Business Intelligence is the talk of a new changing and growing world that can be defined as a set of concepts and methodologies to improve decision-making in business through the use of facts and fact-based systems. The Goal of Business Intelligence is to improve decision-making in business ideas and analysis. Business Intelligence is not just a concept it’s a group of concepts and methodologies. Business Intelligence uses analytics and gut feelings for making decisions.
What Is Business Intelligence?
Business intelligence refers to a collection of mathematical models and analysis methods that utilize data to produce valuable information and insight for making important decisions.
Main Components of Business Intelligence System:
- Data Source
- Data Mart / Data Warehouse
- Data Exploration
- Data Mining
- Optimization
- Decisions
1.Data Source:
To begin, the first step is gathering and consolidating data from an array of primary and secondary sources. These sources vary in origin and format, consisting mainly of operational system data but also potentially containing unstructured documents like emails and data from external providers.
2.Data Mart / Data Warehouse:
Through the utilization of extraction and transformation tools, also known as extract, transform, load (ETL), data is acquired from various sources and saved in databases designed specifically for business intelligence analysis. These databases, commonly known as data warehouses and data marts, serve as a centralized location for the gathered data.
3.Data Exploration:
The third level of the pyramid offers essential resources for conducting a passive analysis in business intelligence. These resources include query and reporting systems, along with statistical methods. These techniques are referred to as passive because decision makers must first develop ideas or establish criteria for data extraction before utilizing analysis tools to uncover answers and confirm their initial theories. For example, a sales manager might observe a decrease in revenues in a particular geographic region for a specific demographic of customers. In response, she could utilize extraction and visualization tools to confirm her hypothesis and then use statistical testing to validate her findings based on the data.
4.Data Mining:
The fourth level, known as active business intelligence methodologies, focuses on extracting valuable information and knowledge from data. Part II of this book will delve into various techniques such as mathematical models, pattern recognition, machine learning, and data mining. Unlike the tools discussed in the previous level, active models do not rely on decision makers to come up with hypothesis but instead aim to enhance their understanding.
5.Optimization:
As you ascend the pyramid, you’ll encounter optimization models that empower you to choose the most optimal course of action among various alternatives, which can often be quite extensive or even endless. These models have also been effectively incorporated in marketing and logistics.
6.Decisions:
At last, the pinnacle of the pyramid reflects the ultimate decision made and put into action, serving as the logical end to the decision-making process. Despite the availability and effective utilization of business intelligence methodologies, the decision still lies in the hands of the decision makers, who can incorporate informal and unstructured information to fine-tune and revise the suggestions and outcomes generated by mathematical models.
Role Business Intelligence:
The characteristics of a business intelligence analysis can be summarized by a rational and methodical approach.
- Firstly, the objectives are clearly identified and performance indicators are chosen to evaluate different options.
- Next, mathematical models are created by utilizing the connections between control variables, parameters, and evaluation metrics.
- Finally, “what-if” scenarios are explored to understand the impact of changing control variables and parameters on performance.
Process Used in Business Intelligence:
BI(Business Intelligence) uses a set of processes, technologies, and tools (such as Informatica/IBM) to transform raw data into meaningful information and then transform information to provide knowledge. Then afterward some beneficial insights can be extracted manually and by some software then the decision-makers can make an impactful decision on the basis of insights. 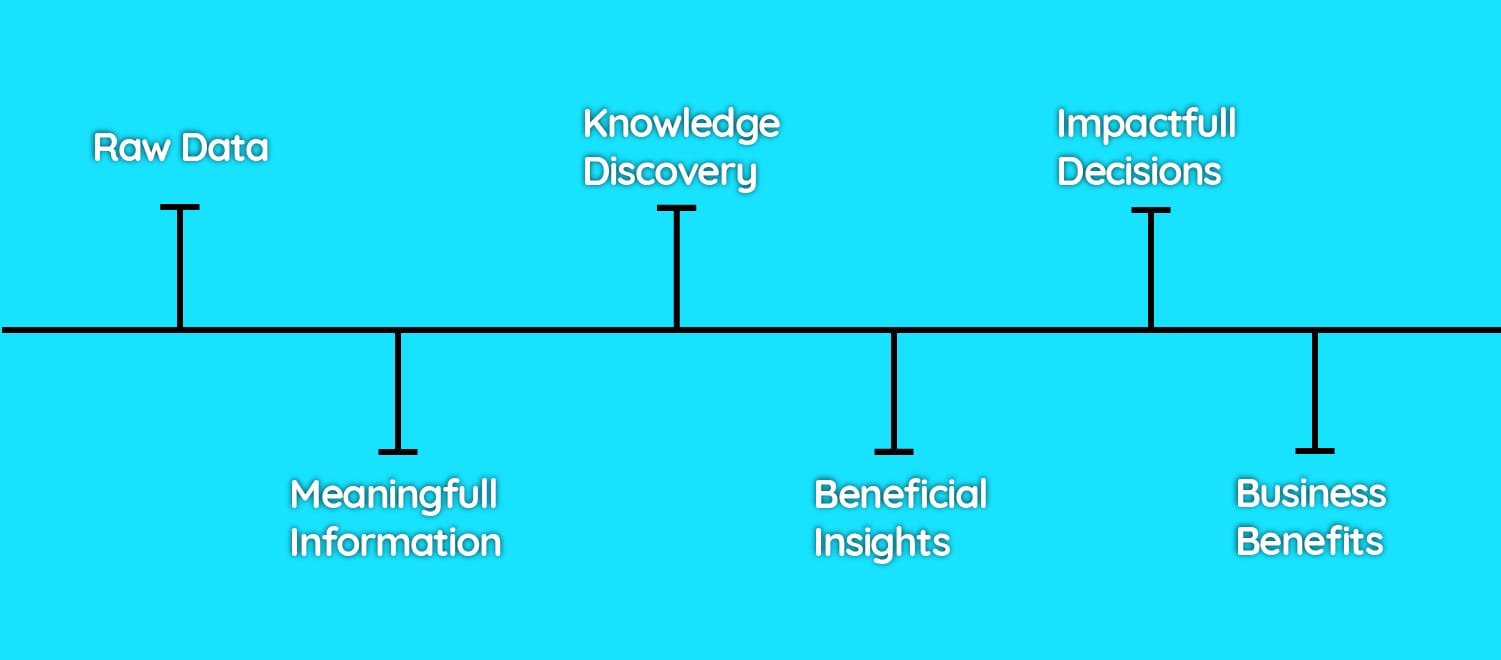
- Fact-based decision making.
- 360 degrees perspective on your business.
- Virtual team members are on the same page.
- Measurement for creating KPI (Key Performance Indicators) on the basis of historic data fed into the system.
- Identify the benchmark and then set the benchmarks for different processes.
- Business Intelligence systems can use to identify market trends and also to spot business problems that need to be identified and solved.
- Business Intelligence helps in data visualization will increase the quality of data and then also increases the quality of decision making.
- Business Intelligence systems can be used by large enterprises, and organizations along with Small and Medium Enterprises, because it is quite affordable.
Types of Users of Business Intelligence:
- Analyst (Data Analyst or Business Analyst): They are the statistician of the company, they used BI on the basis of historical data priorly stored in the system.
- Head or Manager of the Company: Head of the company uses Business Intelligence used to increase the profitability of their company by increasing the efficiency in their decisions on the basis of all the knowledge they discovered.
- IT Engineer: For his company.
- Small Business Owners: Can be used by a small businessman because it is quite affordable too.
- Government Officials: In the decision-making of the government.
Types of Decisions Supported by Business Intelligence:
- Strategic Level: The strategic level is the level where the Heads of the company decide the strategies of any business.
- Tactical Level: Once the strategy is made though for handling all the details and matters have a tactical level where all the technologies and methodologies come under one umbrella. This level is further responsible for continuously updating the data.
- Operational Level: Operation decisions are made at this level. Operational decisions help in operating the system.
Applications of Business Intelligence:
- In Decision Making of the company by decision-makers of the organizations.
- In Data Mining while extracting knowledge.
- In Operational Analytics and operational management.
- In Predictive Analytics.
- In Prescriptive Analytics.
- Making Structured data from unstructured data.
- In Decision Support System.
- In Executive Information System (EIS).
Business Intelligence Tools and Software
- Tableau: A business intelligence and data visualization application that enables users to connect to different data sources, build interactive dashboards, and share findings with others.
- Microsoft Power BI: A cloud-based business intelligence program that enables users to connect to a variety of data sources, produce visualizations, and communicate findings.
- QlikView is a business intelligence and data visualization platform that enables users to build interactive dashboards and examine data in novel ways.
- Data visualization, reporting, and analytics tools are all included in SAP BusinessObjects, a complete business intelligence suite.
- IBM Cognos: A tool for performance management and corporate intelligence that enables users to build reports, scorecards, and dashboards.
- Data visualization, reporting, and analytics technologies are all part of the full business intelligence suite known as Oracle Business Intelligence.
- Create dynamic dashboards and reports with MicroStrategy, a business intelligence and data visualization tool.
- Data visualization, reporting, and analytics tools are all part of the full business intelligence suite known as SAS Business Intelligence.
- TIBCO Spotfire is a business intelligence and data visualization platform that enables users to build interactive dashboards and investigate data in novel ways.
- Looker: A tool for business intelligence and data visualization that enables users to build interactive dashboards and investigate data in novel ways.
Advantages of Business Intelligence
- Decision-making is improved because users have access to real-time data and insights through business intelligence tools. This enables users to base their decisions on correct and current information.
- Efficiency gain: Many manual data analysis operations are automated by business intelligence systems, freeing up time and resources for other tasks.
- Better data management: Business intelligence technologies aid in the administration and organization of data, making it simpler to locate the facts required for decision-making.
- Greater visibility: Business intelligence solutions give users a comprehensive picture of the functioning of the firm, enabling them to spot areas that could use improvement.
- A better understanding of customers: Business intelligence technologies helps firms understand their customers better, enabling them to customize products and services to suit their needs.
- Cost savings: Business intelligence technologies assist firms in locating inefficiencies and cost savings, which boosts revenue.
- Better forecasting: Organizations may evaluate past data and predict future patterns using business intelligence technologies, which enables them to plan more successfully for the future.
- Competitive advantage: By granting access to important data and insights that can guide them in making better decisions, business intelligence technologies provide firms a leg up on their rivals.
- Collaboration is improved as a result of using business intelligence technologies to disseminate information between teams and departments. This promotes better decision-making and collaboration.
- Better Monitoring: Business intelligence technologies assist firms in tracking important metrics like revenue, customer happiness, and staff performance and in monitoring performance.
Disadvantages of Business Intelligence
- Complexity: The implementation and upkeep of business intelligence systems can be extremely difficult and complicated. This may be a drawback for companies with constrained IT resources.
- High costs: Some businesses find it prohibitively expensive to implement and purchase business intelligence technologies.
- Business intelligence strongly depends on accurate and current data. The insights produced by business intelligence technologies could not be accurate if the data is inconsistent, erroneous, or incomplete.
- Data Security: Business intelligence systems handle and store a lot of sensitive data, which, if not adequately protected, is susceptible to security breaches.
- Dependence on IT: Because business intelligence solutions frequently rely largely on IT assistance, it may be challenging for enterprises to quickly get the data they require.
- Limited scalability: For firms with huge data volumes, business intelligence solutions may not be able to handle enormous amounts of data.




