Introduction
One evening, I was catching up with a friend over a few drinks – let’s call him Jon (name changed). He seemed determined to become a data scientist and was charting out his career plan accordingly.
I quizzed him around his awareness of what a data scientist does and sniffed that he wasn’t sure. So I threw this puzzle to him:
There are 4 people A, B, C and D, each with one of the these designations: A Data Scientist, A Data Engineer, A Data Analyst and a Data Architect. I also had job descriptions of their roles, which I passed on to Jon. He had to match the description to the right designation.
To penalize him for his errors, he had to take an alcohol shot for every wrong match he did. Can you guess the number of shots he took that evening? How many would you end up taking, if you were in this situation?
I would just say that he was lucky that I didn’t throw this puzzle at him with all the 8 designations I had JDs of that evening.
The problem
While the demand for various data science roles is increasing by the day, people in industry have used the designations and descriptions a bit loosely. Hence, there is a lot of confusion around who does what in the industry!
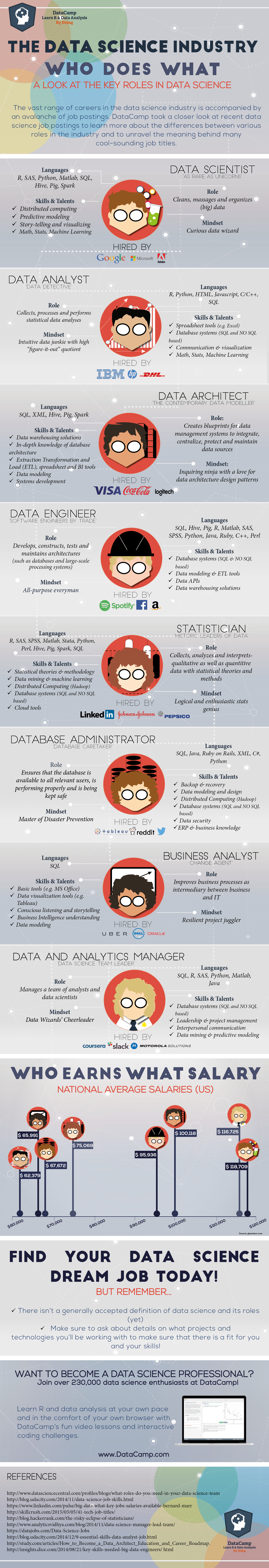
We hope this infographic “The Data Science Industry: Who Does What designed by DataCamp” helps you to find out ideal job role. We have provided a brief description of these roles and an infographic for you to take away.
If you have any questions related to designations and roles, feel free to ask them through comments below. I will be as helpful as my time can permit. Enjoy!
Description of various data science roles:
The Data Scientist
Data Scientist is most likely one of the most sizzling job titles that you can have these days, and with a yearly average salary of $118,70, they are amongst the top earners in the data science industry. The data scientist has the ability to handle the crude data using the latest technologies and techniques, can perform the necessary analysis, and can present the acquired knowledge to his associates in an informative way.
The Data Analyst
Languages like R, Python and SQL are part of the data analyst’s basic knowledge. Much like the data scientist role, a broad skillset is also required for the data analyst role, which combines technical and analytical knowledge with ingenuity. This profile is often looked for by companies such as HP and IBM.
The Data Architect
Data is (being collected) everywhere and as a consequence, more and more organizations are in need of a data architect. Industries like banking and FMCG use data architects to integrate, centralize, protect and maintain their data sources. These architects often work with the latest technologies such as Spark and always need to be on top of the game to stay relevant.
The Statistician
The title of statistician is regularly overlooked by or replaced by fancier sounding job titles. This is a bit of a pity, given that the statistician, with his solid foundation in statistical theories and methodologies, can be seen as the pioneer of the data science field. It is often he who reaps the information from the data and transforms it into actionable insights. To end, although the title can sound a bit dull compared to the others in this list, modern statisticians are always ready to rapidly ace new advancements and utilize these to benefit their research.
The Database Administrator
As a database administrator, you ensure that the database is accessible to every stakeholder in the organizations, is performing legitimately and that the necessary safety measures are in place to keep the stored data save. You need to master different technologies going from SQL and XML up to a more general programming language like Java.
The Business Analyst
This is probably the least technical profile mentioned on the infographic. However, the business analyst compensates for this lack of technical knowhow with a profound understanding of the various business processes that are in place. A business analyst therefore often performs the role of the middle person between the business folks and the techies. Organizations searching for business analysts are companies like Uber, Dell and Oracle.
Data and Analytics Manager
The data and analytics manager steers the direction of the data science team. This individual consolidates strong and specialized skills in a various arrangement of advancements (SQL, R, SAS, … ) with the social aptitudes required to deal with a group. It’s a hard employment but if you feel up for the challenge, make sure to have a look at offerings from companies such as Coursera, Slack. Luckily, with a yearly average salary of $116k, the financial compensation is in line with the high requirements.
Author:
Martijn Theuwissen is co-founder of DataCamp, which helps people learn R and Data Science from their browser and their comfort through fun videos and interactive coding challenges.