Introduction
Most children under the age of five can recognize digits and letters – small characters, huge characters, handwritten, machine printed or rotated – all of which are easily identified by the young. Humans can do the best pattern recognition in most cases, but we don’t understand how they accomplish it.
The continuously increasing volume of data created makes human interpretation impractical, boosting the need for machines to be able to spot patterns quickly and effectively. The capacity to automatically recognize patterns and regularities in data has many uses, ranging from facial recognition software to tumor diagnosis. Pattern recognition is one of the most popular applications of machine learning. There are patterns everywhere. It permeates all aspects of our everyday existence. Everything, from the style and color of our clothing to the use of clever voice assistants, includes a pattern.
Learning Objectives:
- Understanding pattern recognition in data analysis.
- The Working of pattern recognition.
- Understanding the application and use cases projects
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of using pattern recognition?
This article was published as a part of the Data Science Blogathon.
Table of Contents
- What does Pattern Recognition mean?
- How is Pattern Recognition Implemented?
- Different Types of Pattern Recognition
- Applications and Use Cases of Pattern Recognition
- Advantages of Pattern Recognition
- Disadvantages of Pattern Recognition
- Conclusion
What Does Pattern Recognition Mean?
Pattern Recognition is a way to find global or local trends in a pattern. A pattern is something that follows a movement and has some form of regularity. It can be accomplished physically, mathematically, or using algorithms.
A pattern in literature or film would be a description of a genre. If a user consistently chooses to watch dark comedy on Netflix, the streaming service is unlikely to suggest any sad melodramas.
In the context of machine learning, “pattern recognition” refers to the use of complex algorithms to identify patterns in the input data. Computer vision, voice recognition, face identification, etc., are only a few of the many contemporary technical applications of pattern recognition.
How is Pattern Recognition Implemented?
The notion of learning is used to produce pattern recognition. Learning allows the system to be taught and become more adaptive, resulting in more accurate outcomes. A portion of the dataset is used to train the system, while the remainder is used to test it.
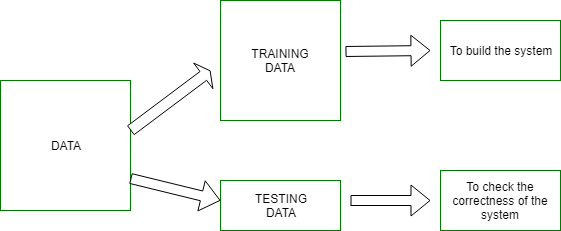
The training set comprises pictures or data that will be used to train or develop the model. Training rules provide the criterion for output decisions.
Training algorithms are used to match a set of input data with an output choice. The algorithms and rules are then used to help in training. The system generates results based on the information gathered from the data.
The testing set is used to validate the system’s accuracy. After the system has been trained, the testing data is used to determine whether the accurate output is obtained. This data accounts for around 20% of the total data in the system.
The Pattern Recognition method is divided into five stages. These stages can be described as follows:
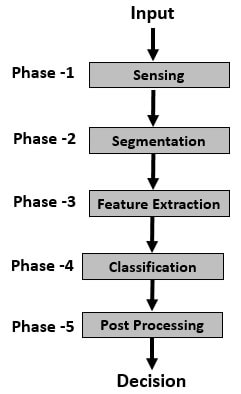
- Phase 1 Sensing: The system turns the incoming data into similar data during this step.
- Phase 2 Segmentation: The perceived objects are isolated during this step.
- Phase 3 Feature extraction: In this step, the features or qualities of the objects are computed and sent for further classification.
- Phase 4 Classification: The detected objects are classified or arranged in groups or cases at this step.
- Phase 5 Post-processing: Here, further considerations are done before concluding.
Different Types of Pattern Recognition
Image:
This form of pattern recognition identifies certain things portrayed in photographs. Image recognition is a fundamental element of computer vision, which is a machine’s capacity to recognize pictures and execute appropriate actions (e.g., a self-driving car slowing down after identifying a pedestrian ahead).
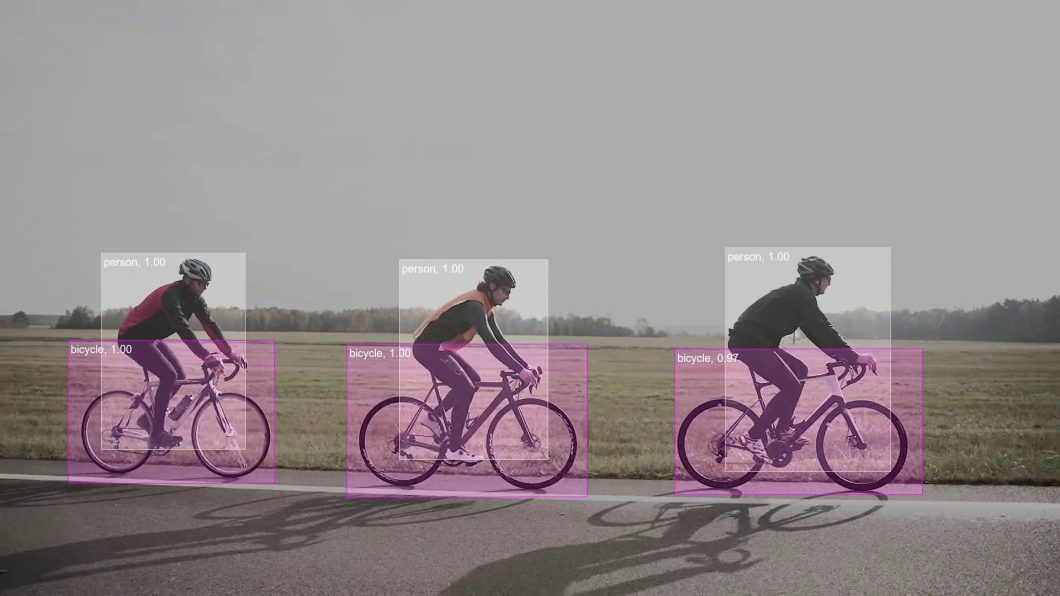

Image recognition is often used in operations like Face detection, visual search, and OCR (optical character recognition).
Sound:
This pattern recognition approach is used to detect distinct sounds. After evaluating them, the system identifies audio signals as belonging to a certain category. Here are some applications for sound pattern recognition:
- Surveillance alarm detection
- Animal species identification
- melody recognition
Voice:
This kind of pattern recognition examines human speech sounds to identify the speaker. Unlike voice recognition, it does not include language processing and only detects personal features in a speaking pattern. It is usually used for security purposes (personal identification).
Common applications involve- the Internet of things and mobile or web apps.
Speech:
Speech recognition catches aspects of a language in the sound of a person speaking, similar to how optical character recognition detects letters and words on an image.
Popular applications for this technology include- Voice-to-text converters, video auto-captioning, and virtual assistants.
Applications and Use Cases of Pattern Recognition
- Seismic Analysis: studies how natural phenomena like earthquakes influence rocks, structures, and soils. Pattern recognition is used in seismic events to detect and understand patterns.
- Trend Analysis: It aids in spotting trends in data so that suitable analysis may be performed. For example, future sales may be forecasted by examining current trends in a company’s or organization’s sales.
- Healthcare: It is used in the healthcare industry to enhance health services. Medical practitioners keep patient data and use it for future studies. This process is used to identify objects or damage in human bodies too.
- Fingerprint Recognition: This method recognizes fingerprints on computer and smartphone devices. Modern smartphones have a fingerprint recognition function that allows you to unlock your phone after authenticating your fingerprint.
- Computer Vision: The user interacts with the system by providing input as an image or video. The system compares them to hundreds and millions of photographs recorded in its database to detect comparable patterns. The fundamental characteristics are drawn using an algorithm designed primarily for grouping similar appearing items and patterns. An example is cancer detection.
Advantages of Pattern Recognition
- Even the tiniest concealed or untraceable data may be identified and predicted using it.
- The challenge of biometric detection is solved through it.
- It is used to address categorization difficulties.
- It can help visually impaired blind persons recognize fabric patterns.
- In the medical sector, it is helpful for forensic investigation and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequencing.
- It can recognize and identify an object at different distances.
- Using learning approaches provides appropriate predictions.
- It not only aids in the prediction of unknown data but in the formulation of meaningful recommendations too.
Disadvantages of Pattern Recognition
Several limitations can affect its performance and accuracy:
-
Overfitting: occurs when a model is trained too well on the training data, resulting in poor generalization to new, unseen data. This can be mitigated by using techniques like regularization and cross-validation.
-
Underfitting: Underfitting occurs when a model is not complex enough to capture the underlying patterns in the data. This can be mitigated by using more complex models or by increasing the amount of training data.
-
The Curse of Dimensionality: As the number of features in the data increases, the amount of data required to model the patterns in the data accurately increases too. This can be mitigated by using dimensionality reduction techniques.
-
Data Bias: If the training data is not representative of the population, the model will not be able to generalize well to new, unseen data. This can be mitigated by using techniques like oversampling or SMOTE.
-
Noise and Outliers: Noise and outliers in the data can make it difficult for the model to identify the underlying patterns. This can be mitigated by using robust estimation techniques or removing outliers from the data.
-
Nonlinearity: Some patterns in the data may not be linear, making it difficult for linear models to capture the underlying patterns accurately. This can be mitigated using non-linear models like neural networks or decision trees.
-
Lack of Interpretability: Some models, like neural networks, can be difficult to interpret and understand, making it hard to understand why a particular decision was made.
Conclusion
To summarize, pattern recognition is a subfield of artificial intelligence that uses several algorithmic techniques to detect and characterize reoccurring patterns in data. This approach may be used in many different contexts, like computer vision, bioinformatics, and image/speech recognition. The performance of its systems has dramatically increased due to advancements in machine learning and deep learning, yielding more accurate and trustworthy findings. On the other hand, there are still obstacles to overcome, including dealing with huge and complicated data sets and overcoming uncertainty and noise in the data. Pattern recognition, despite these obstacles, is a fast-expanding area with the potential to transform many sectors and enhance our daily lives.
A few important takeaways from the article are as follows:
-
Pattern recognition systems are heavily based on AI and machine learning techniques.
-
It identifies global or local trends in a pattern.
-
With Pattern Recognition, it’s possible to recognize and identify an object from a far distance.
-
Data analysis is aided by pattern recognition since it makes it easier to identify patterns in the data.
The media shown in this article is not owned by Analytics Vidhya and is used at the Author’s discretion.




