There are a number of methods to crack a user’s password, but the most prominent one is a Password Guessing Attack. Basically, this is a process of attempting to gain the system’s access by trying on all the possible passwords (guessing passwords). If the attacker manages to guess the correct one, he has complete access to the remote system, can manipulate the data, and may demand a ransom in exchange for the system data.
Classification of Password Guessing attack:
Most commonly, these types of attacks are classified into two:
1. Dictionary Attack:
There are a number of most commonly found passwords online in the form of dictionaries. This dictionary consists of a list of passwords leaked in a data breach or commonly used passwords.
Example: abc123, 123456789, password, abcdef, etc. To learn more, please refer to the article Dictionary Attack.
Prevention:
- Include a combination of upper case letters, lower case, and special symbols into the password to make it more secure.
- Make sure the password manager you are using is secure and is not engaged in the selling of data.
- Avoid creating weaker passwords (like password, abc123, etc.), instead create a strong password (like !ush3r, sn00pdoggyd0G, etc.)
- Create a password with at least 8 characters long, which makes it difficult to carry out brute-force attacks.
2. Brute force Attack:
This method includes trying all the possible permutations of passwords until finding the correct one. The time taken depends on the complexity of passwords, weaker passwords can be cracked within a couple of minutes while the stronger ones may take several hours or days.
Generally, these types of attacks may be detected by the system and the account may be locked to prevent unauthorized access due to many failed login attempts, though attackers find ways to bypass the detection and successfully crack the password. To learn more, please refer to the article Brute force attack.
Prevention:
- Avoid creating weaker passwords (like password, abc123, etc.), instead create a strong password (like !ush3r, sn00pdoggyd0G, etc.)
- Create a password with at least 8 characters long, which makes it difficult to carry out brute-force attacks.
- Regularly change your password in case it is compromised.
- Never include personal information in passwords like name, date of birth, mobile number, etc. which makes it easier for attackers to guess correctly.
3. Keylogger Attack:
Keyloggers are malicious software made with the purpose to record all the keystrokes of the user and report them back to the hacker. Mostly, the user installs software from unofficial sources believing it to be legitimate, but that software installs keyloggers without the user knowing it. This results in all the keystrokes being recorded and reported to the hacker; in many cases, the hacker is able to guess the password easily. Please refer to the article Keylogger to learn more about this.
Prevention:
- Regularly update your software for security patches.
- Buy antivirus software from a reputed company and have a system scan from time to time.
- Make sure you don’t plug in unknown media devices like pen drives.
4. Man-in-the-middle attack:
Basically, in these types of attacks, the hacker intercepts (or get access to the compromised system) the original connection between the user and Web App/Server and acts as a middleman between the client and the server. In this way, the hacker has access to the information passing between the client and server, including passwords. Please refer to the article Man-in-the-middle attack for more details about this.
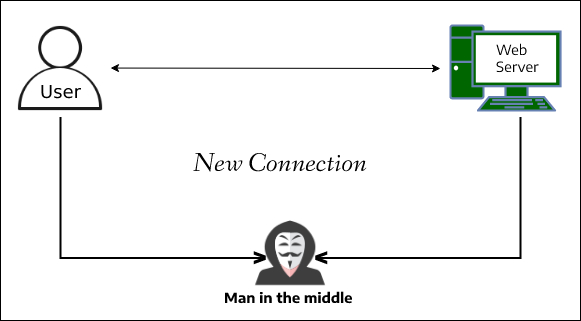
Prevention:
- Ensure you have a strong password and two-factor authentication turned on.
- Make sure your router is encrypted.
- Avoid using public Wi-Fi and use a VPN for proper encryption of traffic.
- Make sure the web application you are using is secure and follows HTTPS protocol.
5. Credential Stuffing Attack:
One day or the other, we all get to know about data breaches of various websites (mostly weak and disrepute). The hacker takes advantage of this. Generally, some people do not frequently change their passwords or if they change, it would be quite similar to the old one, so in times of data breaches, the hackers try to find your records in the breach and attempt to gain access to your account by trying different permutations of the leaked password.
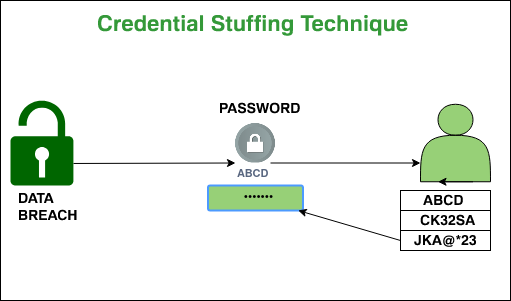
Prevention:
- Regularly monitor your account for unusual activity.
- Check whether your credentials were ever involved in data breaches.
- Regularly change your password in case it is compromised.
- Have a complex password and make sure they aren’t similar to older ones.
- Make sure your browser or device doesn’t save your passwords, so it is not leaked in case your device is lost.




