The OWASP Amass Project is a tool used by security professionals to perform network mapping of attack surfaces as well as external asset discovery. It uses several techniques that include open-source information gathering and active reconnaissance. This tool written in the Go language allows in-depth DNS, ASN numbers, and subdomain enumeration.
Below is a list of the techniques and the data sources involved in information collection:
- DNS: FQDN Similarity-based Guessing, Brute force, Reverse DNS sweeping, Zone transfers, NSEC zone walking FQDN alterations/permutations
- Routing: NetworksDB, ARIN, BGPView, IPdata, RADb, Robtex, BGPTools, ShadowServer, TeamCymru, IPinfo
- Scraping: Ask, Baidu, Bing, Gists, HackerOne, HyperStat, IPv4Info, PKey, RapidDNS, Riddler, Searchcode, DNSDumpster, DuckDuckGo, Searx, SiteDossier, Yahoo, AbuseIPDB
- WHOIS: AlienVault, DNSlytics, ONYPHE, SpyOnWeb, Umbrella, WhoisXMLAPI, AskDNS, SecurityTrails
- Web Archives: Arquivo, ArchiveIt, CommonCrawl, HAW, Wayback, UKWebArchive
- Certificates: Crtsh, Active pulls (optional), CertSpotter, Digitorus, Censys, FacebookCT, GoogleCT
- APIs: Quake, BufferOver, BuiltWith, C99, Chaos, CIRCL, N45HT, PassiveTotal, PentestTools, Shodan, Cloudflare, DNSDB, DNSRepo, Detectify, FOFA, FullHunt, GitHub, GitLab, Greynoise, HackerTarget, Hunter, IntelX, LeakIX, Maltiverse, Mnemonic, SonarSearch, Spamhaus, ThreatCrowd, ThreatMiner, Twitter, URLScan, VirusTotal, ZETAlytics, ZoomEye, 360PassiveDNS, Ahrefs, AnubisDB, BinaryEdge, Spyse, Sublist3rAPI, ThreatBook
The features associated with the OWASP Amass Project are:
- OWASP Amass is installed by default and can be managed like any other Kali package
- Offers a precompiled version with each release
- It uses open-source information to perform network mapping of attack surfaces and external asset discovery
- The volume argument allows the Amass graph database to persist between executions and output files to be accessed on the host system
This guide covers the steps on how to install and use Amass for in-depth Attack Surface Mapping and Asset Discovery.
Install OWASP Amass on Your System
Installing OWASP Amass can be done through several methods. The methods covered here are:
1. Using Docker
I assume that you already have Docker installed on your system. If not, use the guide below to achieve this.
Now you can pull the Amass docker image using the command:
docker pull caffix/amassYou can also build a container image:
docker build -t amass https://github.com/OWASP/Amass.gitGet the docker images:
$ docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
amass latest be4990590056 5 seconds ago 46.7MB
<none> <none> d6128fb91090 16 seconds ago 680MB
alpine latest e66264b98777 3 weeks ago 5.53MB
caffix/amass latest 77cec86f7fb4 8 weeks ago 46.8MB
golang 1.16-alpine 7642119cd161 3 months ago 302MB
Run the container with the image when executing the Amass commands. For example:
docker run -v OUTPUT_DIR_PATH:/.config/amass/ caffix/amass enum -share -d example.com
##OR
docker run -v OUTPUT_DIR_PATH:/.config/amass/ amass enum -share -d example.comRemember to provide the OUTPUT_DIR_PATH in order to persist the data/output files on the host system.
2. Using Package Managers
There are several package managers that provide Amass. These include:
- Homebrew:
brew tap caffix/amass
brew install amass- Snapcraft:
Ensure snap is installed:
- Install Snapd and Use snap on Kali Linux
- How To Install Snap on Ubuntu / Debian
- How To Install Snap on Arch Linux / Manjaro
- Install Snapd and Snap Applications on CentOS 7 / CentOS 8
- Install Snapd and Snap applications on Fedora
Once installed and running, use the command below to install Amass
$ sudo snap install amass
2022-06-15T06:43:33-04:00 INFO Waiting for automatic snapd restart...
amass v3.19.2 from Jeff Foley (caffix) installed3. From Sources
Ensure that Go is installed on your system:
Download OWASP Amass;
go get -v github.com/OWASP/Amass/v3/...@master
Now you have the binary in $GOPATH/bin
Perform In-depth Attack Surface Mapping and Asset Discovery with Amass
Once installed, you can now use Amass to perform in-depth attack surface mapping and asset discovery. There are 6-subcommands used. These include:
- amass intel – Used to discover targets for enumerations
- amass enum – Used to perform enumerations and network mapping
- amass viz – To visualize enumeration results
- amass track – to track differences between enumerations
- amass db – used to manipulate the Amass graph database
- amass dns – To resolve DNS names at high performance
1. Amass intel
This Amass subcommand helps one discover more root domain names associated with the organization.
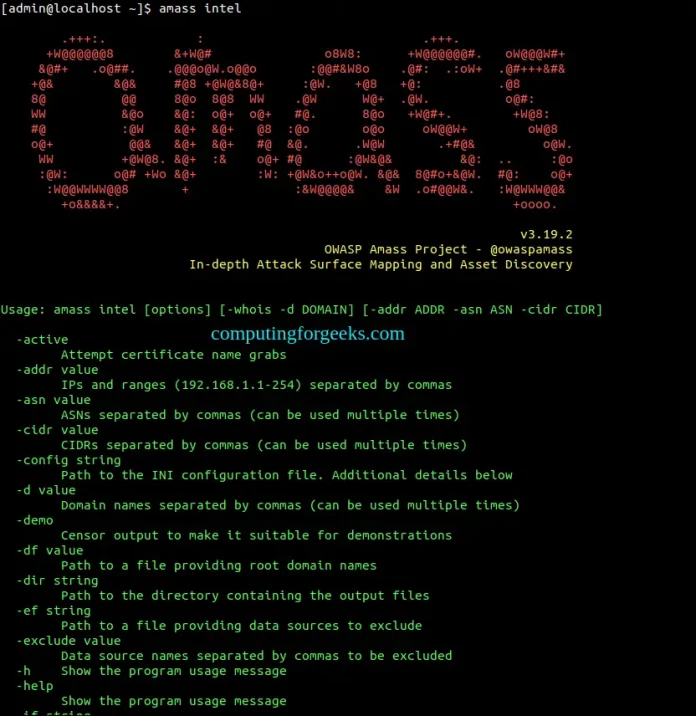
To get available options, run:
amass intelSample Output:

The subcommand uses several techniques that include WHOIS and IPv4Info. You can specify the technique as shown below:
$ amass intel -d owasp.org -whois
owasp.org
modeltime.com
blockster.comFor docker, the command above will be:
docker run -v OUTPUT_DIR_PATH:/.config/amass/ amass intel -d owasp.org -whois
##OR
docker run -v OUTPUT_DIR_PATH:/.config/amass/ caffix/amass intel -d owasp.org -whoisYou can also look for organizations that return ASN IDs assigned to the target. For example:
$ amass intel -org 'Example Ltd'
111111, MAIN_PRODUCT -- Example Ltd
222222, SECONDARY_PRODUCT - Example Ltd
[...]
Please note that the above data is fictitious for demonstration purposes. Retrieved ASN IDs could then be fed back into Amass. The below command attempts to retrieve parent domains on the specified ASN ID and return them along with the IP address they resolve to (127.0.0.1 in this case for demonstration purposes):
$ amass intel -active -asn 222222 -ip
some-example-ltd-domain.com 127.0.0.1
[...]2. Amass Enum
This subcommand allows one to perform DNS enumeration and mapping of the target to determine the attack surface exposed. It can be run in passive or active modes. The passive mode is quicker but doesn’t validate the DNS information. For example, to search for domains associated with an organization, the command will be:
amass enum -passive -d owasp.org -src -dir amass4owaspSample Output:

The active mode can be used to obtain more accurate results using default/specific resolvers.
amass enum -active -d owasp.org -brute -src -ip -dir amass4owasp -o amass_results_owasp.txtSample Output:

3. Amass Track
This subcommand is used to compare the enumeration results performed against the same domain/target.
For example, to compare the last two enumerations performed, the command will be:
amass track -dir amass4owasp -d owasp.org -last 2Sample Output:

4. Amass db
This can be used to make interactions with the Amass graph database. For example, listing all the enumerations performed on a domain stored in a database called amass4owasp.The command will be:
$ amass db -dir amass4owasp -list
1) 06/15 11:21:31 2022 UTC -> 06/15 11:21:56 2022 UTC: owasp.org
2) 06/15 11:17:31 2022 UTC -> 06/15 11:18:48 2022 UTC: cloudflare.com, owasp.org, google.comTo retrieve assets identified during the enumeration modify the above command as below:
amass db -dir amass4owasp -d owasp.org -enum 1 -show5. Amass Viz
This command allows you to visualize the data in the Amass graph database. The results obtained can then be imported into Maltego for analysis.
To generate a d3-force HTML graph from the graph database, say, amass4owasp, the command will be:
amass viz -d3 -dir amass4owaspThe end!
We have triumphantly gone through how to perform in-depth attack surface mapping and asset discovery using Amass. I hope this was important to you.
More guides on this page:
Install and Use WPScan – WordPress security scanner
Install Nessus Vulnerability Scanner on Debian
Scan Docker Container Images for Vulnerabilities with Trivy
Scan PHP|JavaScript|C#|HTML using Sonar Scanner and Jenkins