HeartBeats: How Distributed Systems Stay Alive
#8 System Design – Heartbeats
In a distributed system, things fail.
Hardware malfunctions, software crashes, or network connections drop.
Whether you’re watching your favorite show online, making an online purchase, or checking your bank balance, you’re relying on a complex network of interconnected services.
But, how do we know if a particular service is alive and working as expected?
This is where heartbeats come into play.
In this article, we’ll learn about what heartbeats are, why they’re important, how they work, and real-world examples where they’re used.
If you’re finding this newsletter valuable and want to deepen your learning, consider becoming a paid subscriber.
As a paid subscriber, you’ll receive an exclusive deep-dive article every week, access to a structured System Design Resource (100+ topics and interview questions), and other premium perks.
What exactly is a Heartbeat?
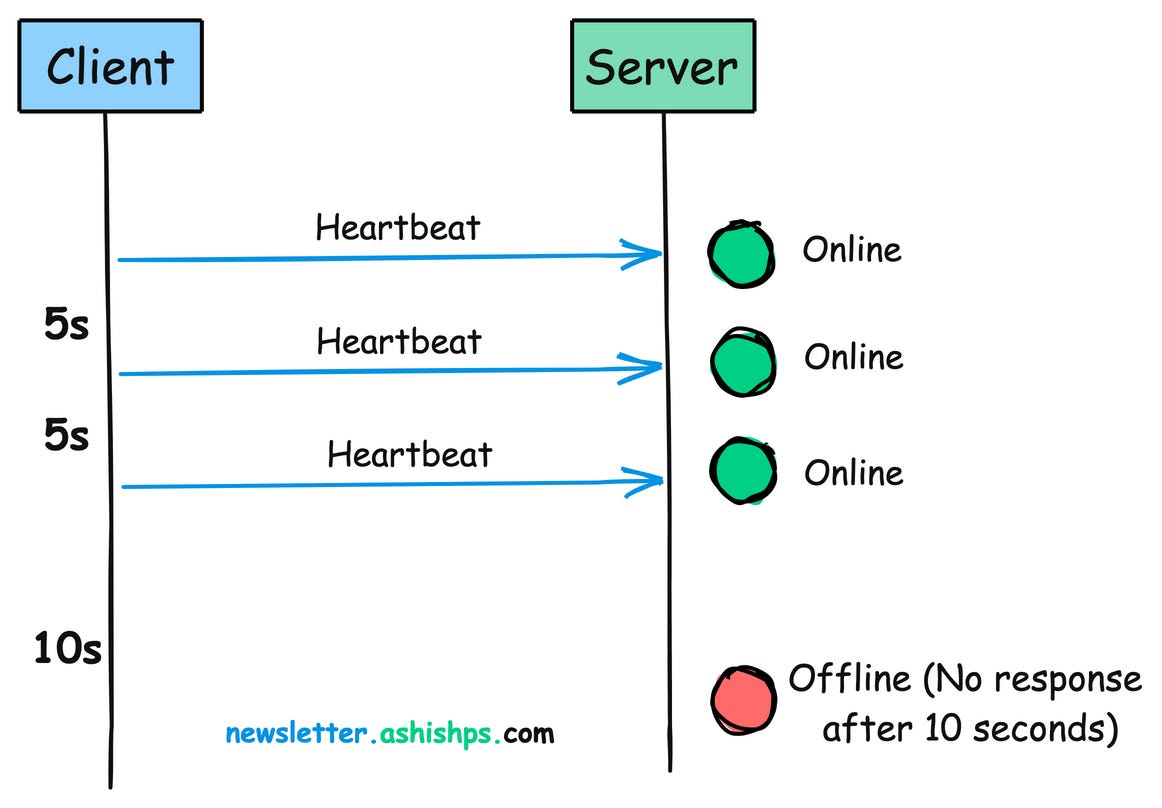
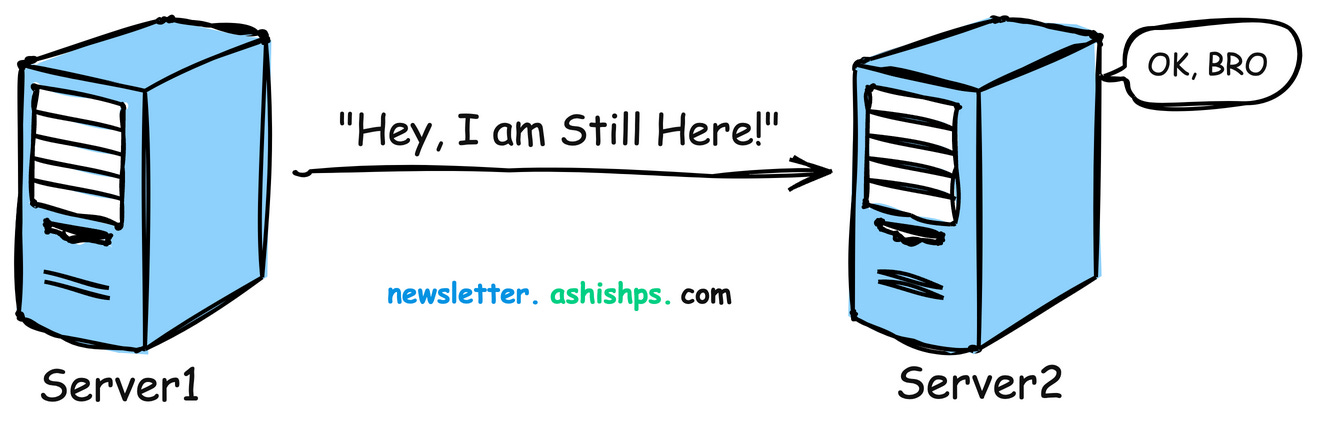
In distributed systems, a heartbeat is a periodic message sent from one component to another to monitor each other’s health and status.
Its primary purpose is to signal, “Hey, I’m still here and working!”
This signal is usually a small packet of data transmitted at regular intervals, typically ranging from seconds to minutes, depending on the system’s requirements.
Why Do We Need Heartbeats?
Without a heartbeat mechanism, it’s hard to quickly detect failures in a distributed system, leading to:
-
Delayed fault detection and recovery
-
Increased downtime and errors
-
Decreased overall system reliability
Heartbeats can help with:
-
Monitoring: Heartbeat messages help in monitoring the health and status of different parts of a distributed system.
-
Detecting Failures: Heartbeats enable a system to identify when a component becomes unresponsive. If a node misses several expected heartbeats, it’s a sign that something might be wrong.
-
Triggering Recovery Actions: Heartbeats allow the system to take corrective actions. This could mean moving tasks to a healthy node, restarting a failed component, or letting a system administrator know that they need to step in.
-
Load Balancing: By monitoring the heartbeats of different nodes, a load balancer can distribute tasks more effectively across the network based on the responsiveness and health of each node.
How Do Heartbeats Work?
The heartbeat mechanism involves two primary components:
-
Heartbeat sender (Node): This is the node that sends periodic heartbeat signals.
-
Heartbeat receiver (Monitor): This component receives and monitors the heartbeat signals.
Here’s a simplified overview of the process:
-
The node sends a heartbeat signal to the monitor at regular intervals (e.g., every 30 seconds).
-
The monitor receives the heartbeat signal and updates the node’s status as “alive” or “available”.
-
If the monitor doesn’t receive a heartbeat signal within the expected timeframe, it marks the node as “unavailable” or “failed”.
-
The system can then take appropriate actions, such as redirecting traffic, initiating failover procedures, or alerting administrators.
While conceptually simple, heartbeat implementation has a few nuances:
-
Frequency: How often should heartbeats be sent? There needs to be a balance. If they’re sent too often, they’ll use up too much network resources. If they’re sent too infrequently, it might take longer to detect problems.
-
Timeout: How long should a node wait before it considers another node ‘dead’? This depends on expected network latency and application needs. If it’s too quick, it might mistake a live node for a dead one, and if it’s too slow, it might take longer to recover from problems.
-
Payload: Heartbeats usually just contain a little bit of information like a timestamp or sequence number. But, they can also carry additional data like how much load a node is currently handling, health metrics, or version information.
Types of Heartbeats
There are two primary types of heartbeats:
-
Push heartbeats: Nodes actively send heartbeat signals to the monitor.
-
Pull heartbeats: The monitor periodically queries nodes for their status.
Challenges and Considerations
While heartbeats are a fundamental part of maintaining system integrity, they are not without challenges:
-
Network Congestion: If not managed correctly, the constant flow of heartbeat signals can contribute to network congestion.
-
False Positives: Poorly configured heartbeat intervals might lead to false positives in failure detection, where a slow but functioning component is incorrectly identified as a failed one.
-
Resource Usage: Continuous monitoring requires computational resources, which must be optimized to prevent undue strain on the system.
-
Split-Brain Scenarios: In some rare cases, a network failure can partition a system, and both sides might declare the other dead. This requires more sophisticated failure-handling mechanisms.
Heartbeats in Action: Real-World Examples
-
Database Replication: Primary and replica databases often exchange heartbeats to ensure data is synchronized and to trigger failover if the primary becomes unresponsive.
-
Kubernetes: In the Kubernetes container orchestration platform, each node sends regular heartbeats to the control plane to indicate its availability. The control plane uses these heartbeats to track the health of nodes and make scheduling decisions accordingly.
-
Elasticsearch: In an Elasticsearch cluster, nodes exchange heartbeats to form a gossip network. This network enables nodes to discover each other, share cluster state information, and detect node failures.
Heartbeats are the invisible pulses that keep distributed systems alive and well-coordinated.
So, the next time you encounter a distributed system, take a moment to appreciate the silent guardians – the heartbeats – that work tirelessly to keep the system’s pulse steady and strong.
Thank you for reading!
If you found it valuable, hit a like ❤️ and consider subscribing for more such content every week.
If you have any questions or suggestions, leave a comment.
P.S. If you’re finding this newsletter helpful and want to get even more value, consider becoming a paid subscriber.
As a paid subscriber, you’ll receive an exclusive deep dive every week, access to a comprehensive system design learning resource , and other premium perks.
There are group discounts, gift options, and referral bonuses available.
Checkout my Youtube channel for more in-depth content.
Follow me on LinkedIn, X and Medium to stay updated.
Checkout my GitHub repositories for free interview preparation resources.
I hope you have a lovely day!
See you soon,
Ashish