Wireshark is an open source computer software that supports network troubleshooting and surveillance. It allows users to monitor and analyze network traffic. This software runs on a personal computer or on a mobile device, allowing users to capture and view packets captured on a network. Analyzing the data captured by Wireshark helps in detecting security issues and repairing the issues that the data reveals. Before you can analyze any network traffic, you must first configure Wireshark to do so. This is done by selecting the Capture options from the main menu. Each option represents a different type of capture and has its own unique name. The options are as follows:
- 1. Packet captures: All packets captured by Wireshark are saved in real time to the system’s memory. To save captured packets, select the Save as file option from the Capture options window. The saved packets are saved in a file named Packet_Capture_Output_Filename.pcap on your computer’s hard drive.
- 2. Packet filter captures: To save packets in real time, you must first filter them using a chain of packet capture filters. Select the Create packet filter option from the Capture options window and create a packet capture filter with appropriate options. Once you’ve created your packet capture filter, select it from the list and click Apply to apply the filter to all packets being captured by Wireshark. Note that there is an option to copy the filter to another app on your phone, so you don’t have to recreate it every time. Once applied, all packets will be captured and saved as files rather than in memory.
- 3. Display mode: You can view captured information in several ways, including packets, conversation threads and call graphs among others. To change display modes, select one of the following views from the Views drop-down menu:
- Packet List: Displays a list of all recorded packets along with their corresponding IP addresses, port numbers and other relevant information.
- Conversation List: Lists all conversations recorded during a specific session in chronological order with associated data presented below each conversation box. You can also change which channels conversations occur on using radio buttons at the bottom of each channel box. You can also quickly skip over conversations using forward and backward arrows at either end of the timeline view tab to navigate through conversations faster.
- Call Graph: Shows all calls placed during a specific session along with associated data such as time stamps, phone numbers called and immediately followed by caller ID information for both parties involved in each call along with call duration information for each call (time spent on phone call vs time waiting for phone call).
Using these capture options, you can configure Wireshark to record whatever you want at any particular point in time or save it until you decide to view it later. It is also easy to apply filters to records, so you can examine only certain parts of a network traffic log or only certain types of network traffic such as HTTP or UDP traffic using separate chains of packet capture filters or one large chain that applies all applicable filters simultaneously.
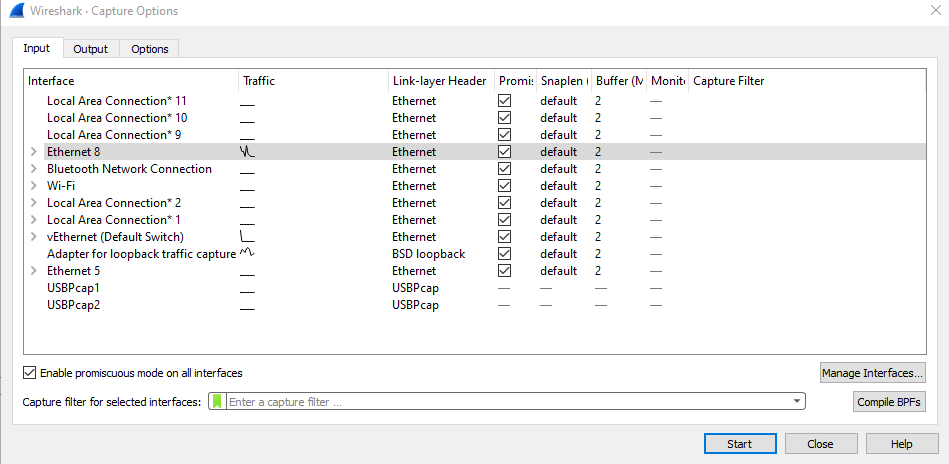
Selecting Capture → Options gives rise to the dialog box with Input Tab / Output Tab / Options in Wireshark . The Capture Options dialog box is a configuration dialog box that allows the user to specify various settings for capturing packets. The Capture Options dialog box has two tabs, namely the General tab and the Details tab. The General tab contains various settings related to capturing packets. These include options like the interface name, buffer size, promiscuous mode and so on. The Details tab displays more specific information about the network interface card (NIC) and packet capture driver being used for packet capture.
Input Tab:
The Input Tab consists of Interfaces, Traffic, Link Layer Header Type , Snap Length, Buffer Size , Traffic Level and Others.
- The Interfaces contain all the information that is required to build your system for managing one or more Network Interface cards.
- The Traffic displays the signal strength in the form of a graph
- The Link-Layer Header specifies the Type of Header associated.
- The Snapshot length specifies the number of bytes that needs to be captures
- We can also add our own capture Filter .
- Compile Selected BPFs is used to Generate the Output Table for a Local File (LF), or as long term storage device/networks by including all appropriate Data Structures in Network Mode with Configuration Tag attached such that they can be viewed using IP Address Viewer Tools like PPPoE-AES.
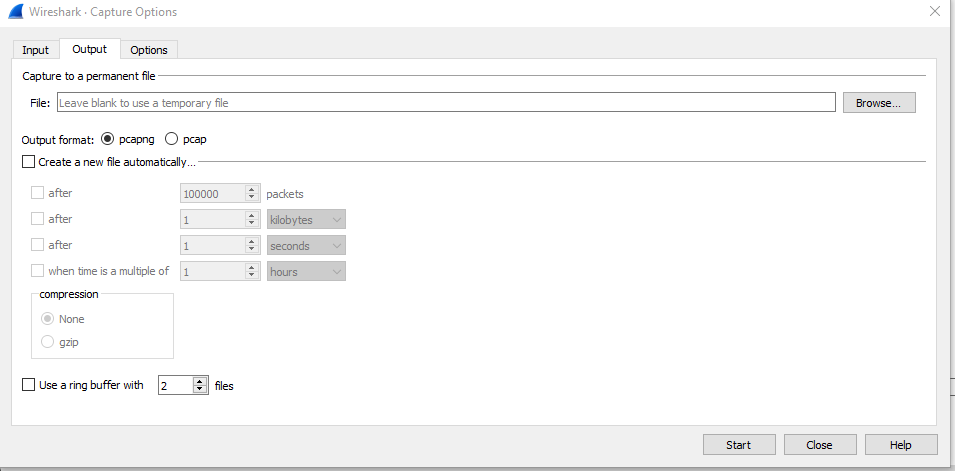
Output Tab:
- The Output Tab asks for a Capture to a permanent File.
- We can select output format as pcapng or pcap.
- Also, this has options to auto save files using “Create a new file automatically option”.
- We can also use a Ring buffer with n files, We can form a single file from multiple files,
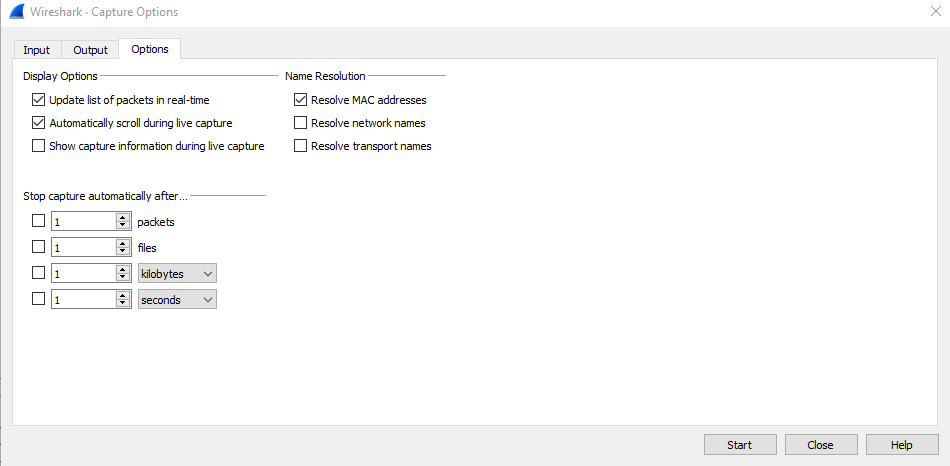
Options Tab:
Wireshark provides a number of options.
- We can view/unview the list of packets live while capturing.
- Also, it automatically scrolls so that we see the live capture.
- We can also enable the provision to see more information during live capture.
- There are 3 options for Name Resolutions – Resolve MAC Address, Network Names, Transport Names. Also, there are provisions to stop packet capture based on packet count, file count, KB/MB Size , Time duration.