Kelvin Kiogora
Published on: July 22, 2025
Fact-checked by Sam Boyd
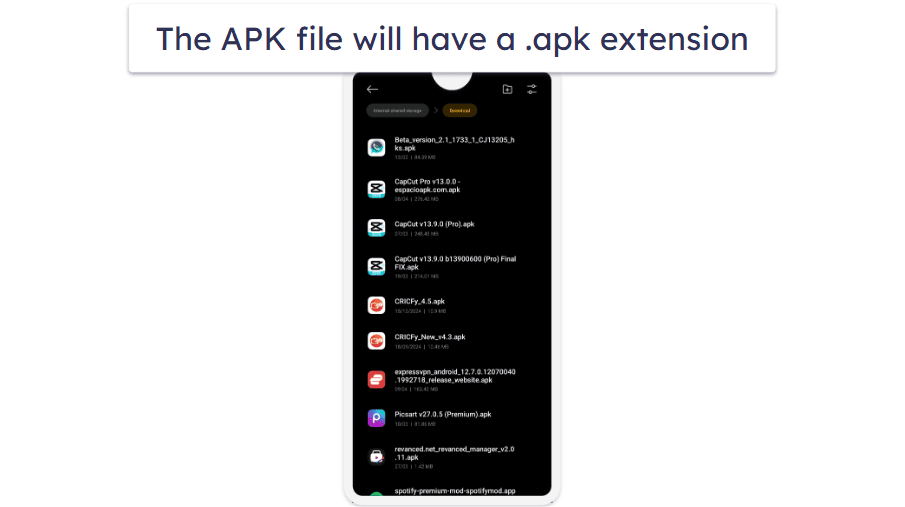
An APK file is the package that installs an app on your Android device. It’s how apps are delivered and installed, whether from the Google Play Store or somewhere else. You can think of it like a zip file that holds everything an app needs to run on your device.
Understanding APKs gives you more control over your Android device. It helps you access apps that aren’t available in your country, test unreleased features, or install apps on a rooted phone. It also helps you avoid risky downloads and protect your personal data.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know about APK files — what they are, how they work, and how to use them safely. To stay safe from shady or malicious APKs, consider using tools like TotalAV Mobile Security for Android, which can help protect your device in real time.

What Is an APK File and Why Does It Matter?
An APK file is short for Android Package Kit, and it is the format used to package and distribute applications for Android devices. It contains all the necessary files and code needed to install and run an app on your phone or tablet. Think of it as a ready-to-install app bundle, similar to how software on other platforms comes in specific installer formats.
For comparison, iOS apps use a different format called .ipa files, which serve a similar purpose but are designed exclusively for Apple devices. On desktop computers, Windows applications commonly come as .exe files, which are executable installers you run to set up software. APK files are Android’s equivalent of these, tailored to work within its operating system and ecosystem.
Why Android Uses APK Files
Android uses APK files for distributing and installing apps because they bundle all components of an app — code, resources, assets, and metadata — into a single, portable package. This makes it easy to share, install, and update apps across millions of devices running different versions of Android. APKs ensure apps install correctly and maintain compatibility across the Android ecosystem.
Additionally, APK files include digital signatures that Android uses to verify the app’s integrity and security before installation, ensuring you get a safe and reliable app experience.
Why Some Apps Are Only Available as APKs
Not all apps are on the Google Play Store, and some exist only as APK files outside it. Developers often release APKs to test new features, provide early access to beta versions, or distribute apps (for example, VPNs) in regions where the Play Store may restrict availability.
Additionally, alternative app stores like F-Droid or websites like APKMirror host APK files that offer open-source or older versions of apps. This flexibility allows you to install apps that aren’t officially published or updated through Google Play. However, caution is required to avoid unsafe app versions.
How Do APK Files Work on Android Devices?
APKs act as a bridge between the app’s code and your Android device’s operating system. This connection allows your device to understand exactly how to run the app, manage its resources, and control its permissions.
What’s Inside an APK File
An APK file is a compressed archive similar to a ZIP file, containing multiple components essential for the app’s functionality:
- Classes.dex. This contains the app’s executable code designed to run on Android’s runtime environment.
- AndroidManifest.xml. This file declares important information about the app, such as its name, version, permissions required (like access to camera or contacts), and components like activities and services.
- Resources.arsc. Contains precompiled resources such as strings, colors, and styles used by the app.
- Res/ folder. Holds uncompiled resources like images, layouts, and UI elements.
- Lib/ folder. Contains native libraries compiled for different processor architectures (ARM, x86, etc.).
- META-INF/ folder. This stores metadata, including the app’s digital signature and certificate, used to verify the app’s integrity and source.
All these parts are packaged together so that Android can properly install and run the app on various devices and Android versions.
What Happens When You Install an APK File?
Installing an APK file triggers a series of steps on your Android device:
- Verification. Android first checks the APK’s digital signature to confirm the app hasn’t been altered and is from a trusted source. If the signature doesn’t match a previously installed version or is missing, your Android will either issue a warning or the installation will be blocked.
- Parsing the manifest. The system reads the AndroidManifest.xml to understand what permissions the app requires and what components it contains. This step is important for security and managing app behavior.
- Unpacking files. The APK’s contents — code, resources, and libraries — are extracted and stored in appropriate locations on the device. For example, native libraries are placed where the system can access them based on the device’s CPU architecture.
- Setting up the environment. Android creates a private directory for the app’s data, including user preferences, databases, and files the app needs while running.
- Registering the app. The system adds the app to the installed apps list, making its icon available in your launcher and allowing it to run. It also registers any services, broadcast receivers, or background tasks defined by the app.
- Optimization. On some devices, Android performs an optimization step called Ahead-Of-Time (AOT) compilation, where parts of the app’s code are precompiled to improve performance.
After these steps, the app is fully installed and ready to use. This entire process happens quickly and seamlessly.
When Do You Need to Use an APK File?
There are several situations where using an APK file becomes necessary or beneficial. APKs give you the flexibility to install apps that might not be easily accessible otherwise. Here are a few such scenarios:
Installing Apps Not Available in Your Region
Some apps are restricted by geographic location and won’t appear in your Play Store. This is common for streaming services, banking apps, VPNs, or region-specific tools.
Using an APK file lets you bypass these restrictions by installing the app manually. This gives you access to apps that are otherwise locked to certain countries, regardless of where you live (though these apps might not always work outside their respective region when you try running them).
Installing Older or Discontinued App Versions
App updates can sometimes introduce bugs, remove features, or change interfaces you prefer. Some apps also get pulled from the Play Store entirely, making them unavailable for download. APK files allow you to install older versions that still work well for you or discontinued apps that you can no longer find officially. This is especially useful if you rely on a specific version for work, compatibility, or personal preference.
Accessing Beta or Pre-release Features
Developers often release beta or experimental versions of their apps as APK files before making them available on the Play Store. Installing these APKs gives you early access to new features, improvements, or fixes that haven’t been officially released yet. You can test upcoming functionality and even provide feedback to help improve the app before the full release.
Using Apps on Rooted/Customized Devices
Some apps detect if your Android device is rooted or heavily customized and may refuse to install from the Play Store due to security concerns. By manually installing APK files, you can bypass these restrictions and use apps on devices that don’t meet the Play Store’s official requirements. You’ll find this useful if you often customize your devices for extra control or performance.
Sharing Apps Offline
APKs provide a simple way to share apps with a friend or family member who has limited internet access. You can send APKs via Bluetooth, Wi-Fi Direct, USB transfer, or file-sharing apps without the need to download the app from the internet again. This is handy in places with poor connectivity or to avoid using mobile data for app downloads.
How to Open and Install an APK File on Android
Installing an APK file on your Android device is straightforward once you know the right steps. Since APK files come from outside the Google Play Store, your device requires permission to install apps from unknown sources. Follow this guide to safely open and install APK files on your Android phone or tablet.
Before you begin, ensure your device has enough storage space, as insufficient storage can trigger “app not installed” errors.
- Enable installation from unknown sources.
- Go to Settings on your device and navigate to Privacy Protection.
- Scroll to Special Permissions.
- Find Install Unknown Apps.
- Select the app you’ll use to open the APK (usually your browser or file manager).
- Toggle Allow from this source.
- Download the APK file. Use your browser or file-sharing app to download the APK file to your device. Make sure the file is from a trusted source to avoid malware. An antivirus with a bundled VPN, like TotalAV, can help protect your privacy and block malicious downloads.

- Locate the APK file. Open your device’s File Manager app and navigate to the Downloads folder or the location where the APK was saved.
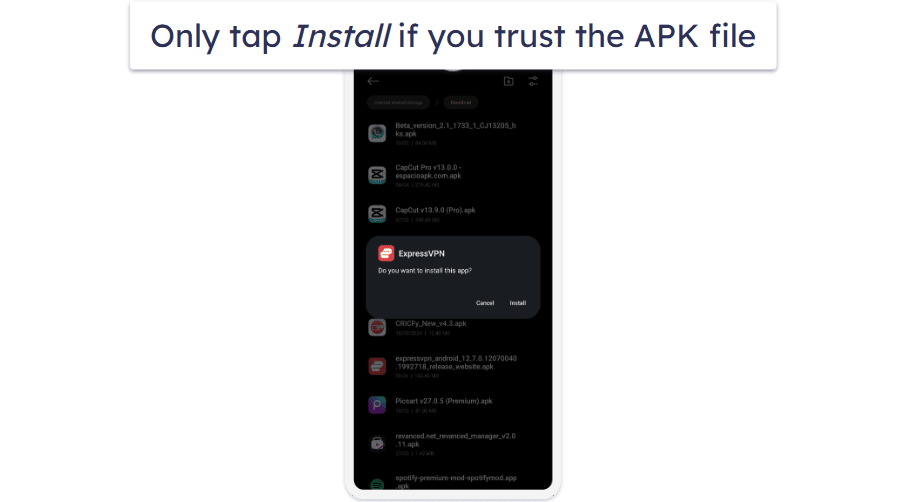
- Open the APK file. Tap the APK file to start the installation process. Your device will display a prompt asking if you want to install the app.
- Wait for installation to complete. The app will install in a few seconds. Once finished, you’ll see a confirmation message.
- Open the app. Tap Open to launch the app immediately, or find the app icon in your app drawer later.
- Review permissions. On the first start, most apps will request permissions to access features they need to run. Carefully read the permissions the app requests and tap Allow if you’re comfortable with them.
- Disable installation from unknown sources (optional but recommended). For security purposes, go back to the settings where you enabled unknown sources and toggle it off after installation.
Following these steps helps you safely install APK files while minimizing security risks on your Android device.
Common Issues When Installing APK Files and How to Fix Them
You’ll sometimes run into issues when installing APK files on your Android device, from simple mistakes during the installation process to more complex compatibility problems. Below are some of the most frequent issues, along with troubleshooting steps to resolve them.
“App Not Installed” Error
This typically occurs if the APK file is corrupted or incompatible, or if a conflicting app is already installed. Here are a few solutions you can try to fix the issue:
- Check the APK file. Make sure the file was completely downloaded and isn’t corrupted. If you’re unsure, try downloading it again from a trusted source.
- Remove the existing app. If the app is already installed, uninstall the previous version and try installing the APK again.
- Ensure compatibility. Check the app’s requirements to confirm that the APK is compatible with your Android version.
Insufficient Storage Space
If your device doesn’t have enough storage space, the APK won’t install successfully. To fix this, free up some storage by going to Settings > Storage and removing unnecessary files or apps to free up space.
Clearing cache files from apps can also help recover some storage space. Go to Settings > Apps and clear the cache of apps you don’t use often.
Installation Blocked by Device Settings
If installation from unknown sources is disabled, your device will block APK installation. Luckily, fixing this is easy. Go to Settings > Privacy Protection > Special Permissions > Install Unknown Apps, select your file manager, and toggle Allow from this source.
Are APK Files Safe to Use?
While they can be a convenient way to get otherwise unavailable apps, APK files also come with risks. APKs can be modified or tampered with, so downloading and installing them without caution may expose your device to malware, data theft, or other security issues. Understanding these risks and how to avoid them is essential to keep your Android device safe.
Using APK Files on Other Devices
There are ways to use APK files on computers and other non-Android devices with special software. However, some devices, like iPhones, are not compatible with APKs at all due to different operating systems and app ecosystems.
Running APKs on PC or Mac with Emulators
To run APK files on a PC or Mac, you need an Android emulator — a program that mimics Android on your computer. Emulators create a virtual Android environment on your computer, allowing you to run APKs just like you would on a phone or tablet.
Popular emulators such as BlueStacks, LDPlayer, and MEmu offer user-friendly interfaces and support for a wide range of Android apps. These emulators are especially popular among gamers who want to play mobile games with a keyboard and mouse. They are also handy for developers who want to test apps across different screen sizes and environments.
To use an APK on an emulator, download the APK file onto your computer, then open it through the emulator’s interface to install and run it. While this process provides excellent flexibility, keep in mind that emulators require a relatively powerful computer and may not perfectly replicate the performance or features of a physical Android device.
Why APKs Don’t Work on iPhone
APK files are completely incompatible with iPhones because Apple’s iOS uses a different app format called .ipa (iOS App Store Package). These two file types are built for fundamentally different operating systems with unique architectures, security models, and development environments.
iOS apps are tightly controlled through Apple’s App Store ecosystem, which requires apps to be signed and distributed under strict guidelines. APK files lack the necessary components to run within iOS’s sandboxed environment, making it impossible to install or open them on iPhones or iPads.
Potential Risks of Downloading APK Files
Downloading APK files from unofficial or untrusted sources can expose your device to serious security threats. Some of the main risks include:
- Malware and viruses. Malicious actors can inject harmful code into APK files, such as viruses, spyware, ransomware, or trojans, which can steal your data or damage your device.
- Fake or cloned apps. APK files can disguise fake apps as legitimate ones, tricking you into installing them and potentially compromising your privacy or security.
- Lack of automatic updates. Apps installed via APK don’t receive automatic updates through the Play Store. This leaves you exposed to known vulnerabilities if you don’t manually update the app.
- Compatibility issues. Some APKs may not be optimized for your specific device or Android version, causing crashes, freezes, or other performance issues.
- Data theft and privacy risks. Malicious APKs can request excessive permissions to access sensitive information like contacts, messages, or financial data without your knowledge.
How to Identify Safe APK Sources
It’s essential to rely on safe and trustworthy sources to reduce the risks associated with APK files. Here are some things to keep in mind when downloading APK files:
- Download APKs only from known, reputable, and secure websites. Trusted platforms such as APKMirror and F-Droid rigorously check each APK to ensure it matches the original developer’s release and is free from malware.
- Verify digital signatures. Check that the digital signature of the APK matches the official developer’s signature to confirm the file hasn’t been tampered with.
- Avoid downloading APK files from random websites, email links, or untrusted social media posts.
- Confirm app details. Verify the APK’s version number, developer name, and other app details against official sources or the developer’s website.
- Read user reviews and community feedback on the source website to identify any reports of suspicious or malicious files.
Smart Practices for Keeping Your Device Safe
You can take several practical steps to protect your Android device when using APK files:
- Enable Google Play Protect on your device to scan apps regularly for harmful behavior.
- Use trusted antivirus apps such as TotalAV Mobile Security or Norton Mobile Security to scan APK files before installing them. These tools can detect malware in real time, ensuring your device stays protected even if you download from lesser-known sources.
- Review app permissions carefully during installation, granting access only to what is essential for the app’s function.
- Keep your Android operating system and security patches up to date to guard against vulnerabilities.
- Monitor your device for unusual behavior after installing an APK, such as excessive battery drain, slow performance, or unexpected pop-ups.
- Uninstall any suspicious apps immediately and run a security scan using your Android antivirus if you notice problems.
- Regularly back up your important data so you can recover it in case of any issues caused by harmful apps.

Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between an APK and an app?
An APK is the actual file format used to distribute and install an app on Android devices. Think of it as the package that contains all the code, resources, and instructions needed to install the app. An app, on the other hand, is the software you interact with on your device after it has been installed. It’s the program that runs and performs tasks like messaging, gaming, or browsing. Put simply, the APK is the installer file, while the app is the fully installed and usable software on your phone or tablet.
Where are APK files located on my Android device?
APK files on your Android device are typically stored in different locations, depending on how you obtained them. If you manually download an APK file from the internet, it’s normally saved in the Downloads folder or whichever folder your browser or file manager uses by default.
Once an app is installed, its APK file is stored in a protected system directory (usually /data/app/), which you cannot easily access without rooting your device. For pre-installed system apps, the APKs are located in the /system/app/ or /system/priv-app/ folders, which are also inaccessible on unrooted devices.
Why is my APK file saying “app not installed?”
If your APK file shows an “App not installed” error, it could be due to several reasons. Common issues include corrupted or incomplete APK files, incompatibility problems, an app that is already installed, signature conflicts, and insufficient storage space. The error can also appear if installation from unknown sources is disabled.
To fix the issue, check that your APK file is complete and from a trusted source, and that your device meets the app’s requirements. Clear storage space if needed and ensure the proper permissions for installing APKs are enabled. If the problem persists, uninstall any existing version of the app before trying again.
Can I install APKs on Android TV?
Yes, you can install APKs on Android TV, but you need to sideload them manually since they’re not from the Google Play Store. First, download the APK file from a trusted source. Then, use a file manager app or a sideloading tool like Send Files to TV to transfer the APK to your Android TV. Before installing, ensure that you enable Unknown Sources in the device’s security settings. Always be careful when sideloading APKs to avoid installing malicious or incompatible software.
How do I update an app installed via APK?
Since APKs installed manually don’t update through the Play Store, you need to download and install the newer version yourself. First, find a trusted source for the updated APK version. Download the file, transfer it to your device (if needed), and install it over the existing app. Most of the time, your data remains intact, but it’s a good idea to back up important information before updating.