NetBIOS is an acronym that stands for Network Basic Input Output System. It enables computer communication over a LAN and the sharing of files and printers. TCP/IP network devices are identified using NetBIOS names (Windows). It must be network-unique and limited to 16 characters, with 15 reserved for the device name and the 16th reserved for identifying the type of service running or name record type.
Uses of NetBIOS Enumeration:
An attacker who discovers a Windows OS with port 139 open can investigate what resources are accessible or viewable on the remote system. To enumerate the NetBIOS names, the remote system must have file and printer sharing enabled. Depending on the availability of shares, NetBIOS enumeration may allow an attacker to read or write to the remote computer system or launch a (Dos).
NetBIOS Enumeration Tools:
NetBIOS’s enumeration tools explore and scan the network for security loopholes or flaws in networked systems within a given range of IP addresses and computer lists. In addition, these tools list the operating system, users, password policies, groups, service packs and hotfixes, services, NetBIOS shares, discs, transmits, sessions, SIDs and security event logs.
Netstat:
Netstat is a utility for obtaining protocol statistics, NetBIOS name table, name cache information and current TCP/IP connections over NBT (NetBIOS over TCP/IP), assisting in the resolution of NetBIOS name resolution issues. Name resolution is normally performed when NetBIOS over TCP/IP is operational.
Netstat Parameters and their respective functions :
| Nbtst Parameters | Functions |
|---|---|
| -a RemoteName | Displays the NetBIOS name table of a remote computer, where RemoteName is the remote computer’s NetBIOS computer name. |
| -A IPAddress | Displays the NetBIOS name table of a remote computer, as specified by the remote computer’s IP address (in dotted decimal notation). |
| -c | The contents of the NetBIOS name cache, as well as the table of NetBIOS names and their resolved IP addresses, are listed. |
| -n | Displays the names that NetBIOS applications, such as the server and redirector, have registered locally. |
| -r | Displays the total number of names resolved by a broadcast or WINS server. |
| -R | Removes all #PRE entries from LMHOSTS and clears the name cache. |
| -RR | All names are released and reregistered with the name server. |
| -s | The NetBIOS sessions table is listed, with destination IP addresses converted to computer NetBIOS names. |
| -S | Lists the current NetBIOS sessions, along with their status and IP addresses. |
| Interval | Displays selected statistics again, pausing for the amount of time specified in Interval between each display. |
Examples:
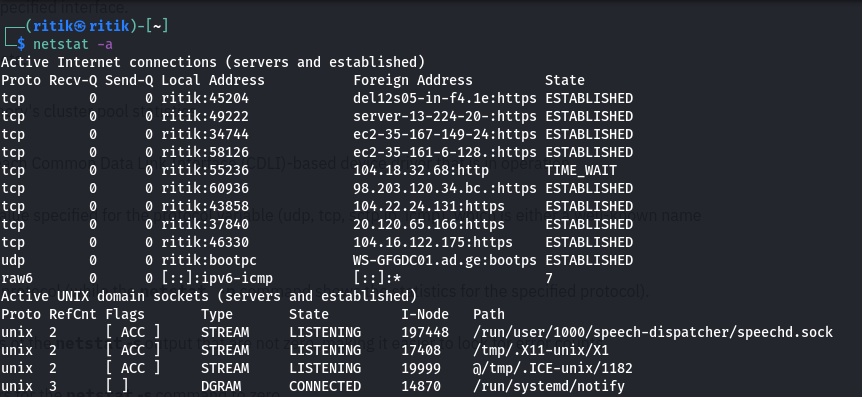
1. To display the NetBIOS name table of a remote computer
Netstat -a
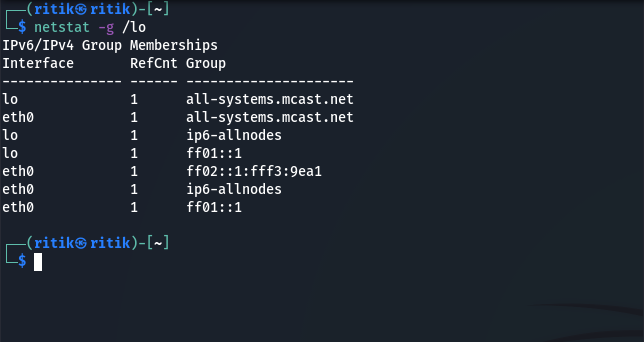
2. To see IPv4/IPv6 Group Memberships
Netstat -g
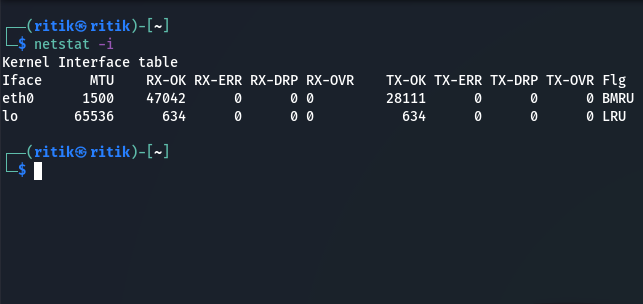
3. To display kernel interface
Netstat -i
Hyena:
Windows operating systems are managed and secured by Hyena. For all operations, it employs a Windows Explorer-style interface. Users, groups (both local and global), shares, domains, computers, services, devices, events, files, printers, print jobs, sessions, open files, disc space, user rights, messaging, exporting, job scheduling, processes, and printing are all supported. It displays Windows server and domain controller shares and user log on names.
It shows a graphical representation of Microsoft Terminal Services, Windows Network, Web Client Network, and so on.
Features:
- Active Task Matching Options – Active Directory update tasks, a key match option has been added to Active Task. When updating directory objects, the new key option allows any unique directory characteristic to be employed as a ‘match’ field.
- Group Member Matrix – in a simple grid all members of multiple groups, including direct, indirect (nested), and primary membership.
- Active Editor Enhancements – The new Hyena release includes new Editor feature enhancements such as account expiration date, support for multivalued attributes, and multi-selection and update capabilities.
PsExec:
PsExec is a lightweight telnet replacement that can execute processes on other systems, complete with full interactivity for console applications, without the need for manual client software installation. PsExec’s most powerful applications include launching interactive command prompts on remote systems and remote-enabling tools such as Ipconfig, which would otherwise be unable to display information about remote systems.
PsFile:
PsFile is a command-line utility which displays a list of files that have been opened remotely on a system and can close opened files by name or file identifier. PsFile’s default behaviour is to list the files on the local system that have been opened by remote systems. Typing a command followed by “-” showcases details about the command’s syntax.
PsGetSid:
PsGetSid converts SIDs to display names and vice versa. It is compatible with built-in accounts, domain accounts, and local accounts. It also displays the SIDs of user accounts and translates a SID into its corresponding name. It can query SIDs remotely across the network.
PsKill:
PsKill is a kill utility that can end processes and kill processes on remote systems. When you run PsKill with a process ID, it will kill the process with that ID on your local computer. If you define a process name, PsKill will kill all processes with that name. PsKill does not require the installation of a client on the targeted device to terminate a remote process.
SuperScan :
SuperScan is a free proprietary graphical application tool for enumerating Windows machines for Windows which was built by Foundstone and later acquired by McAffe. This tool is no longer available for download from the McAffe website.
NET VIEW:
NET VIEW is a command-line tool for locating shared network resources. NetBIOS is required for the NET VIEW command. When NetBIOS is disabled, greatest modern networks will return an incomplete list of nearby computers, or none at all. It is used in.
- net view \\<computername> – Where<computername> is the name of the computer whose resources you wish to view.
- net view /workgroup:<workgroupname> – Where <workgroupname>is the name of the workgroup from which you want to view the shared resources.
NetBIOS Protection Ways:
A security hole in the NetBIOS protocol allows a Windows VPS with this service enabled to be used in an amplification DDoS attack. The following security controls are in place to prevent NetBIOS enumeration attacks:
- Reduce the attack surface by removing unnecessary services such as Server Message Block (SMB).
- On Windows, disable file and printer sharing.




