Introduction
Do you ever wonder what sets successful businesses apart from the rest? The answer lies in the power of data-driven decision making! Data-driven decision making is using facts, metrics, and data to guide strategic business decisions that align with your goals, objectives, and initiatives.
According to a PwC’s survey, highly data-driven organizations are 3X more likely to report significant improvements in decision-making compared to those who rely less on data.
Imagine the impact that data-driven insights can have on your own business!
In this article, we will unravel the secrets of data-driven decision making and explore its incredible potential to transform how you do business. From uncovering hidden patterns in customer behavior to optimizing operations and predicting market trends, data-driven decision making is the game-changer you’ve been searching for.
Table of contents
- What is Data-Driven Decision Making?
- How Data-Driven Decision-Making Works?
- Importance of Data Driven Decision Making
- Follow These Steps and Use Data in Your Favour
- Common Challenges
- Best Practices for Data-Driven Decision Making
- Examples of Data Driven Decision Making
- Business Outcomes of Data-Driven Decision Making
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Data-Driven Decision Making?
Data-driven decision-making involves using metrics, information, and facts obtained from data to align business decisions with objectives, goals, and initiatives. It’s a logical approach that utilizes market research and customer preferences to understand the next steps for a business. By leveraging the full potential of collected data, companies can make informed choices that maximize profitability.
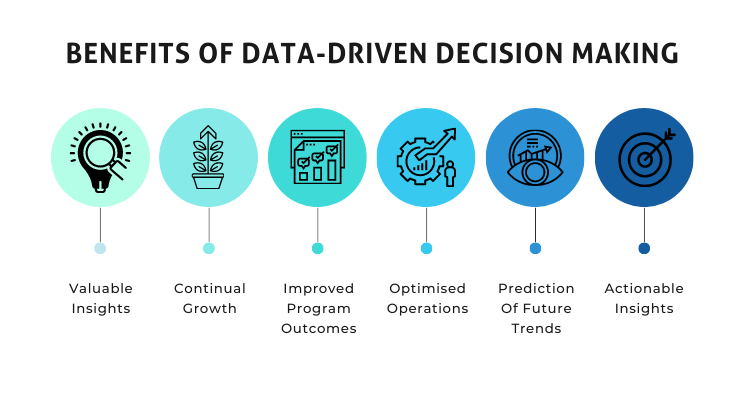
How Data-Driven Decision-Making Works?
Data-driven decision-making brings clarity by helping employees understand the problem and identify specific aspects to address. It involves collecting and categorizing relevant data, saving time and effort. Data is then organized, processed, and analyzed using statistical methods, machine learning, and visualization tools. By considering both qualitative and quantitative aspects, decision-makers can recognize goals and take stepwise actions towards achieving them. The focus is on selecting and deriving information from appropriate data to support decision-making.
Importance of Data Driven Decision Making
Improved Accuracy and Efficiency
The decision made via data collected from the customer is most effective in understanding their needs. It eliminates the assumptive approach and focuses on actual requirements, thus imparting accuracy and efficiency to the business goals.
Cost Savings
The assumptive approach holds the partial risk of failure if it is an unwanted or unliked product or service. However, the data-driven decisions pass and perform according to the expectations. Besides saving investment costs, it helps in saving marketing expenditures. The data helps understand the target audience; hence, the product or service can be aimed directly at them rather than the generalized public to increase sales.
Enhanced Performance and Productivity
With the help of data, businesses can avoid several future risks. The unforeseen risks also include the possibility of easy tackling owing to the clarity and finding alternative routes, making data-based decision-making a productive approach.
Competitive Advantage
The data-driven decisions help align team members with their objectives and the company’s goals, and it helps with efficiency and drawbacks associated with data implementation procedures.
Better Customer Experience
The data generated by companies represent their customers. There is a vast scope for improving the customer communication gap, enhancing long-term user experience, and building relationships with data driven decision making.
Also Read: What is Data Science? Lifecycle, Benefits, Examples & More
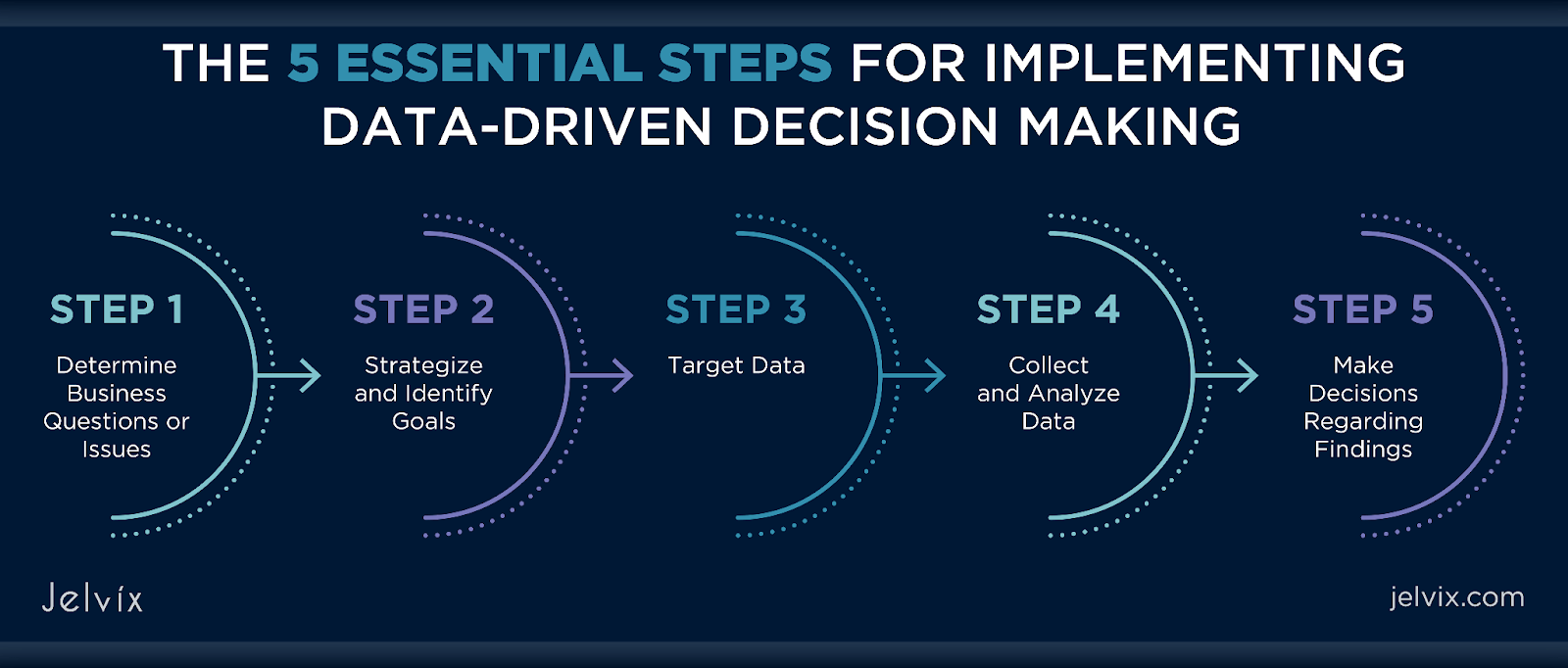
Follow These Steps and Use Data in Your Favour
Time needed: 10 minutes
Follow the following steps to make sure your decisions are backed by data:
- Collecting and Analyzing Data
The collection and analysis of data for data-driven decisions include sources like observations, interviews, surveys, forms, existing databases and multiple other methods. It also requires identifying the specific need for primary or secondary data sources. Post-collection, the analysis is performed through numerous intelligent techniques such as statistical analysis, machine learning, data mining and other methods. The ultimate aim here is to identify the patterns and relations.
- Defining Metrics and KPIs
The performance or progress status towards reaching the goal is a quantifiable indicator available through metrics and KPIs or key performance indicators. Setting up the latter helps identify the relevant information or metrics that align with the goal. Please note that metrics or KPIs for data-driven decisions must always be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant and time-bound (SMART) for effectiveness and efficiency.
- Data Visualization and Communication
Communication and visualization play vital roles in working with data. Results should be presented clearly and concisely. Visualization techniques, such as heat maps, graphs, charts, or animations, can effectively summarize relevant information. The presentation and communication should accurately convey the interpretation. It is the primary method to encourage, motivate, or explain one’s perspective.
- Continuous Improvement and Optimization
Data-driven decision-making is an iterative process requiring continuous will to look for more data and changes and update the existing. The modifications in needs, external factors, and impact of the decision on consumers and businesses encourage finding alternatives or sustainable methods regarding the existing process. It leads to improvement and optimization by repeating the above-stated procedures. The consequence is enhanced effectiveness and productivity by identifying bottlenecks and shortcomings.
Common Challenges
Technical Issues
Data-based decision-making depends on expensive and technologically advanced tools and techniques. Having an infrastructure for complex data analysis, integration and processing with wide data storage capacity and sharing is a big task available only to high-level organizations. Simultaneously maintaining security levels also requires technical expertise and investment, and the issues need instant resolution not to hamper the work.
Data Quality and Accuracy
The data-driven decisions sometimes need help with accuracy and quality. The generated data is often inconsistent, comprises gaps, and might contain outdated or biased data and errors. It requires high expertise, timely, efficient decisions, quality processing and cleanup. The lack of any of these can compromise quality and accuracy.
Ethical and Legal Issues
Data-based decision-making is full of challenges in using private data. Publicizing such data raises legal and ethical issues where a person’s data is exhibited. Organizations using these data types must take mindful steps based on laws and regulations. For instance, the European Union has formulated General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) concerning ethical and legal issues with data.
Best Practices for Data-Driven Decision Making
Establishing a Data-Driven Culture
An organization requires equal contribution from every employee to practice data-driven decision-making. Introducing a cultural environment focussing on the same by laying the foundation of work on data and information is among the recommended actions for leaders. They are suggested to focus on the importance of data, change their mindset to make data-driven decisions and recognize their capabilities. Exchange real-life examples to establish a data-driven culture.
Data Governance and Security
Governance and security become major practices while ensuring data-driven decisions. It requires precise policies and procedures concerning data access, usage and storage. It also includes distributing specific roles and responsibilities to practice efficient data management. Also, it assigns accountability and ensures the safety of sensitive information. Regular audits for proper compliance and quality maintenance are also significantly important.
Training and Education
New and old employees may need to become more familiar with current and updates in data-based decision-making. They will need training and education in data concepts, visualization, communication and analysis. Ensure effective education and training to gain maximum output from such an efficient technology.
Collaborative Decision Making
Increasing engagement by involving cross-functional teams, stakeholders, team members, and subject matter experts helps get widened perspectives, and newer insights, avoiding bias and encouraging diverse thinking. It also brings along more technical ideas based on different domains of expertise, promotes teamwork and increases the outcome quality.
Examples of Data Driven Decision Making
Example 1: Airline
Lufthansa is an airline company currently the second largest concerning number of carried passengers. The company needed more uniform analytics, and using a specific analytics platform increased revenue by 30% across the company. The reason was specific data collection and analysis followed by company employees’ data-driven decisions.
Example 2: Information Technology
Google compared its employee retention rate with more than thousands of performance reviews to make data-driven decisions. It helped them identify behaviors of high-performing managers who were further educated to other employees to improve efficiency. The results were synchronous with expectations, increasing from 83% to 88% in median favorability scores.
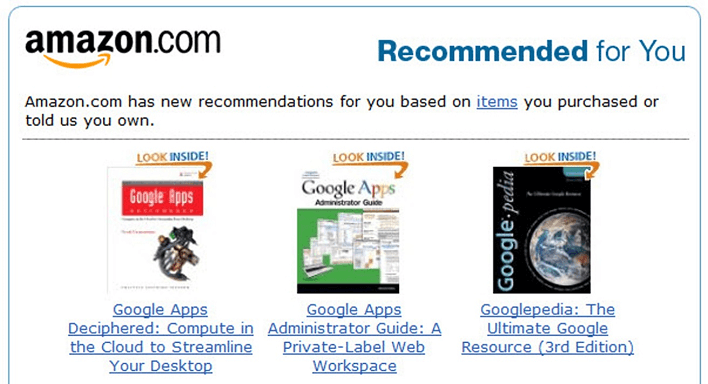
Example 3: E-commerce
Amazon used data-based decision-making in product recommendations to customers. Instead of random suggestions, the data utilized here is previous purchases and search patterns. The data-driven decision-making combined with technological advances brought around 35% profit to the company.
Business Outcomes of Data-Driven Decision Making
Besides the above examples, numerous big brands have incorporated data-based decision-making. The business outcomes summary is as follows:
- Strategic planning that increases success probability, overcomes competition and aids in risk mitigation
- The better operational output that optimizes the processes and workflows and works on shortcomings
- Reduces investment in designing and targeting audience based on assumptions
- Increase in customer satisfaction due to the ability to meet their demands, preferences and needs by providing personalized suggestions and recommendations
Conclusion
Data-driven decision-making is an efficient and proven approach guiding multiple organizations to grow. Coupled with best practices, these decisions allow numerous benefits such as enhanced productivity, promotion in efficiency and work operations. It provides valuable insights into the problem’s requirements, the organization’s current status and future goals imparting clarity and assisting in problem-solving. It also identifies opportunities and helps in risk mitigation. The companies utilizing the same must also focus on challenges associated with the same to avoid any loss.
Frequently Asked Questions
A. The steps of data-driven decision-making involve the following:
1. Identifying the problem, vision, goals and objective.
2. Finding data sources and data collection
3. Data organization, cleaning, processing and organization
4. Analysis and data interpretation followed by visualization and communication
A. Examples of data-based decision-making include designing and optimizing products and services based on customer preferences. Finding the right target audience and providing personalized recommendations based on their information or data.
A. Data-driven decision-making involves informed choices based on data rather than assumptions. It’s vital for businesses, offering clarity, optimized management, meeting customer expectations, competing effectively, and mitigating risks through strategic planning.
A. The efficiency of this approach has encouraged its usage in startups. Many startups currently use it to help them identify customer preferences, goals, and multiple other factors. For instance, Airbnb, Canva and Casper are some of the famous startups owing their success to data-driven decision-making.