Evan Porter
Updated on: December 20, 2023
We’re all familiar with how hackers are displayed in movies. Brooding criminals in hoodies, frantically hammering lines of code into a computer in order to break through complex security systems.
We know that, in real life, too, hackers are a major threat to our safety.
But what exactly is hacking?
Hacking is a broad term that refers to someone gaining access to digital files or systems without permission, usually with a nefarious intent in mind like stealing information or installing malware.
Here’s our guide to everything you need to know about hackers and how to keep yourself safe from potential attacks.
Examples of Different Types of Hacking
Hackers use brute force, security exploits, social engineering, and other means to gain access to systems without proper permission.
What they do with that access, however, can vary greatly depending on their motivations.
Here’s a look at some of the different kinds of hacks and hackers to be aware of.
Ethical Hacking
Did you know that not all hacking is illegal?
Ethical hackers are experts who work in agreement with organizations, companies, and brands in order to uncover security vulnerabilities.
Essentially, an ethical hacker will try to gain access to a network, computer, or system the same way a criminal hacker would — only if they’re able, they aren’t looking to cause any damage. Instead, they’ll report the vulnerabilities so they can be properly patched and fixed before a malicious hacker finds them.
Hacktivism
Hacktivism, a combination of the words “hacker” and “activism”, is a form of hacking that usually isn’t motivated by monetary gain.
In these cases, a religious, environmental, or other activist may gain access to a system in order to promote their own cause (or hinder the opposition).
For example, a hacktivist group might target an oppressive government regime with a DDoS attack to knock its systems offline, destroy a firewall that’s used to oppress the free speech of citizens, or seek to disrupt financial networks used by terrorists.
These activities are a form of cybercrime and are illegal, regardless of their motivations.
Identity Theft
A more common and classic motivation for hacking into a system would be to steal personal information for identity theft, including social security numbers, credit cards, bank accounts, and more.
This kind of sensitive data can be stolen in a number of different ways including:
- Phishing
- Social engineering
- Password cracking
- Keyloggers & other malware
Malware Hacking
Installing malware on a victim’s computer can be a key part of identity theft, but malware can have other nefarious consequences that have nothing to do with stealing your information.
For example, a hacker could recruit your computer to a botnet using zombieware. This would have minimal impact on you, personally, but it means they could use your computer as part of a larger-scale attack on a high-value target.
A hacker might also infect your computer with ransomware to extort money out of you in exchange for your own personal files.
International Espionage
It’s extremely common for governments to attempt to spy or gather intelligence on rival governments using hacking techniques.
Espionage to this degree could be conducted quietly in order to collect data, or it could be more malicious — for example, foreign hackers could leak internal government documents and communications to the public.
Corporate Espionage
Similarly, some companies and corporations will choose to conduct espionage against their business rivals.
Though highly illegal and far from an acceptable business practice, a company could try to break into a competitor’s network or database to steal confidential information, business plans, communications, financial data, and more.
It’s also not unheard of for companies to conduct more serious attacks to cripple their competitor’s websites or databases and cause financial or brand damage.
Ego Hacking
Finally, some hackers like to break into websites, computers, and systems simply to prove that they can.
In certain hacker communities, accomplishing difficult hacks and bypassing tight security is worn as a badge of honor.
There’s also a sizable contingent of “grey hat” hackers, who seek out exploits and vulnerabilities in order to bring them to the attention of the people in charge of fixing them. The difference between a grey hat hacker and an ethical hacker, however, is that grey hats don’t have permission to do this ahead of time.
How to Protect Yourself from Hackers
There are plenty of reasons hackers and cybercriminals target their victims, including monetary gain, identity theft, or simply the thrill of the chase.
So what can you do to protect yourself?
Here are our top tips for keeping your data, computer, and personal information safe.
Use a Feature-Rich Antivirus
A powerful antivirus on your computer and mobile devices should be your first line of defense against attacks.
There are plenty of good free options available, but the top of the line antiviruses will include critical extra features you don’t want to be caught without, like:
- Phishing protection
- Ransomware protection
- Proactive defense from zero-day attacks
- Secure online shopping
- Home firewalls
- Public WiFi safety tools
- And plenty more
If you do decide to use an antivirus, make sure to keep it up to date. New versions and updates will help protect you from the latest malware and hacking threats.
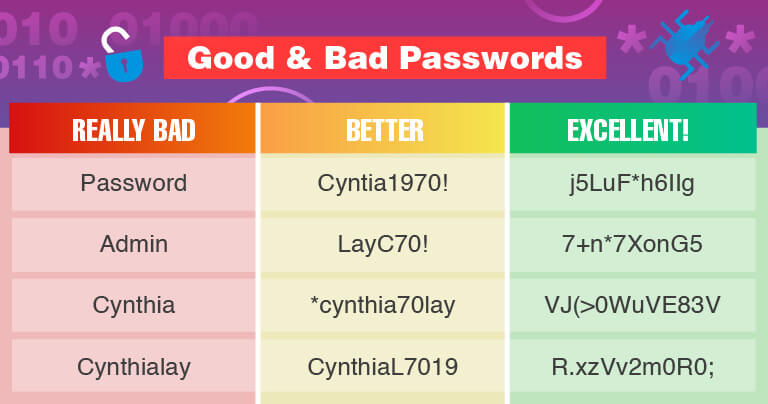
Create Strong, Complex Passwords
Most people create simple passwords that are easy to remember. To criminals, this is a dream come true.
Password cracking techniques have become extremely advanced, so passwords that are short, don’t include special characters, and made up of common dictionary words are serious security threats.
Consider installing a password manager to generate extremely complex passwords and store them securely for you.
Practice Safe Web Browsing
Did you know that certain kinds of websites or ads, sometimes called “malvertising”, can automatically trigger downloads onto your computer without you ever knowing?
These are called drive-by downloads, and they’re one of the most common ways victims end up with malware or spyware on their devices.
The best defense? Along with an antivirus, stay away from shady websites — especially in the adult, gambling, or piracy niches.
Always approach email attachments with caution. Even if they seem innocuous, such as text documents or spreadsheets, they can contain hidden viruses or other malicious software.
Stay Vigilant Against Phishing & Social Engineering
If someone claiming to be an authority figure asks you for your passwords, credit card number, or other secure information, your alarm bells should go off.
Be extremely careful handing over sensitive information, especially on an unsecured channel like email or a phone call.
Phishing and other social engineering attacks — where hackers trick or manipulate you into willingly giving them access or information — have been on the rise for years.
An antivirus can help recognize and block phishing messages, but you should always be 100% positive who you’re giving information to.
Stay Educated
Hacking and cybercrime is a rapidly evolving offense. New viruses, new techniques, and new exploits are discovered almost every single day.
Do your best to stay up to date on the latest scams and how to best protect yourself.