In today’s world, Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks have become a major threat to present computer networks. DDoS is a kind of attack in which an attacker targets the victim’s network resources such as bandwidth or memory so that the victim may stop responding to a legitimate user’s request. The attackers usually try to consume computational resources, such as bandwidth, processor time, and disk space by overloading or flooding the target system so that it becomes unavailable to the authorized users, or it just crashes.
There are many techniques to overload or flood the network resources of a system and one of the methods is the ICMP Flood attack. In Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Flood, an attacker overpowers the computational resource by sending many ICMP echo requests or ping packets to take down the targeted network infrastructure so that it becomes inaccessible to normal traffic.
ICMP provides error control, as IP does not have an inbuilt mechanism for sending error and control messages. It is used for reporting errors and management queries. It is a supporting protocol and is used by network devices like routers for sending error messages and operations information.
Description of Attack :
In this attack, the victim’s network is flooded with ICMP request packets so that it becomes inaccessible to legitimate users while responding with an equal number of reply packets. The tools like “hping” and “scapy” can be used to bring a network target with ICMP request packets. These tools put lots of stress on both the incoming and outgoing channels of the network, consuming significant bandwidth, which results in a denial of service.
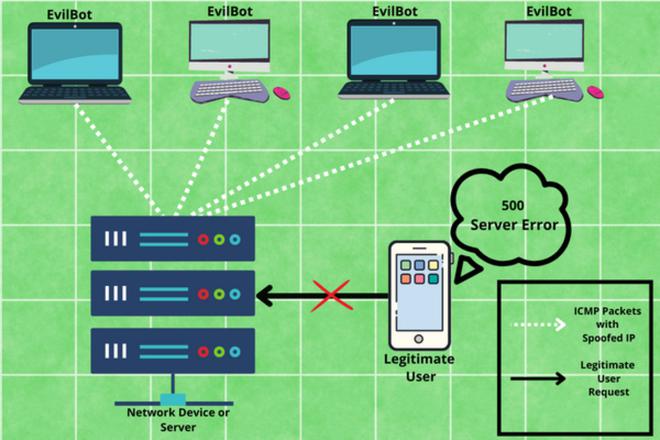
During the attack, an attacker might also use IP spoofing in order to mask their identity, this makes the tracing of DDoS attacks more difficult. The ICMP requests packets are sent as fast as possible without waiting for responses from the target.
ICMP Flood:
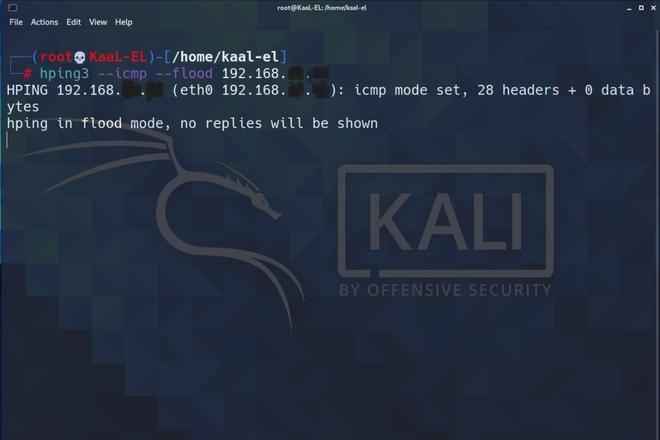
For the practical demonstration, we are using Kali-Linux (Debian 5.10.13-1kali1) as the attacker machine and our Windows 11 as the target machine. To start the ICMP flood, we need to write the following command :
hping3 --icmp --flood <Target IP Address>
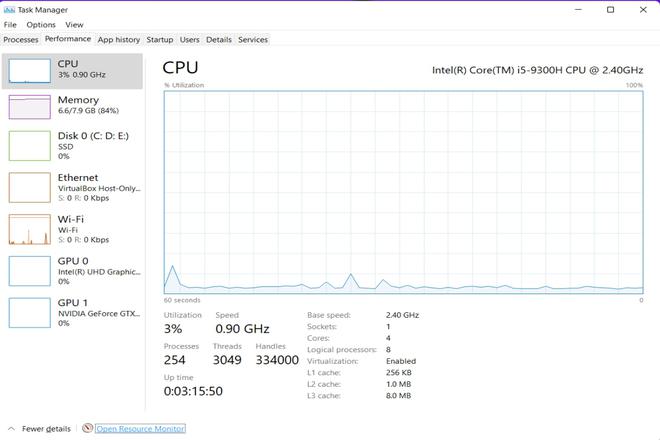
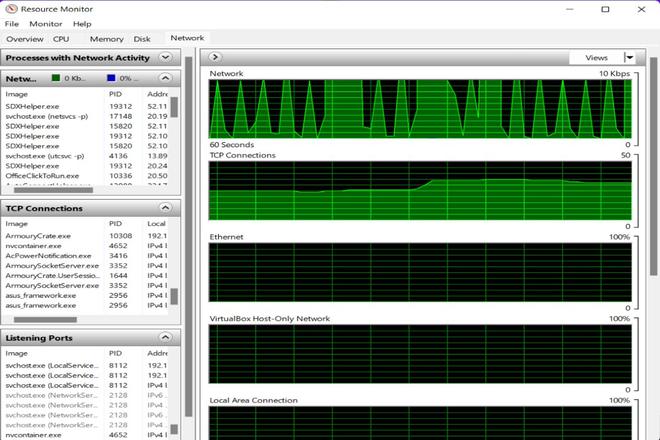
Below is the picture showing the network utilization of the system before the ICMP flood DDoS Attack.
Below is the picture showing the attacker machine running the custom tool hping3 on the terminal :
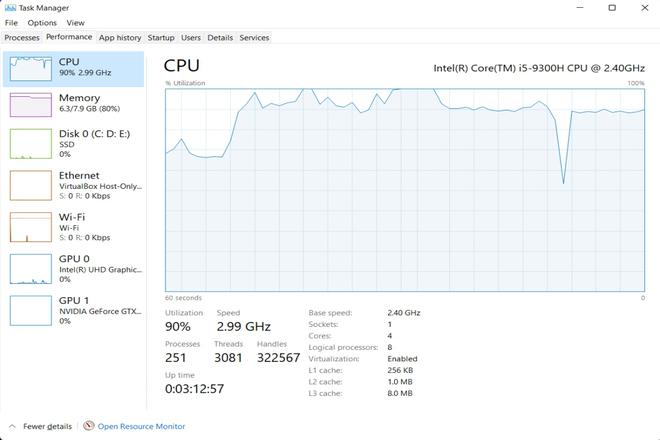
Below is the picture showing the network utilization of the system during the ICMP flood DDoS Attack on Windows 11 :
Below is the picture showing the network activity on Windows 11 :
Prevention of ICMP Flood Attacks :
- By disabling the ICMP functionality of the target system, we can prevent this attack. However, doing this will disable all activities that use ICMP like ping requests, traceroute requests, and other network activities.
- It can also be prevented by reconfiguring the firewall to disallow pings. However, the attacks from within the network cannot be mitigated.
- By limiting the processing rate of incoming ICMP packets, alternatively limiting the allowed size of the ICMP requests.




