The Packet Length determines the size of the whole packet including the header, trailer, and the data that has been sent on that packet. The packet length is actually the size of the captured frame. The size of the packet determines the size of the header on the packet. In Wireshark, packet lengths are helpful to determine the counts of small packet lengths, especially if we’re having a window size issue where it shrinks to such an extent that the data being transmitted is smaller than the header.
Viewing the Packet Lengths in Wireshark:
To view the “Packet Lengths” in Wireshark for a trace file follow the below steps:
- Start the Wireshark by selecting the network we want to analyze.
- Now go into the Wireshark and click on Statistics→ Packet Lengths menu or toolbar item.
This will then bring up Wireshark’s “Packet Lengths” window.
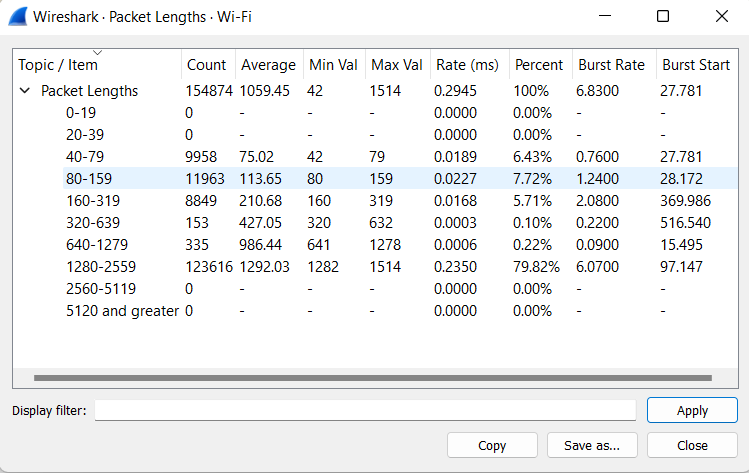
The screenshot above of the Packet Lengths window displays different ranges of packet lengths, counts of packets, and minimum and maximum lengths and percentages in different ranges. As from the above screenshot, most of the packets are between 1280 and 2559 bytes range almost 126316 of them are actually between this packet length. Now, this usually ends up being some sort of data whatever the data is being transferred back and forth.
Packet Lengths Window :
Packet Lengths: It displays different ranges of packet lengths. The range can be configured in the Statistics → Stats Tree menu or toolbar item.
- Count: This field displays the number of packets that fall into this range.
- Average: This field displays the arithmetic mean of the packet lengths in this range.
- Min Val: The field displays the minimum lengths in this range.
- Max Val: The field displays the maximum lengths in this range
- Rate (ms): The field displays the average packets per millisecond for the packets in this range.
- Percent: The field displays the percentage of packets in this range, by count.
- Burst Rate: The bursts of the packets are caught by calculating the total number of packets in a given time interval and comparing that number to the intervals across a window of time. By default, bursts of the packets are caught after 5-millisecond intervals, and intervals are compared across 100-millisecond windows.
- Burst Start: The start time (seconds) from the start of the packet capture, for the interval with the maximum number of packets.
Controls Packet Lengths Window :
- Display filter: In the “Filter” field we can type the filter primitive and press on Apply to apply the filter while displaying the packets.
- Copy: It copies the current statistics to the clipboard.
- Save as: It allows us to save the data as plain text, CSV, YAML, or XML files.




