Load Balancing Algorithms Explained with Code
#14 System Design – Load Balancing Algorithms
Load balancing is the process of distributing incoming network traffic across multiple servers to ensure that no single server is overwhelmed.
By evenly spreading the workload, load balancing aims to prevent overload on a single server, enhance performance by reducing response times and improve availability by rerouting traffic in case of server failures.
There are several algorithms to achieve load balancing, each with its pros and cons.
In this article, we will dive into the most commonly used load balancing algorithms, how they work, when to use them, their benefits/drawbacks and how to implement them in code.
If you’re finding this newsletter valuable and want to deepen your learning, consider becoming a paid subscriber.
As a paid subscriber, you’ll receive an exclusive deep-dive article every week, access to a structured System Design Resource (100+ topics and interview questions), and other premium perks.
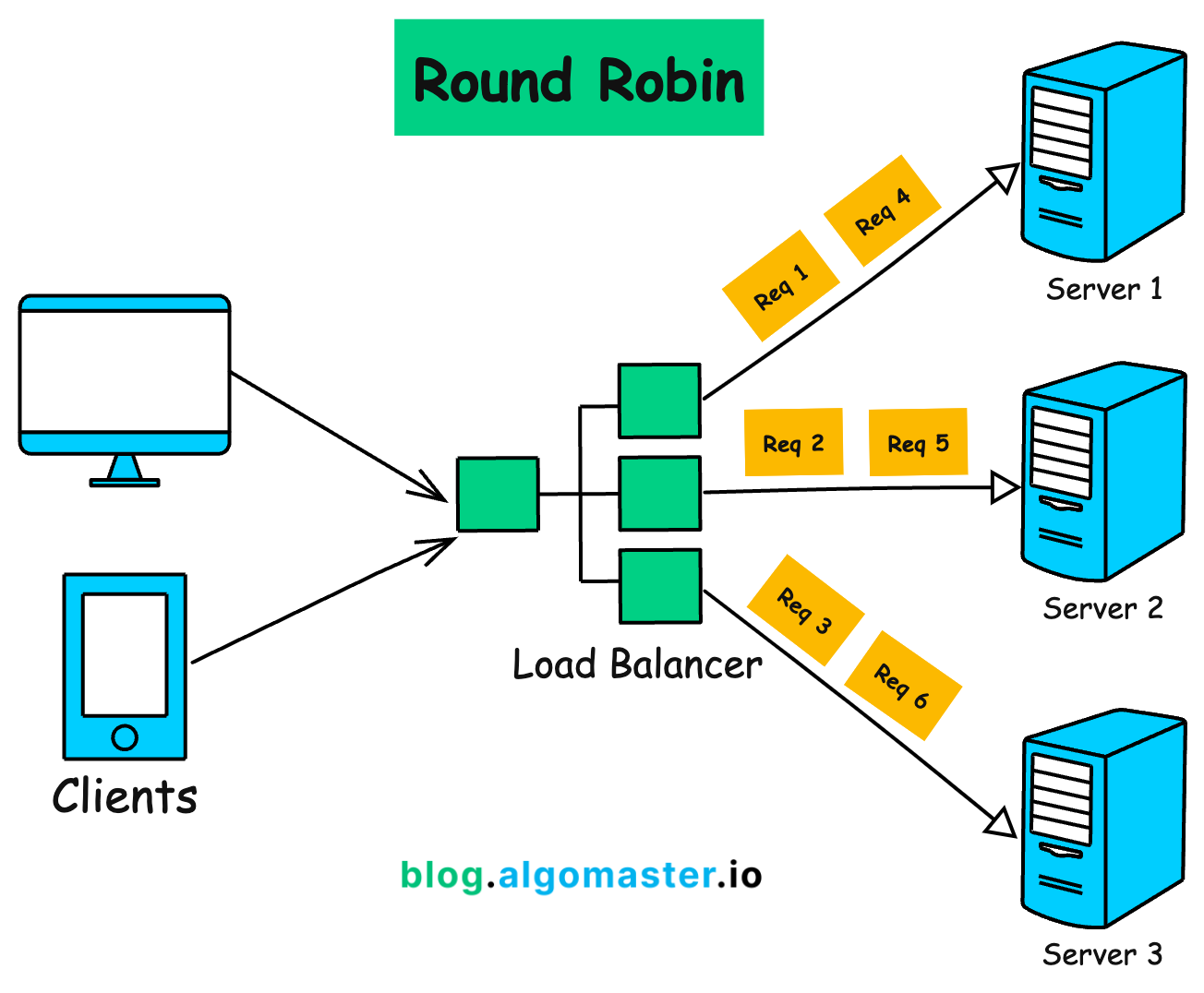
Algorithm 1: Round Robin
How it Works:
-
A request is sent to the first server in the list.
-
The next request is sent to the second server, and so on.
-
After the last server in the list, the algorithm loops back to the first server.
When to Use:
-
When all servers have similar processing capabilities and are equally capable of handling requests.
-
When simplicity and even distribution of load is more critical.
Benefits:
-
Simple to implement and understand.
-
Ensures even distribution of traffic.
Drawbacks:
-
Does not consider server load or response time.
-
Can lead to inefficiencies if servers have different processing capabilities.
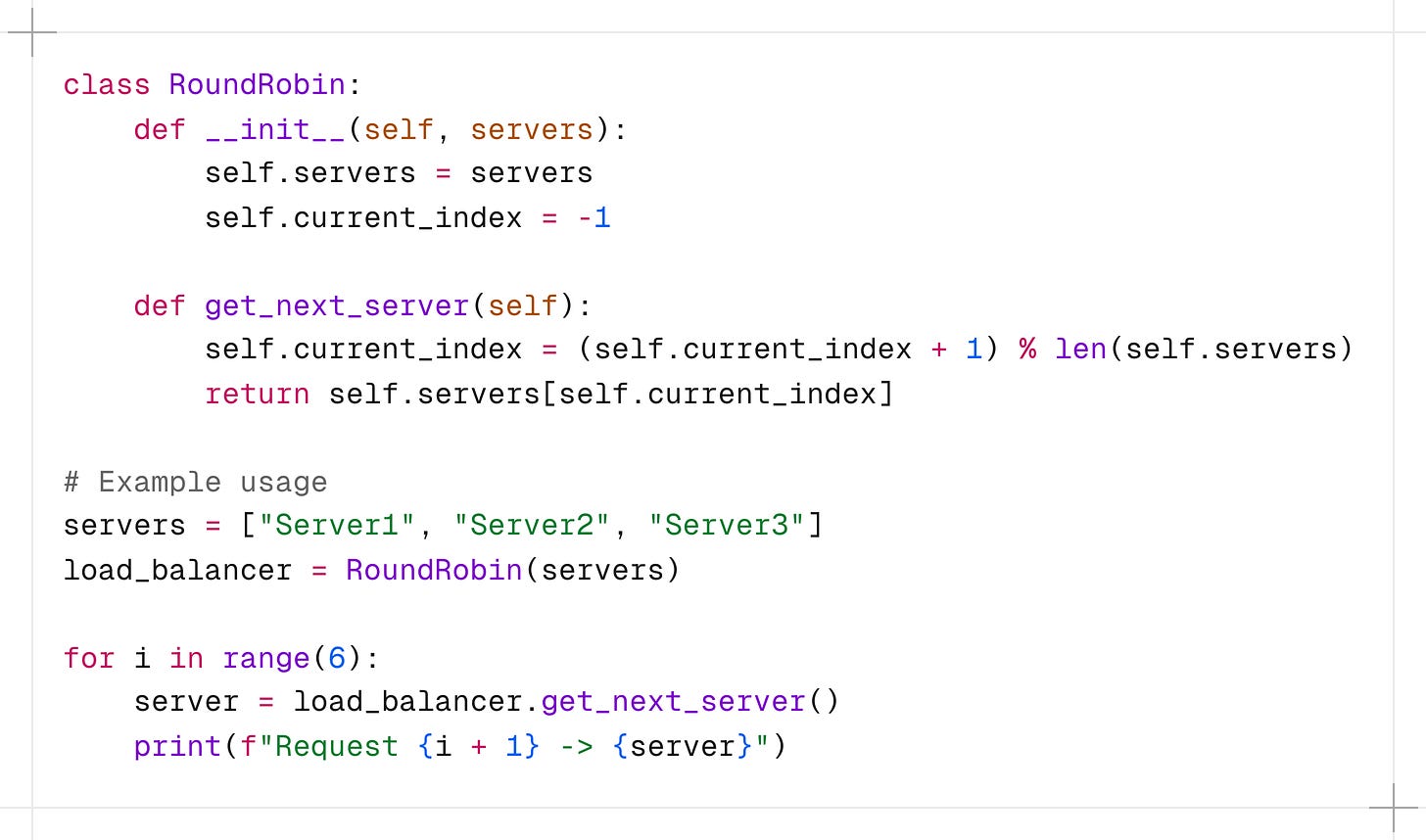
Implementation:
In this implementation, the RoundRobin class maintains a list of servers and keeps track of the current index.
The get_next_server() updates the index and returns the next server in the cycle.
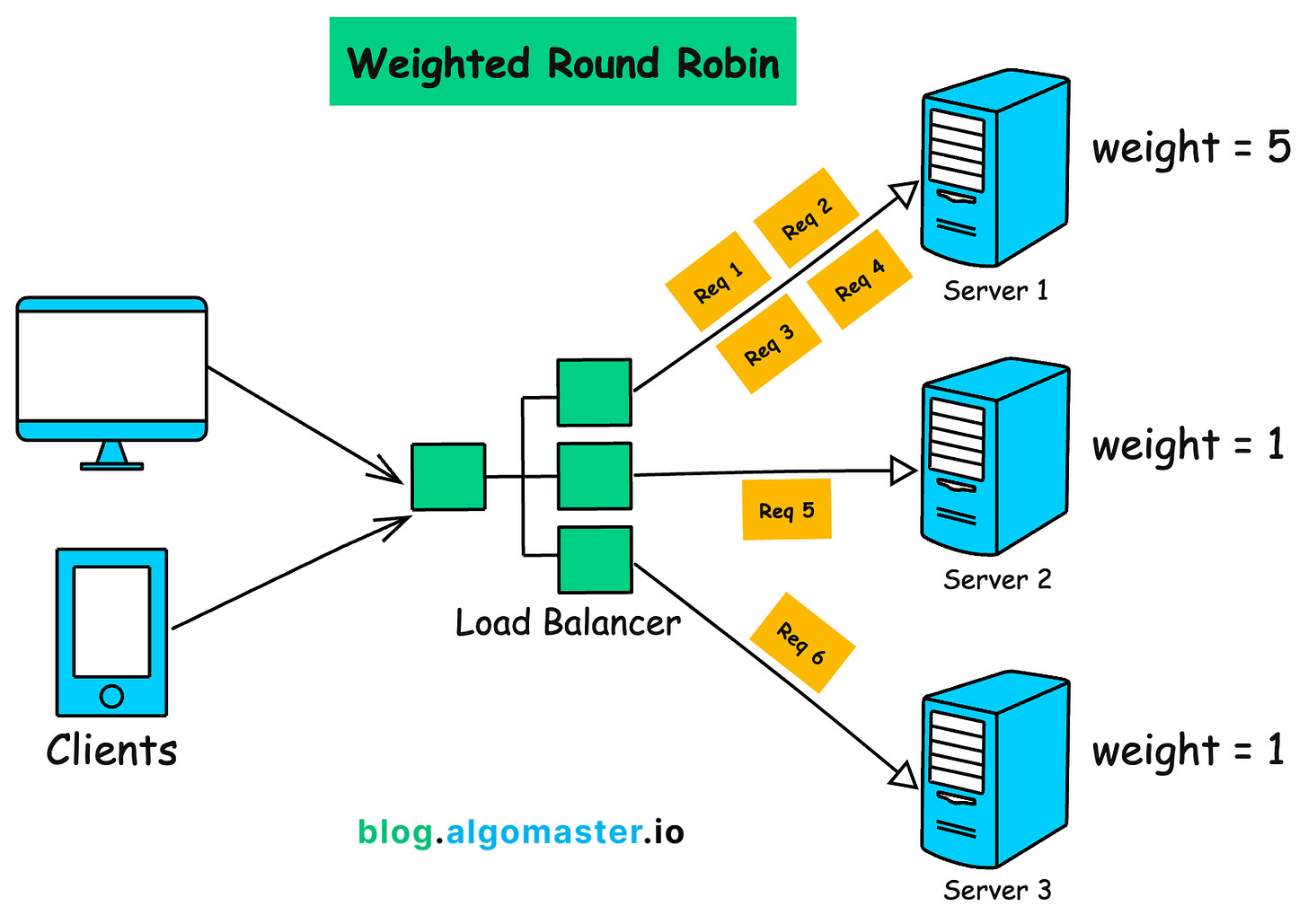
Algorithm 2: Weighted Round Robin
How it Works:
-
Each server is assigned a weight based on their processing power or available resources.
-
Servers with higher weights receive a proportionally larger share of incoming requests.
When to use:
-
When servers have different processing capabilities or available resources.
-
When you want to distribute the load based on the capacity of each server.
Benefits:
-
Balances load according to server capacity.
-
More efficient use of server resources.
Drawbacks:
-
Slightly more complex to implement than simple Round Robin.
-
Does not consider current server load or response time.
Implementation:
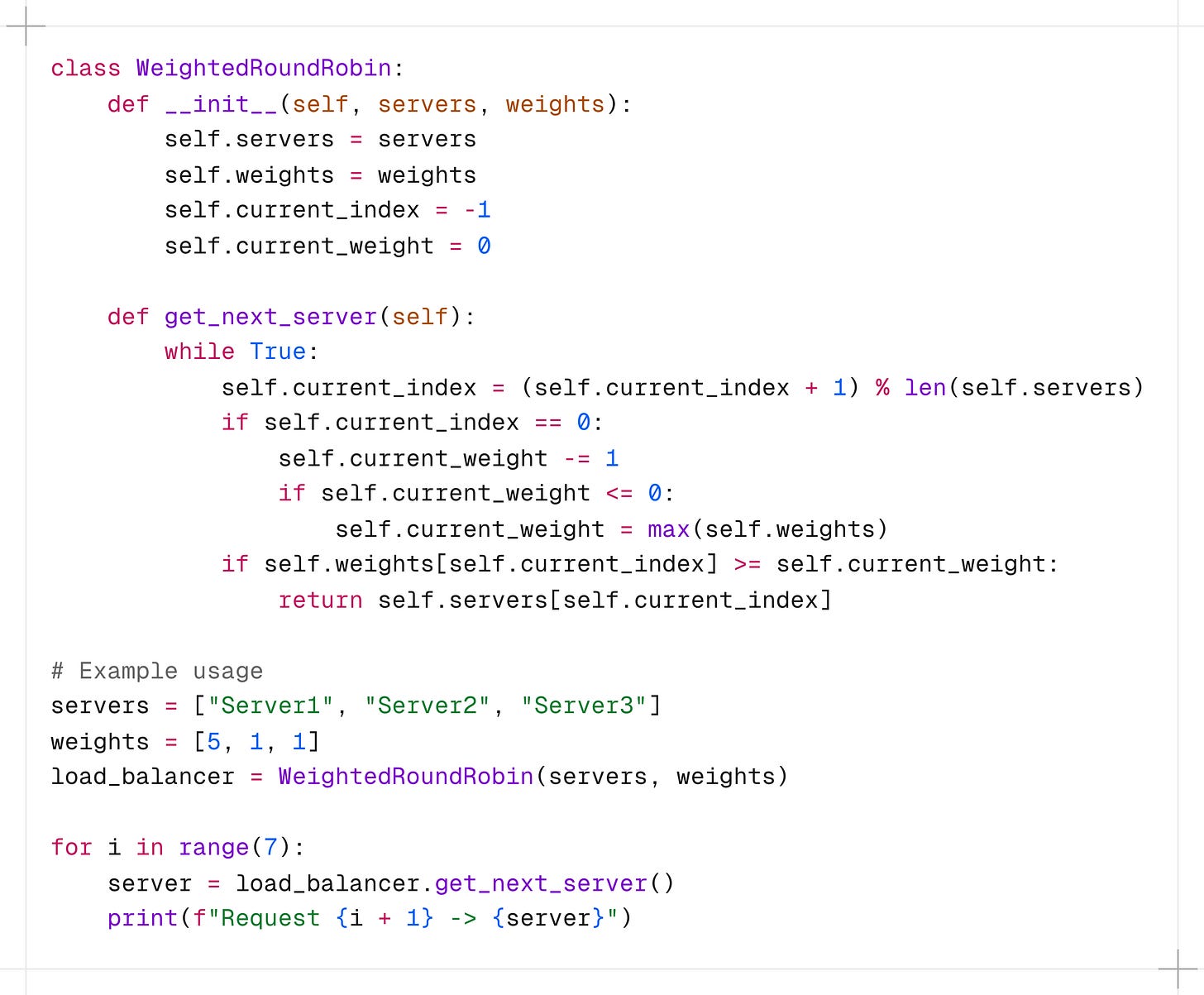
In this implementation, the WeightedRoundRobin class takes a list of servers and their corresponding weights.
The get_next_server() method runs an infinite loop to find a suitable server based on the weights, ensuring that servers with higher weights receive more requests.
The algorithm keeps track of the current weight and adjusts it in each iteration to maintain the desired distribution ratio.
Example: if the weights are [5, 1, 1], Server 1 will be selected 5 times more often than Server 2 or Server 3.
Algorithm 3: Least Connections
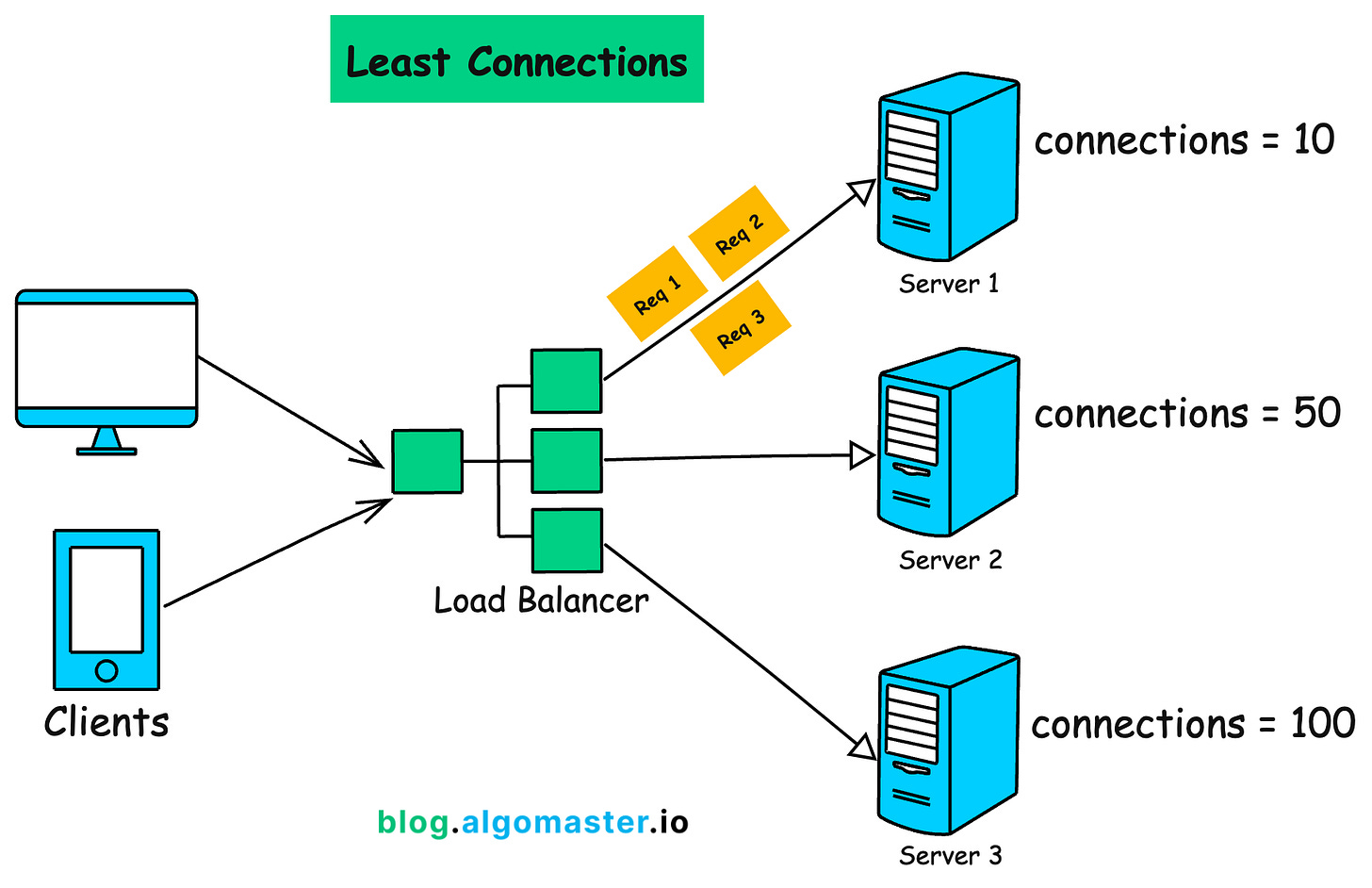
How it Works:
-
Monitor the number of active connections on each server.
-
Assigns incoming requests to the server with the least number of active connections.
When to use:
-
When you want to distribute the load based on the current number of active connections.
-
When servers have similar processing capabilities but may have different levels of concurrent connections.
Benefits:
-
Balances load more dynamically based on current server load.
-
Helps prevent any server from becoming overloaded with a high number of active connections.
Drawbacks:
-
May not be optimal if servers have different processing capabilities.
-
Requires tracking active connections for each server.
Implementation:
In this example, the LeastConnections class maintains a map of servers and the number of active connections for each server.
The get_next_server() method selects a random server with the least number of connections and increments the connection count for that server.
The release_connection() method is called when a connection is closed, decrementing the connection count for the corresponding server.
Algorithm 4: Least Response Time
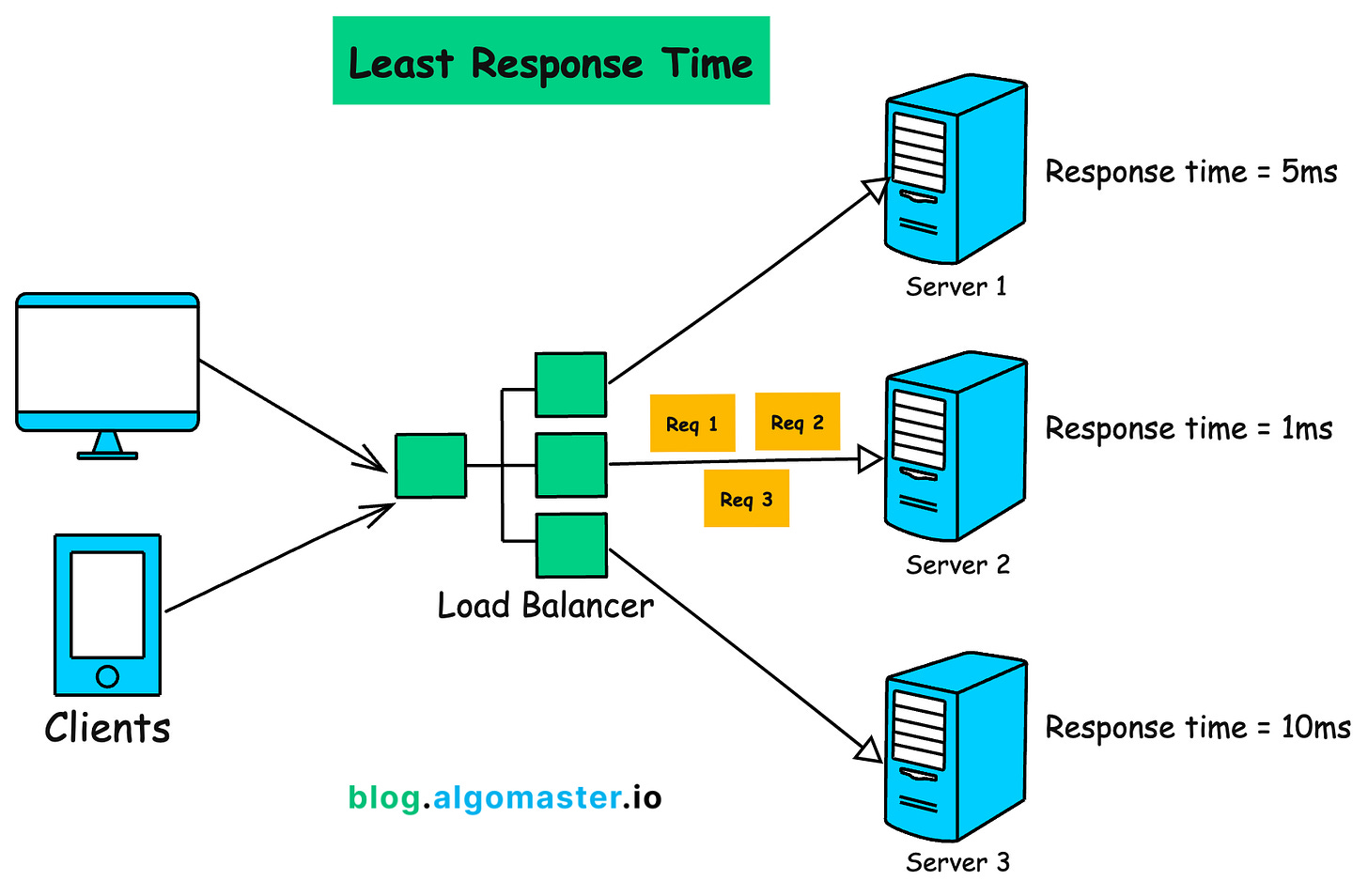
How It Works:
-
Monitors the response time of each server
-
Assigns incoming requests to the server with the fastest response time.
When to Use:
-
When you have servers with varying response times and want to route requests to the fastest server.
Benefits:
-
Minimizes overall latency by selecting the server with the fastest response time.
-
Can adapt dynamically to changes in server response times.
-
Helps improve the user experience by providing quick responses.
Drawbacks:
-
Requires accurate measurement of server response times, which can be challenging in distributed systems.
-
May not consider other factors such as server load or connection count.
Implementation:
In this example, the LeastResponseTime class maintains a list of servers and keeps track of the response time for each server.
The get_next_server() method selects the server with the least response time. The update_response_time() method is called after each request to update the response time for the corresponding server.
To simulate the response time, we use a simulate_response_time() function that introduces a random delay to mimic the server’s response time.
In a real-world scenario, you would measure the actual response time of each server.
Algorithm 5: IP Hash
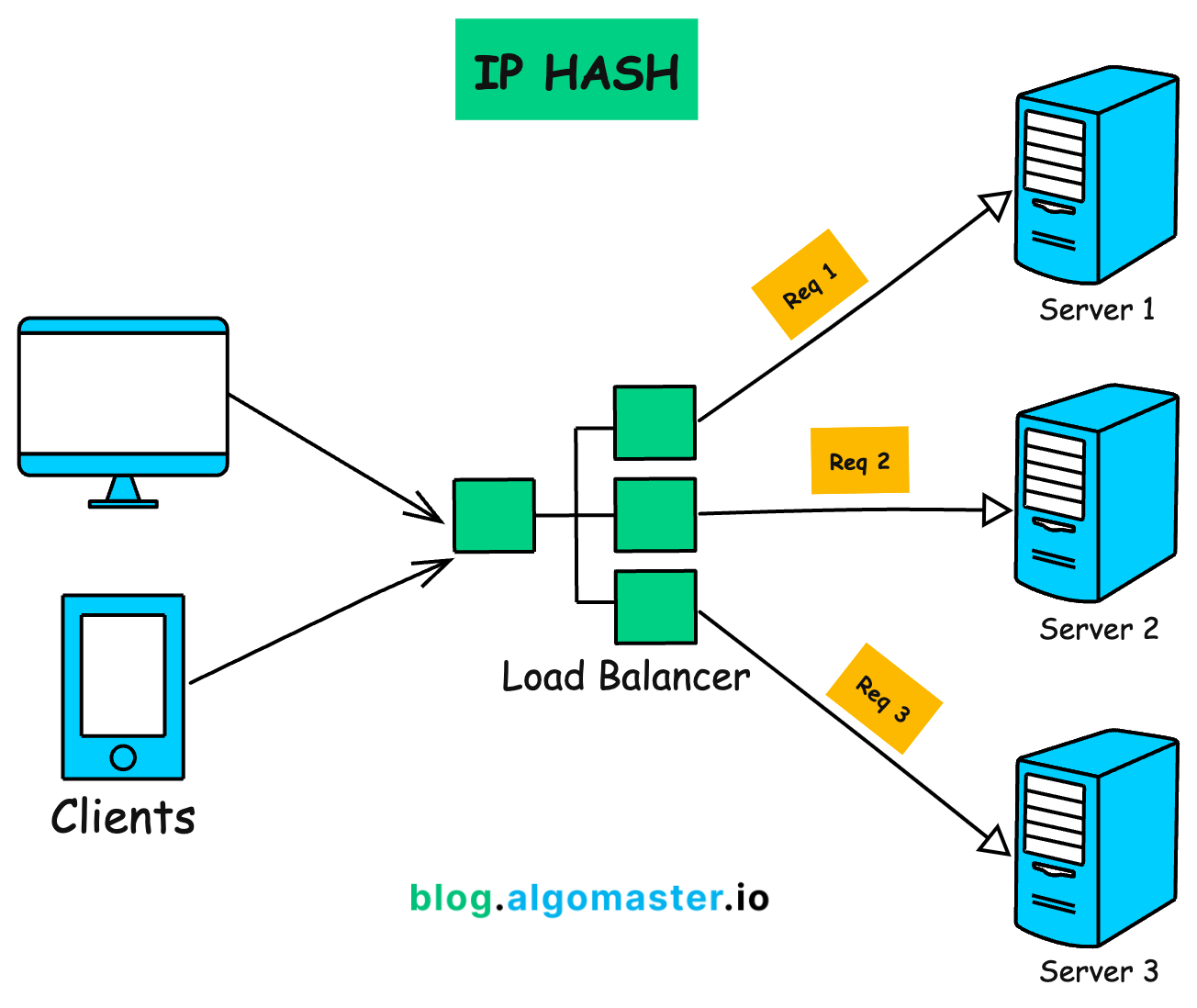
How It Works:
-
Calculates a hash value from the client’s IP address and uses it to determine the server to route the request.
When to Use:
-
When you need session persistence, as requests from the same client are always directed to the same server.
Benefits:
-
Simple to implement.
-
Useful for applications that require sticky sessions.
Drawbacks:
-
Can lead to uneven load distribution if certain IP addresses generate more traffic than others.
-
Lacks flexibility if a server goes down, as the hash mapping may need to be reconfigured.
Implementation:
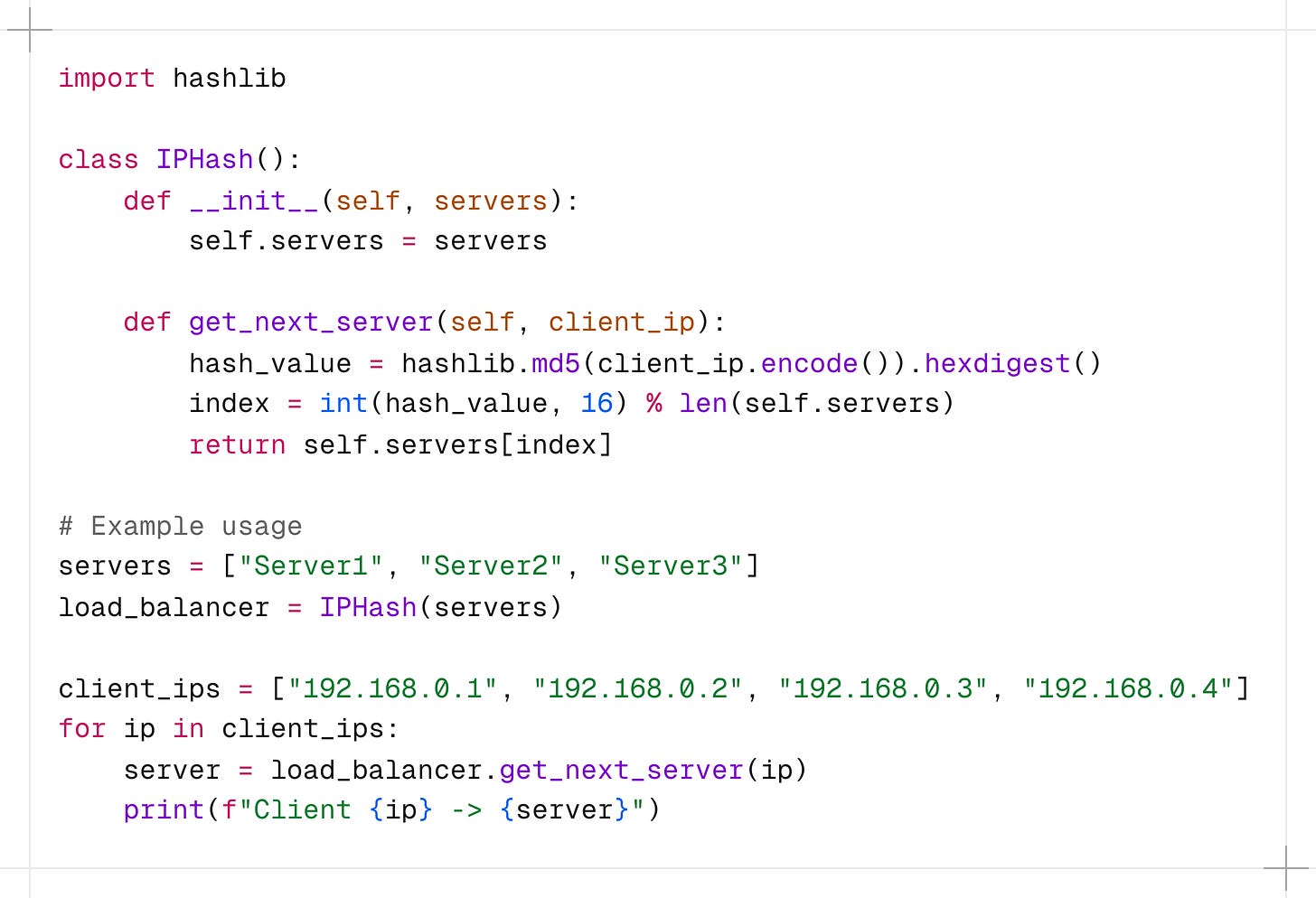
In this implementation, the IPHash class takes a list of servers.
The get_next_server() method calculates the MD5 hash of the client’s IP address and uses the modulo operator to determine the index of the server to which the request should be routed.
This ensures that requests from the same IP address are always directed to the same server.
Summary:
-
Round Robin: Simple and even distribution, best for homogeneous servers.
-
Weighted Round Robin: Distributes based on server capacity, good for heterogeneous environments.
-
Least Connections: Dynamically balances based on load, ideal for varying workloads.
-
Least Response Time: Optimizes for fastest response, best for environments with varying server performance.
-
IP Hash: Ensures session persistence, useful for stateful applications.
Choosing the right load balancing algorithm depends on the specific needs and characteristics of your system, including server capabilities, workload distribution, and performance requirements.
Thank you for reading!
If you found it valuable, hit a like ❤️ and consider subscribing for more such content every week.
If you have any questions or suggestions, leave a comment.
P.S. If you’re finding this newsletter helpful and want to get even more value, consider becoming a paid subscriber.
As a paid subscriber, you’ll receive an exclusive deep dive every week, access to a comprehensive system design learning resource , and other premium perks.
There are group discounts, gift options, and referral bonuses available.
Checkout my Youtube channel for more in-depth content.
Follow me on LinkedIn, X and Medium to stay updated.
Checkout my GitHub repositories for free interview preparation resources.
I hope you have a lovely day!
See you soon,
Ashish