manage your objects.
- In-memory data management: This is when you store your data in the memory of your computer or device, instead of on a disk or a cloud. Memory is faster than disk or cloud, so you can access and process your data more quickly. For example, you can use an in-memory database to store and analyze real-time data, such as stock prices, weather, or traffic. You can use a software called an in-memory database management system (IMDBMS) to create and manage your in-memory data.
- Columnar data management: This is when you store your data in columns, instead of rows. Each column is a type of data, and each row is a record of data. For example, you can have a column of customer names, a column of customer emails, a column of customer phone numbers, etc. You can use a software called a columnar database management system (CDBMS) to create and manage your columns.
Data Management Lifecycle
The data management life cycle is managing data at different stages. It covers various practices to unleash the maximum potential of data. Here is an overview of the life cycle:
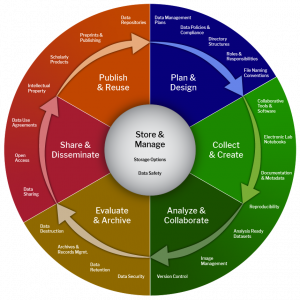
- Data Collection: At the foundational stage, data is collected from various sources, such as internal systems, external partners, or public repositories. Data quality checks and validation processes may be performed to ensure the accuracy and completeness of the data.
- Data Storage: Now that the data is collected, it is time to store and organize it. This stage involves determining the suitable data storage tools and technologies, database design, data modeling, and indexing strategies. Data security measures, such as access controls and encryption, are also implemented at this stage.
- Data Transformation: More often than not, data needs to be integrated and transformed into a comprehensive format for proper analysis. This stage of DMLC encompasses data cleansing, data integration, data transformation, and data enrichment processes.
- Data Archiving: After the data has served its primary purpose, it is best to archive or retain it for future usage or compliance requirements. This process entails establishing data retention policies, ensuring data security during storage, and implementing different strategies for long-term data preservation.
- Data Disposal: Is data no longer needed? Has it touched the end of its purpose? If yes, then it must be time to discard it. At the last stage, organizations dispose of irrelevant data. It is majorly intended to protect privacy and compliance with data protection regulations.
Importance of Data Management
Effective data handling and control is the product of several components and objectives of data management wherein each factor encourages a specific plan or next course of action. So, now that you know what it is, here are the different aspects and goals that bring its practices to action:
Data Quality
Ensuring the quality and accuracy of data is one of the primary objectives. This encompasses implementing processes and controls to validate and cleanse data, identify and rectify errors, and eliminate inconsistent records. High data quality standards strengthen the reliability of accurate information, which aids decision-making, reporting, and analysis.
Data Security
The question of what data management is cannot be answered without mentioning security. Data from unauthorized access, breaches, and loss is a significant objective of data management. This involves implementing security measures such as encryption, user authentication, access controls, and data backup strategies. Safeguarding data allows organizations to maintain the trust of their customers, comply with data protection regulations, and address potential risks.
Data Governance
Data governance implies the overall management and control of data assets within an organization. It is intended for establishing policies, procedures, and frameworks that define the roles, responsibilities, and processes for managing data. Organizations practicing data governance are 42% more confident than the ones that don’t. It involves defining data ownership, establishing data standards, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Data Accessibility
It focuses on ensuring that data is easily accessible and available to authorized users. Organizations establish efficient data storage and retrieval mechanisms, implement data archiving and backup strategies, and optimize data infrastructure and systems to make availability and accessibility easy. This leads to increased operational efficiency and improved decision-making.
Key Concepts
In data management, you will find various vital concepts coming together to ensure the effectiveness of tasks, such as organizing, processing, and utilizing data. Here are the four fundamental concepts:
1. Governance
Data governance entails the entire management of data resources within an organization. It encompasses defining data policies, setting data standards, maintaining data quality and integrity, and assigning responsibilities.
2. Security and Privacy
Privacy concerns make a popular topic in the data world! Data needs eagle-eye handling and security. Thus, it becomes critical to employ compliance with privacy regulations, obtain consent for data collection, and make sure that individuals have the right to control their data.
3. Quality Management
Data Quality management is one of the core concepts as it implies the accuracy, completeness, consistency, and, not to forget, relevance of data. It is crucial to keep up with data quality to make the most of it on various occasions, whether making decisions or conducting analysis.
4. Integration and Interoperability
Data integration emphasizes combining data from multiple sources into a unified view. This concept aims to produce a comprehensive representation of data that fulfills analysis, reporting, and other purposes.
Technologies and Tools for Data Management
These tools and technologies fuel the process of data lifecycle:
Relational Databases and Data Warehouses
To work in the data arena, you must understand relational database management systems. This software system manages relational databases, encompassing everything from organizing data with rows and columns to supporting structured query language (SQL) for data manipulation and retrieval. It is intended for maintaining data standards to the ideal extent.
Data Management Platforms and Software
Data management tools help professionals create and maintain accurate and consistent data within the organization. These tools are designed to facilitate data profiling, matching, quality management, merging, and governance capabilities.
Data Integration and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools

Data integration tools allow organizations to combine data from multiple sources, making management more effective. These tools come with capabilities for data mapping, cleansing, and transformation. Moreover, ETL tools streamline extracting and changing data from various sources into a consistent format.
Data Governance and Metadata Management Solutions
Organizations employ data governance tools to enhance data governance processes, policies, and standards. These tools strengthen the management by assisting in metadata management, classification, data lineage, and compliance with data regulations.
Benefits of Effective Data Management
Here are the top benefits of data management:
Improved Decision-making and Business Intelligence
Data management boosts data’s accuracy and reliability, making it ever-ready for informed decision-making. According to a study, companies implementing data-driven decisions witness a 5 to 6 percent boost in overall output. Since it provides a complete view of the operations, data management clarifies decision-making processes, making them better and faster by quickly analyzing trends and deriving actionable insights from data.
Enhanced Data Accuracy and Reliability
One of the primary benefits of data management practices is that they improve the quality and consistency of data. It allows organizations to define data standards, incorporates validation rules, and perform effective data cleansing, ultimately reducing inaccuracies, duplications, and other potential errors.
Increased Operational Efficiency and Productivity

Furthermore, data management is often equivalent to streamlined business operations, provided it seamlessly optimizes data flow. Proper management unlocks efficiency in data integration, removing obstructions like redundancies and inconsistencies. Ultimately, it helps organizations automate processes and minimize manual efforts and errors.
Mitigation of Risks and Compliance with Regulations
The regulations for data privacy, security, and governance have become an essential part of data management processes globally. Effective data management enables organizations to comply with regulatory requirements. Moreover, implementing the proper data protection measures and keeping up with appropriate data access controls helps organizations adhere to legal and compliance standards and avoid penalties or damage.
Enablement of Data-driven Strategies and Innovation
The benefits mentioned above of data management boil down to this one: innovation. When organizations gain insights about their customers and business performance, it becomes a lot easier for them to develop strategies, or, let’s say, data-driven strategies. It fuels creativity and paves the way for targeted marketing campaigns, allowing businesses to garner customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Challenges
| Focus Area | Challenges |
|---|---|
| Data Volume and Complexity | The exponential growth of data is already making it an uphill job for organizations to manage large volumes efficiently. While scalability is crucial to handle increasing data volumes, there is also a demand to keep the performance at its best. This makes it essential for organizations to develop the proper storage solutions. |
| Data Security and Privacy | As the volume and complexity of data skyrockets, the eyes shift to data security and privacy concerns. Protecting sensitive and confidential data from breaches is the need of the hour and, thus, requires implementing power-packed security measures and encryption techniques along with regular security audits. |
| Data Silos and Integration Issues | Many organizations face data storage issues, namely disparate systems, and formats. Integrating data from multiple sources to create a unified view may sound easy, but it can still be haywire and time-consuming. Monitoring interoperability between different systems and applications is challenging for many businesses as it requires data mapping, transformation, consolidation, and implementing tools and technologies. |
| Data Governance and Compliance Challenges | Organizations must establish and exercise effective data governance practices to ensure compliance with regulatory standards. Data governance also involves establishing data management roles and responsibilities and enforcing data quality and security protocols. However, implementing robust data governance frameworks and maintaining compliance can be challenging for many. |
| Data Quality and Maintenance | Implementing effective data management practices comes with a need for consistency and maintenance. Now, this could be challenging for many reasons, including ever-changing trends. It makes it mandatory for employees to learn new facets of data management and evolving trends, be quick in data-driven decision-making, and require them to embrace new data management processes. Resistance to change, cultural factors, and insufficient training can come in the way of successfully implementing data management practices. |
Why Do Organizations Need Data Management?
Data management plays a pivotal role in how organizations approach their next move. In today’s competitive age, generating vast amounts of data from multiple sources and transforming them into a valuable addition to growth has become critical. Here are the eminent factors welcoming significant changes through effective data management:
Faster and Informed Decision-Making

Data management enables the availability of reliable and relevant data for decision-makers within the confines of an organization. Collecting, organizing, and analyzing data help organizations derive valuable insights and translate them into the most appropriate decisions. There’s no second-guessing the fact that data-driven decision-making assists in identifying market trends, understanding customer behavior, optimizing operations, and developing effective strategies. Thus, improving the efficiency and effectiveness of the organization, leading to tremendous success.
Fewer Errors, Improved Efficiency
Efficient data management practices result in plain-sailing business processes and workflows. By eliminating manual and redundant tasks from the equation, it gets easier for organizations to save time, reduce costs, and improve productivity. For example, automated data integration and reporting can significantly reduce the time spent on data processing and analysis. This allows employees to focus on more strategic tasks, driving innovation and growth within the organization.
Minimum to No Risk

The right way to data management crosses paths with data security, privacy, and compliance with regulatory requirements. When organizations maintain data protection and adhere to data governance frameworks, they experience no hassle mitigating risks associated with data breaches, cyber-attacks, and regulatory non-compliance. By safeguarding sensitive data, organizations build trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders, fostering long-term relationships and maintaining a positive reputation.
Competitive Advantage
In a study, 64% of marketing executives agreed that data-driven strategies were crucial to the economy. Data management opens the door for more innovation by facilitating the comfort of thorough research, analysis, and experimentation. The knowledge of data analytics and machine learning techniques is all an organization needs to get to the bottom of new insights, spot emerging trends, and brainstorm innovative products or services. Data-driven innovation helps organizations gain a competitive edge over other players, allowing them to stay ahead and attract higher investment returns.
Future Trends and Innovations
So, what is data management’s future? Looking at the current whereabouts of data practices and consumption —and how far it has come— it is inevitable that more and more tools and technologies will become a powerhouse of efficient, reliable, and seamless data management. Here are the hot trends that are getting the spotlight:
| Focus Area | Trends |
|---|---|
| Big Data and Analytics | With an unstoppable boom in data, businesses are investing in big data analytics solutions to extract valuable insights and make data-driven decisions. Advanced analytics techniques like machine learning, artificial intelligence, and predictive modeling will be crucial in extracting meaningful information from large datasets. |
| Cloud-based Data Management | Cloud computing has redefined the process of handling and storing data. That’s why it’s becoming a hot favorite among businesses. It adds value by providing scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. So, it makes sense why the future of data management will likely be dominated by cloud-based solutions, allowing easy access, data sharing, and collaboration across different platforms. |
| AI and ML in Data Management | Artificial intelligence/ machine learning is yet another trend in data management to look out for. With massive volumes of data available, refining the relevant from the useless is overwhelming. AI and ML capabilities combat this challenge by exploring and assessing databases faster without compromising accuracy and completeness. |
| Blockchain Technology | Blockchain facilitates secure, transparent, and decentralized data management prowess. These technologies offer immutable and auditable records, removing the demand for intermediaries, and that ultimately powers integrity and trust. Blockchain is increasingly implemented in supply chain management and financial transactions. |
Also Read: How is AI Improving the Data Management Systems?
Conclusion
In conclusion, data management is a vast topic, pacing toward years of dramatic growth, changes, and trends! It established a streamlined system for accumulating and transforming data for greater use. With time, organizations began introducing tools and technologies to minimize errors and breaches and promote efficiency.
We are in 2023, and the face of data management, again, looks different – thanks to the advent of revolutionary trends like AI, ML, and data analytics. Looking at this picture, it is a safe bet for you to sign up for an all-encompassing AI & ML BlackBelt Plus Program. Furthermore, as data science gains momentum, companies are already looking for data experts who have the skill to handle ever-changing trends and knowledge about the role of data in real-world scenarios. Thus, understanding the depths of the data world and the certification will add a noteworthy feature to your resume, helping you gain recognition over other candidates.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. Analytics tools, CRM, data warehouse systems, and marketing tools are the most common types of DMS.
A. Collecting data, processing, transforming, and retaining it are the core methods in data management.
A. Organizations must develop robust data storage and retention strategies, invest in good tools, adhere to data regulations, and establish a flexible data culture to make data management processes effective.
A. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems are a typical example of data management wherein you can collect customer data from various sources, store it, and analyze it to decide the following approach.




