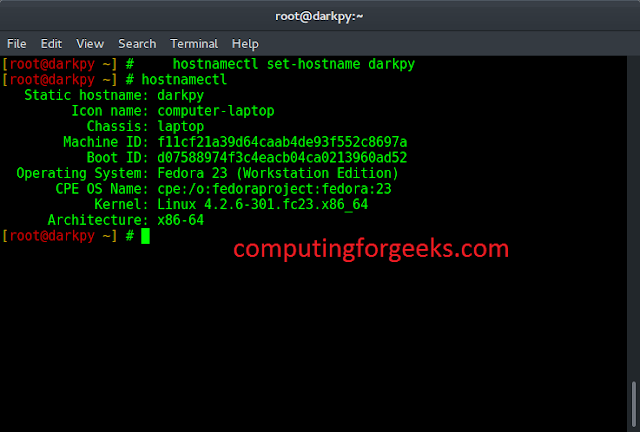
Given two integers N and M, the task is to find the vertex diagonally opposite to the Mth vertex of an N-sided polygon.
Examples:
Input: N = 6, M = 2
Output: 5
Explanation:
It can be observed from the image above that the vertex opposite to vertex 5 is 2.
Input: N = 8, M = 5
Output: 1
Explanation:
It can be observed from the image above that the vertex opposite to vertex 8 is 1.
Approach: The following two cases need to be considered to solve the given problem:
- If M > N / 2: The vertex will always be M — (N / 2).
- If M ? N / 2: The vertex will always be M + (N / 2).
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;// Function to return the// required vertexint getPosition(int N, int M){ // Case 1: if (M > (N / 2)) { return (M - (N / 2)); } // Case 2: return (M + (N / 2));}// Driver Codeint main(){ int N = 8, M = 5; cout << getPosition(N, M); return 0;} |
Java
// Java program for // the above approachclass GFG{// Function to return the// required vertexstatic int getPosition(int N, int M){ // Case 1: if (M > (N / 2)) { return (M - (N / 2)); } // Case 2: return (M + (N / 2));}// Driver Codepublic static void main(String[] args){ int N = 8, M = 5; System.out.print(getPosition(N, M));}}// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji |
Python3
# Python3 program for the # above approach# Function to return the # required vertex def getPosition(N, M): # Case 1: if (M > (N // 2)): return (M - (N // 2)) # Case 2: return (M + (N // 2)) # Driver Code N = 8M = 5print(getPosition(N, M)) # This code is contributed by code_hunt |
C#
// C# program for the above approachusing System;class GFG{// Function to return the// required vertexstatic int getPosition(int N, int M){ // Case 1: if (M > (N / 2)) { return (M - (N / 2)); } // Case 2: return (M + (N / 2));}// Driver Codepublic static void Main(String[] args){ int N = 8, M = 5; Console.Write(getPosition(N, M));}}// This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar |
Javascript
<script>// Javascript program for the above approach// Function to return the// required vertexfunction getPosition(N, M){ // Case 1: if (M > parseInt(N / 2)) { return (M - parseInt(N / 2)); } // Case 2: return (M + parseInt(N / 2));}// Driver Codevar N = 8, M = 5;document.write(getPosition(N, M));</script> |
1
Time Complexity: O(1)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Ready to dive in? Explore our Free Demo Content and join our DSA course, trusted by over 100,000 neveropen!