Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an application layer protocol that runs on UDP and maintains and manages IP network routers, hubs, and switches. SNMP agents run on networking devices in Windows and UNIX networks.
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is an application layer protocol that utilizes the UDP protocol to manage routers, hubs, and switches on an IP network. SNMP is a widely used protocol that is enabled on a wide range of operating systems, including Windows Server, Linux servers, and network devices such as routers and switches.
On a target system, SNMP enumeration is used to list user accounts, passwords, groups, system names, and devices.
Component:
SNMP Enumeration is made up of three major parts:
- Managed Device: A managed device is a device or a host (technically referred to as a node) that has the SNMP service enabled. These devices include routers, switches, hubs, bridges, computers, and so on.
- Agents: An agent is a software component that runs on a managed device. Its primary function is to convert data into an SNMP-compatible format for network management via the SNMP protocol.
- Network Management System (NMS) : NMS are software systems that are employed to monitor network devices.
Working:
The process of enumerating user accounts and devices on a target machine using SNMP is known as SNMP enumeration. SNMP is made up of a manager and an agent; the agent is embedded in every network device, while the manager is installed on a separate computer. To access and configure the SNMP agent from the management station, SNMP stores two passwords:
- Read the community string: By default, it is public and allows viewing of device/system configuration.
- Read/write community string: It is private by default and allows remote configuration editing.
These default community strings are used by attackers to gather information about a machine. Attackers use SNMP to gather data on the network’s resources such as hosts, routers, devices, shares, and so on, as well as network information such as ARP tables, routing tables, traffic, and so on.
The architecture of SNMP Enumeration:
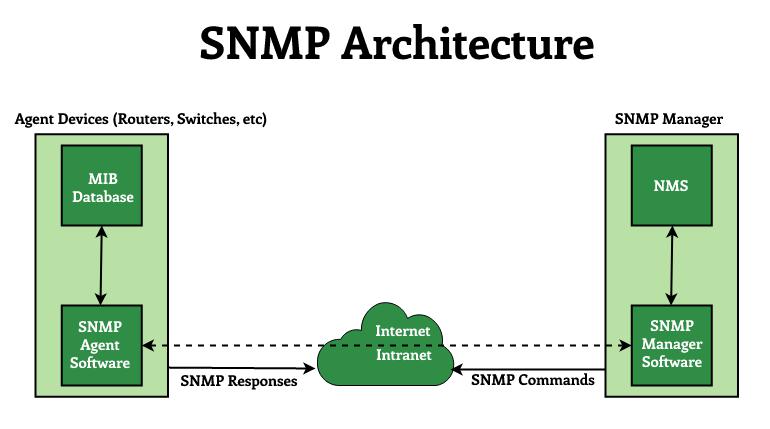
- Management Agent: An application that resides in managed devices such as hosts, bridges, routers, and so on. The agent responds to the operative’s requests for data and actions and may send asynchronous messages to the operative in the event of a critical event.
- Management Station: It serves as the human network manager’s interface to the network management station (or network operation center NOC), from which he monitors and manages the network and assists in fault recovery.
- Network Management Protocol: The network management protocol (SNMP) is used to transfer data and commands between agents and managing entities. For communication between managers and agents, SNMP employs the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) as the transport protocol. The reasons for exploitation of UDP for SNMP area unit are as follows:
- First, it has low overheads in comparison to the protocol, which uses a 3-way handshake for the association.
- Second, in large networks, SNMP over protocol may be a risky strategy because the protocol to ensure dependability can flood the network with retransmissions. SNMP sends and receives requests on UDP port 161, and receives traps from managed devices on UDP port 162.
- Management database (MIB) : A management database is represented as a collection of managed objects. These objects together form the MIB virtual database. Although an agent may implement multiple MIBs, all agents must implement a single MIB, known as MIB-II. This standard defines variables for things like interface statistics (interface speeds, MTU, octets sent, octets received, and so on) as well as various other things related to the system itself (system location, system contact, etc.). MIB-primary II’s goal is to generate general TCP/IP management data.
SNMP Enumeration Tools:
- OpUtils: With its integrated set of tools, OpUtils assists network engineers in monitoring, diagnosing, and troubleshooting their IT resources.
- Engineer’s Toolset:
- The engineer’s Toolset uses ICMP and SNMP to perform network discovery on a single subnet or a spectrum of subnets.
- It scans a single IP, IP address range, or subnet in real-time and displays network devices discovered.
Protective Measure from SNMP Enumeration
- SNMP agents on hosts should be removed or disabled.
- All perimeter network access devices should block port 161.
- Access should be limited to specific IP addresses.
- Make use of SNMPv3 (more secure)
- Add the Group Policy security option “Additional restrictions for anonymous connections” to your configuration.
- Null session pipes, null session shares, and IPsec filtering should all be restricted as well.




